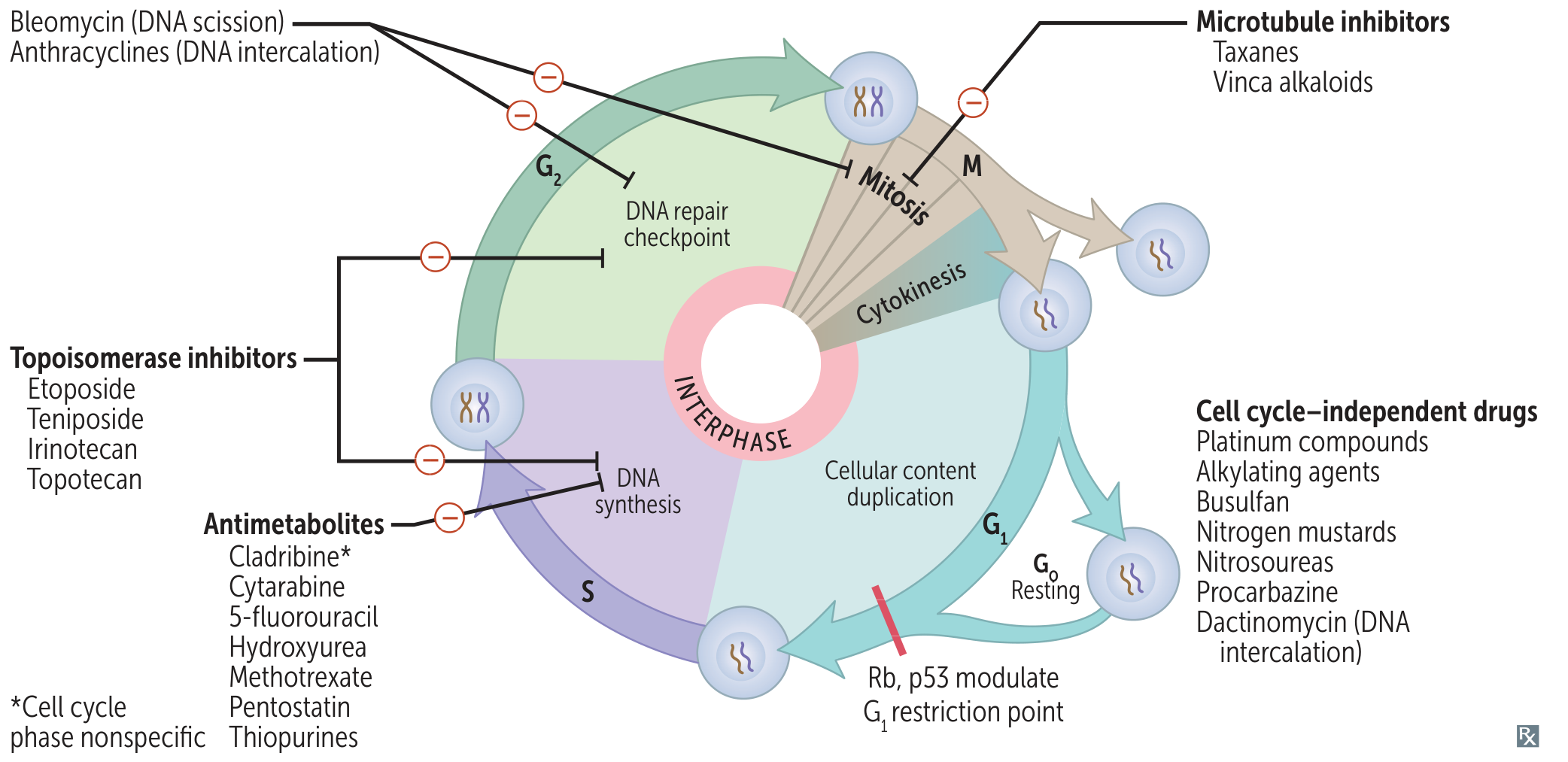
Cell phases
- Interphase (G1, S, G2)
- G0: Quiescent/resting state. Permanent cells (neurons, cardiac muscle) are terminally in G0. Stable cells (hepatocytes) can re-enter cycle.
- G1: Cell growth. Synthesis of components needed for S phase. The crucial G1/S checkpoint is here, regulated by p53 and Rb. t
- S: DNA replication (synthesis). Sister chromatids are formed. DNA content doubles from 2N → 4N. Target of antimetabolite chemotherapy.
- G2: Final growth and check for DNA replication errors before division. The G2/M checkpoint ensures fidelity.
- M Phase (Mitosis)
- Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase (PMAT).
- Nuclear and cellular division.
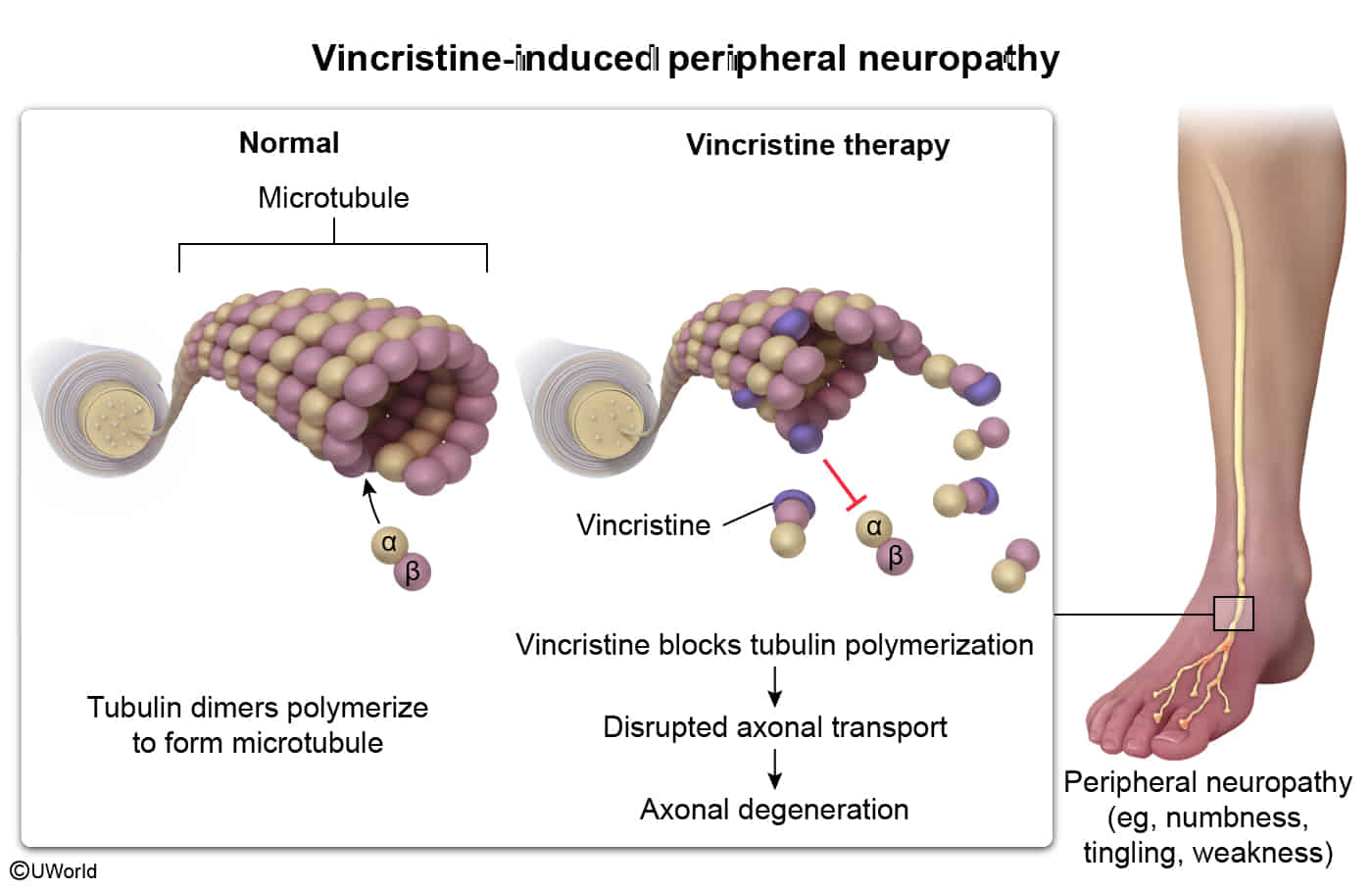
- Target of microtubule inhibitors (Vinca alkaloids, Taxanes).
- Key Regulators
- Cyclins & CDKs: Positive regulators that drive the cell cycle forward.
- p53 & Rb: Tumor suppressors that act as “brakes” at the G1/S checkpoint to halt division if DNA is damaged. Mutations lead to cancer.
Microtubule inhibitors (M phase)
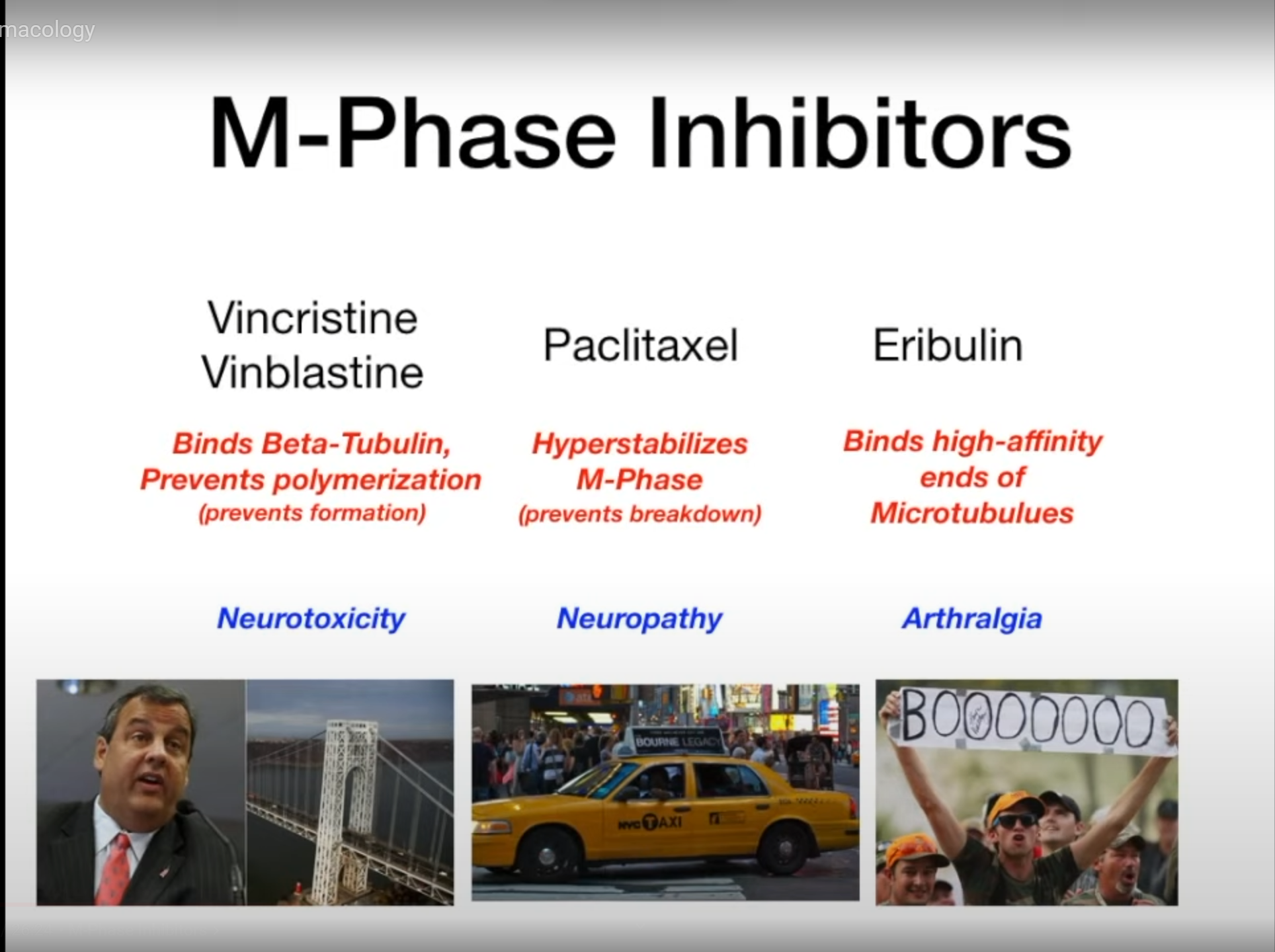
Mnemonic
两颗长杉树,围成一个门。门里有个蛋,从此不合成:两颗长杉树-长春碱、长春新碱、紫杉醇,门-门冬酰胺酶氨,蛋&合成-干扰蛋白质合成。
- Chris Christie closed lanes at George Washington Bridge
- He is toxic
- Need to take taxi
- People boo
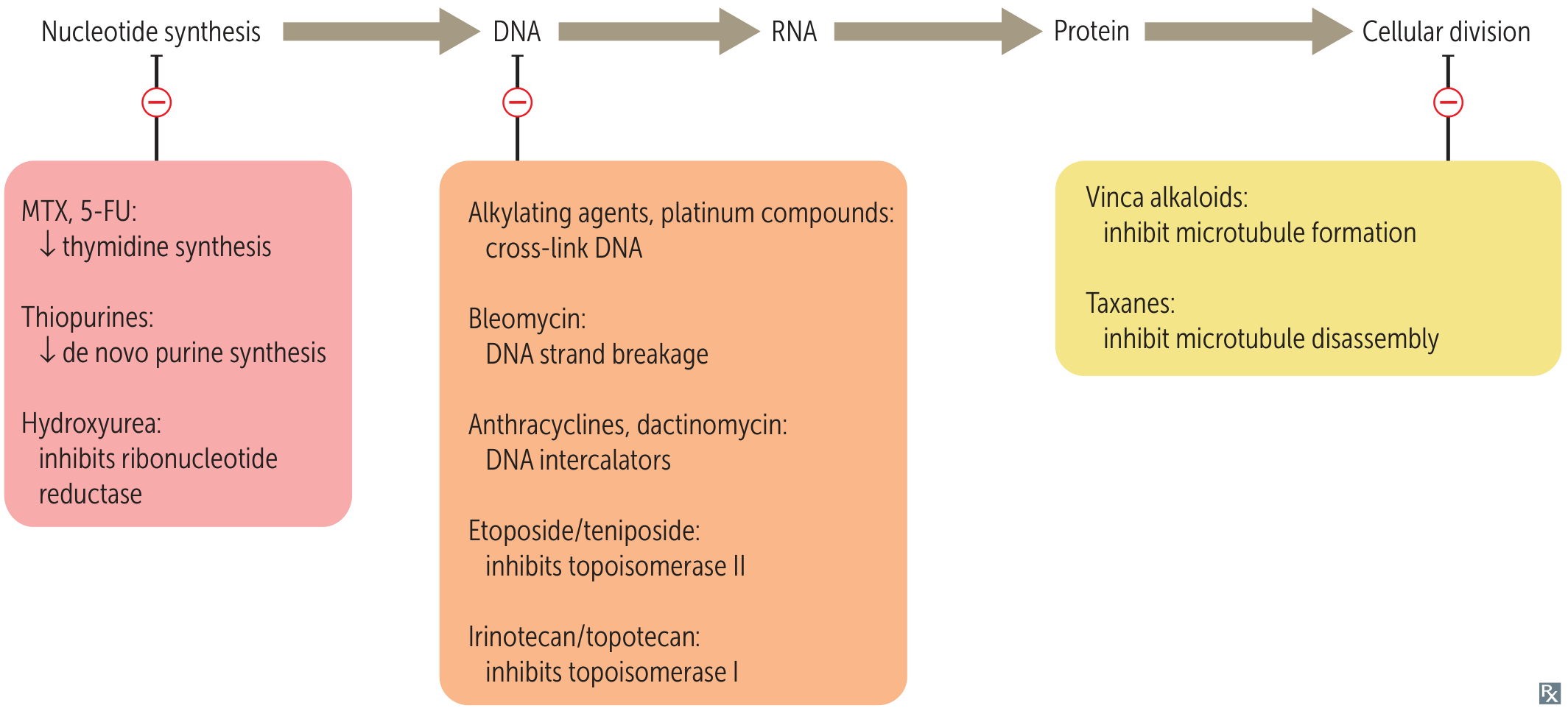
Cell‑cycle independent agents
- Alkylating agents
- Busulfan
- Nitrogen mustards
- Cyclophosphamide
- Ifosfamide
- Nitrosoureas
- Carmustine
- Lomustine
- Procarbazine
- Platinum compounds
- Cisplatin
- Carboplatin
- Oxaliplatin
- Dactinomycin (an antibiotic)
“G1 inhibitors” is incorrect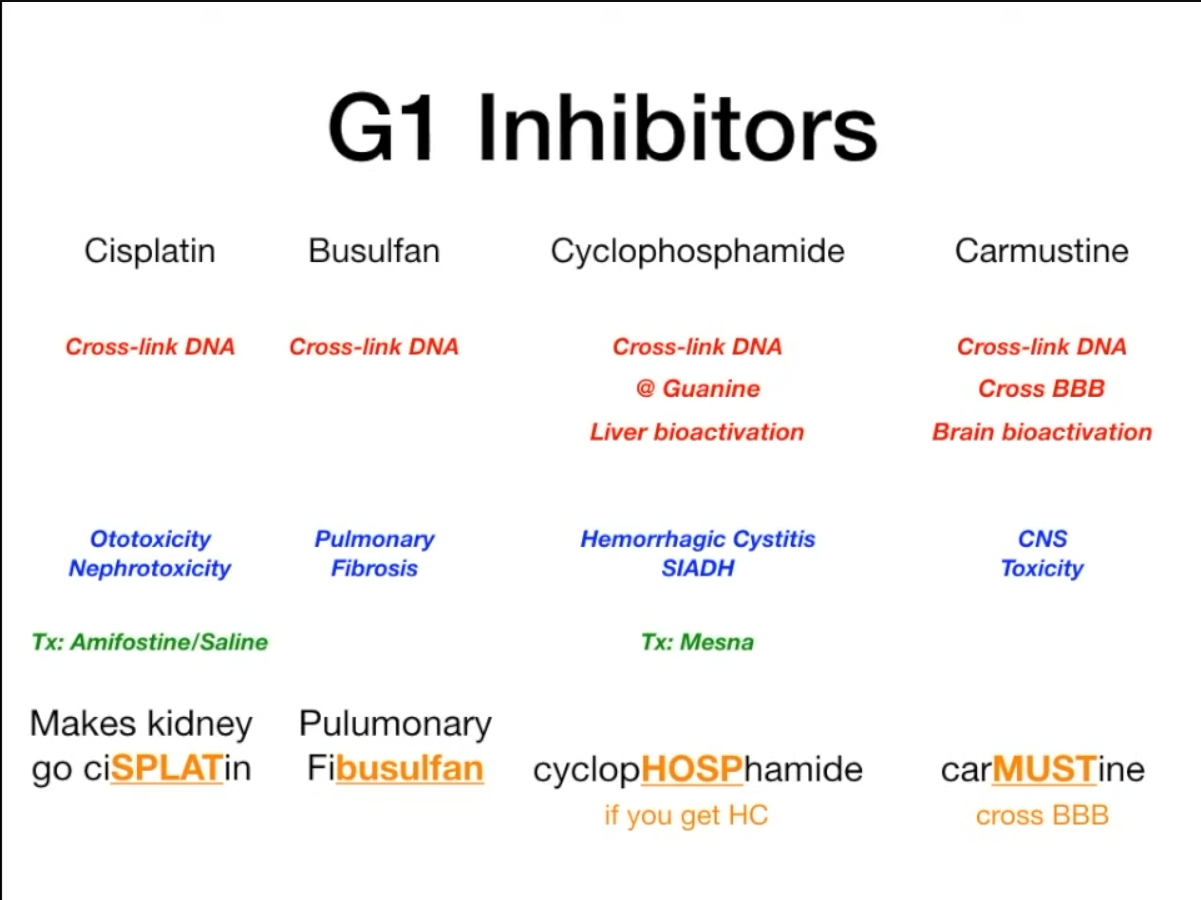
Mnemonic
两安两素一铂金,破坏结构真闹心:两安-环磷酰胺、白消安(Busulfan),两素-丝裂霉素、博来霉素,一铂金-顺铂,破坏结构-直接破坏DNA 结构和功能药。
- Cyclophosphamide
- Belongs to Nitrogen mustards / Oxazaphosphorines
- Indications
- Malignancies
- Solid tumors (e.g., breast cancer, ovarian cancer, small cell lung cancer)
- Leukemias
- Lymphomas
- Multiple myeloma
- Nonneoplastic conditions
- Autoimmune diseases (e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, granulomatosis with polyangiitis)
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Malignancies
- Adverse effects
- The extensive DNA damage inhibits replication and causes apoptosis of malignant cells. However, nonmalignant cells are also affected and can aquire new mutations (due to erroneous DNA repair) that contribute to development of secondary malignancies. For instance, DNA alterations in hematopoietic stem cells can lead to the formation of treatment-related myeloid neoplasms.
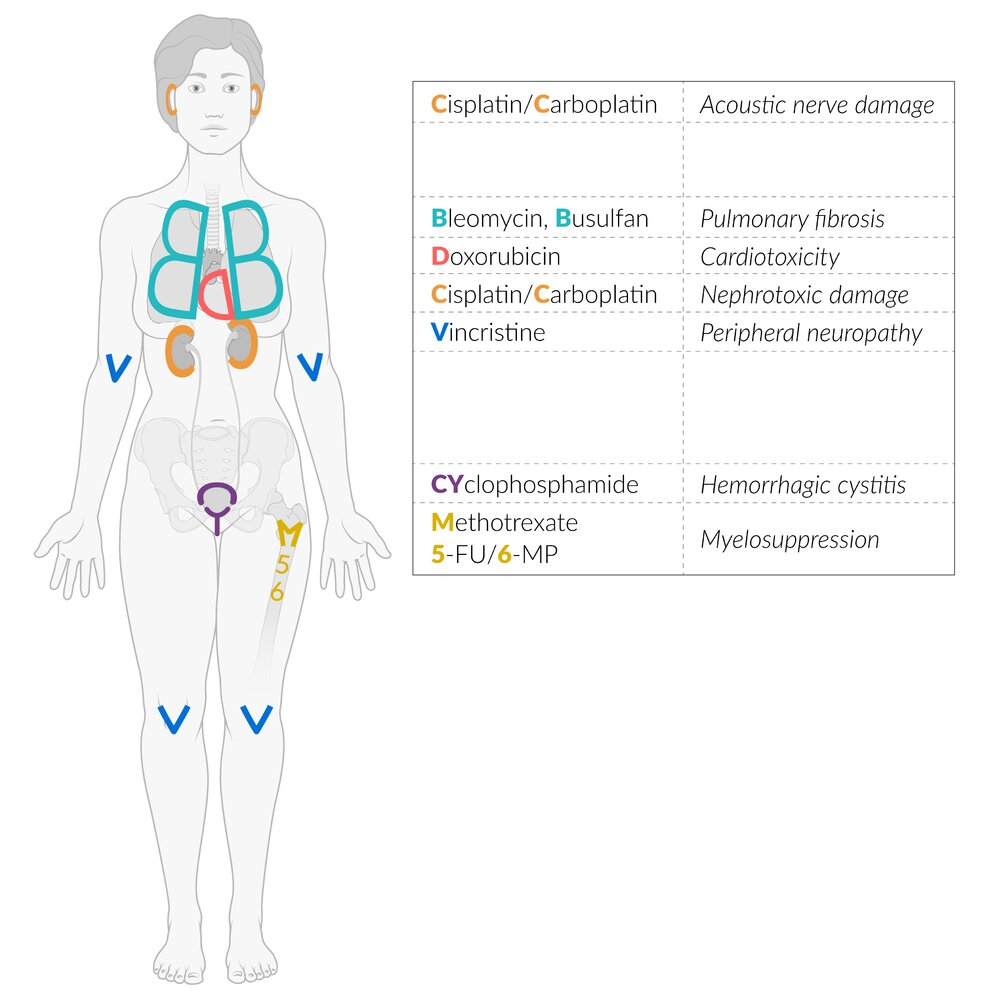
- Bladder toxicity: metabolism of oxazaphosphorines produces the urotoxic substance acrolein
- Hemorrhagic cystitis: inflammation of the bladder, damaging to the epithelium and blood vessels
- Bladder carcinoma
- Myelosuppression
- Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)
- Pulmonary toxicity
- Cardiac toxicity
- Infertility
- Fanconi syndrome (ifosfamide)
- Neurotoxicity (ifosfamide)
Detoxifying agents for antineoplastic treatment
- Platinum-based agents
- Prevent Nephrotoxicity
- Amifostine: free radical scavenger
- IV saline: induces chloride diuresis → ↑ urine chloride concentration → ↓ cisplatin reactivity
- Oxazaphosphorines
- Prevent Bladder toxicity
- Hemorrhagic cystitis
- Bladder carcinoma
- Mesna (2-MErcaptoethane Sulfonate Na) and fluids
- Prevent Bladder toxicity
- Antifolates
- Prevent
- Myelosuppression
- Mucositis
- Hepatotoxicity
- Pulmonary fibrosis
- Leucovorin (folinic acid)
- Precursor of tetrahydrofolate
- Application 24 h after the administration of antifolates
- Prevent
- Anthracyclines
- Prevent Cardiotoxicity
- Dexrazoxane: iron chelating agent
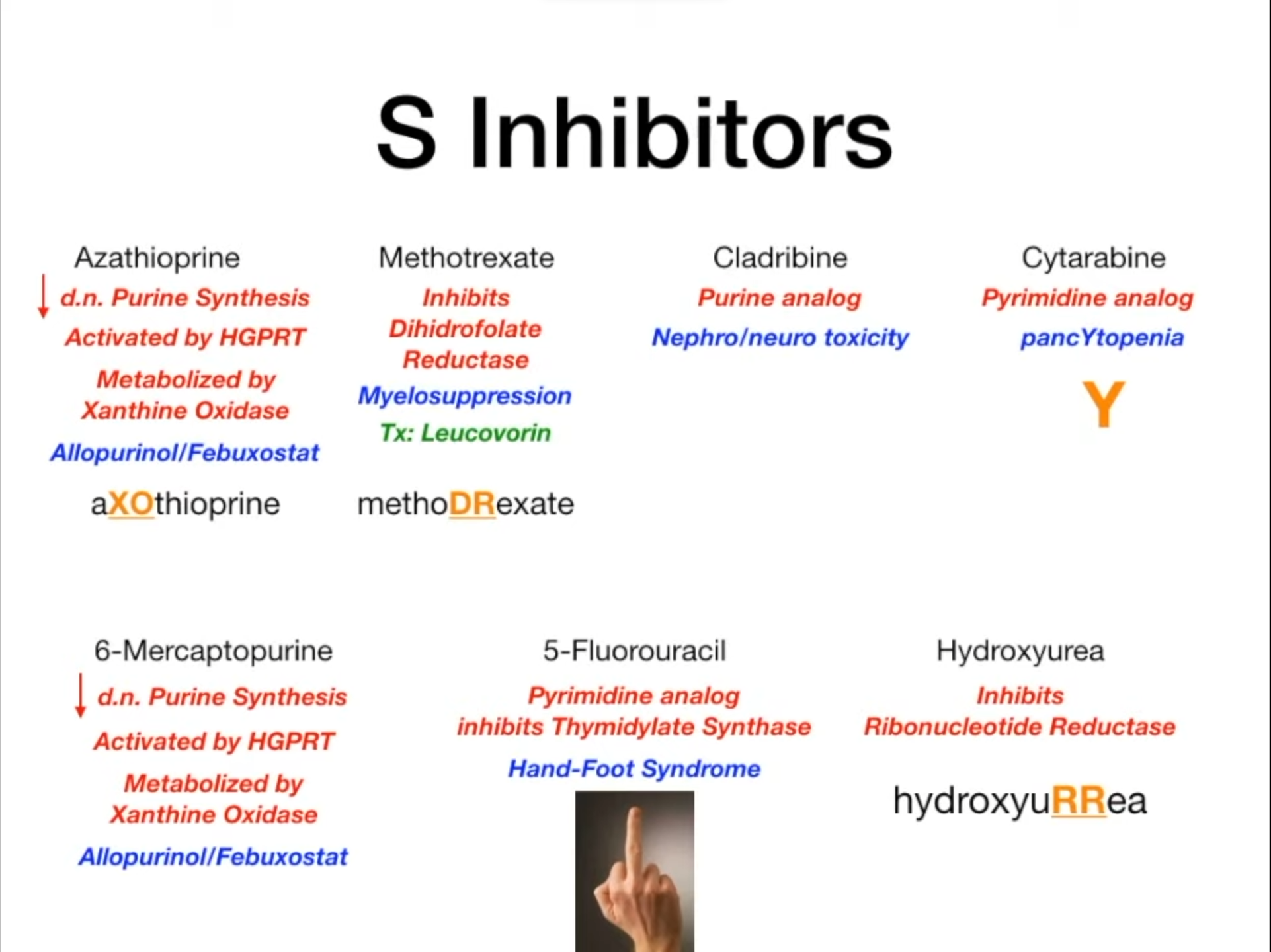
Antimetabolites (S phase)
Mnemonic
- 嘌呤核苷酸合成抑制剂:巯嘌呤(Azathioprine),嫖娼者,二流子
- 胸苷酸合成酶抑制剂:氟尿嘧啶,胸前戴座佛
- 二氢叶酸还原酶抑制剂:甲氨蝶呤,二甲
- 核苷酸还原酶抑制剂:羟基脲(Hydroxyurea),核战争,还用抢?
- DNA 多聚酶抑制剂:阿糖胞苷,多聚聚,才甜蜜。
- See De novo pyrimidine and purine synthesis
- Purine antagonists
- Azathioprine is the prodrug of 6-MP
- Azathioprine and 6-MP are purine analogs, so they are metabolized to inactivate forms by xanthine oxidase like purines
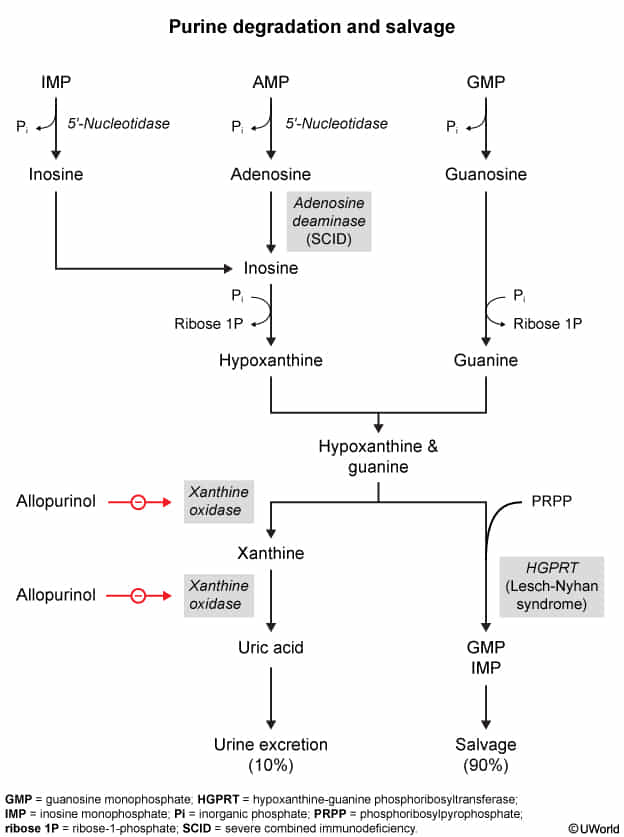
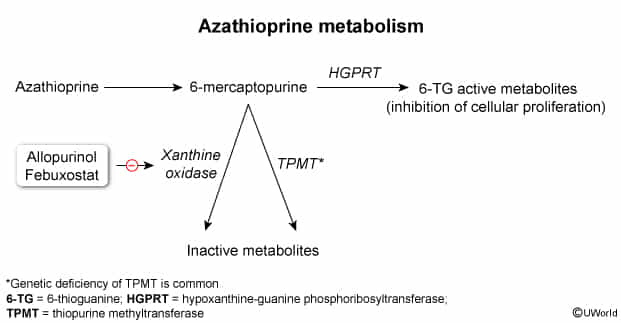
- When taken together, allopurinol inhibits the metabolism of azathioprine, leading to increased levels of 6-mercaptopurine. This can result in potentially severe side effects such as bone marrow suppression, leading to leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, or anemia. Therefore, when used together, azathioprine dose typically needs to be reduced by 50-75%.
- See Treatment, Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
- Azathioprine and 6-MP are purine analogs, so they are metabolized to inactivate forms by xanthine oxidase like purines
- Azathioprine is the prodrug of 6-MP
- Antifolates
- Methotrexate
- Adverse effects
- Myelosuppression, anemia
- Hepatotoxicity, hepatic fibrosis
- Pulmonary fibrosis, pneumonitis
- Nephrotoxicity
- Mucositis (e.g., oral ulcerations)
- Birth defects (due to folate deficiency), e.g., neural tube defects
- Adverse effects
- Methotrexate
Topoisomerase inhibitors (G2 phase)

Mnemonic
- Eight (Etoposide) + II = Ten (Teniposide)
- I (Irinotecan) + I = Two (Topotecan)
- Topoisomerase I
- Cleaves only one of both DNA strands
- Has nuclease activity to cut DNA strands
- And has ligase activity to reseal the ligated strand
- Does not require ATP
- Topoisomerase II
- Cleaves both DNA strands for larger structural alterations of DNA
- Requires ATP
Antitumor antibiotics
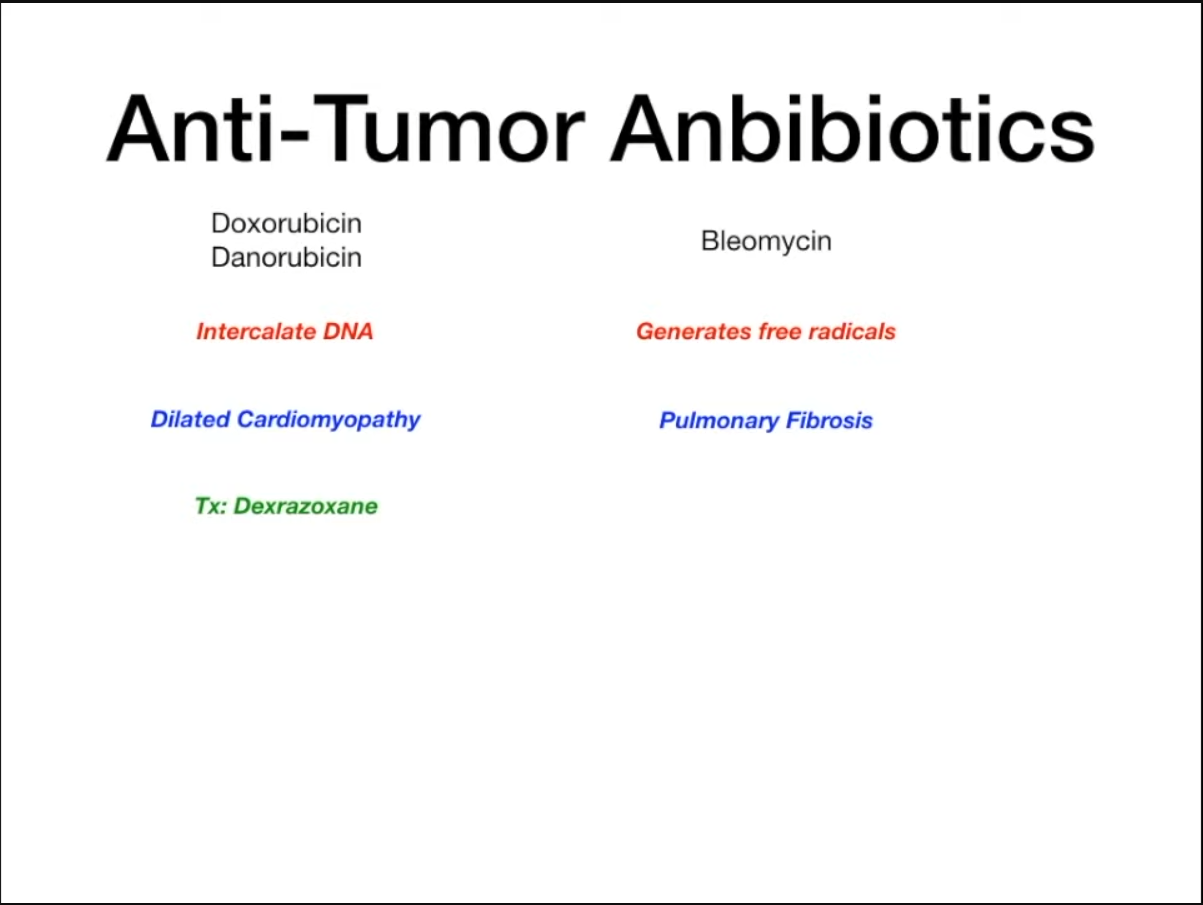
- Anthracyclines (Doxorubicin, Daunorubicin)
- MOA: Generates free radicals, intercalates in DNA. t
- Clinical Use: Solid tumors, leukemias, lymphomas.
- Toxicity: Dilated cardiomyopathy (cardiotoxicity); prevent with Dexrazoxane (iron chelator). Alopecia.
- Bleomycin
- MOA: Induces free radical formation → breaks in DNA strands. G2-phase specific.
- Clinical Use: Testicular cancer, Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Toxicity: Pulmonary fibrosis, skin hyperpigmentation. Minimal myelosuppression.
Mnemonic
- 多么温柔,令人放心啊:温柔-多柔比星,放心-放线菌素D,啊-干扰RNA合成。
- Mnemo I use for Doxorubicin /Daunorubicin:
- They both end in -rubicin → ruby (= red) → the heart is red → cardiotoxicity
- Dilated cardiomyopathy because it starts with D like Doxorubicin
- Dexrazoxane used to prevent it → also starts with D and sounds like Roxane (‘Roxane, you don’t have to put on the red light’, song by the police) → again red for RUBYcin and heart.
- Bleomycin: bleo → fibro
Protein kinase inhibitors
CDK inhibitors
- Palbociclib
- Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4 and 6 → inhibition of cancer cell growth and induction of apoptosis
- Indications
- Metastatic breast cancer
- Myelosuppression
- Side effects
- Pulmonary toxicity (e.g., pneumonitis)
Proteasome inhibitor
- Mechamism
- The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway (UPP) is responsible for degrading damaged or unnecessary ubiquitinated proteins within cells.
- Cancer cells, particularly multiple myeloma (MM) plasma cells, produce large quantities of monoclonal proteins and have a high protein turnover, making them highly dependent on the proteasome.
- Proteasome inhibitors (PIs) block the function of proteasomes, leading to an accumulation of misfolded or unfolded proteins. This buildup causes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, which activates the unfolded protein response (UPR) and ultimately triggers apoptosis (programmed cell death).
- PIs also work by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway, which is crucial for the growth and survival of myeloma cells.
Anticancer treatment-related complications
Chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV)
- Acute-phase CINV (<24 hours after chemotherapy) is mediated primarily by the release of serotonin from intestinal enterochromaffin cells that have been damaged by chemotherapy. Serotonin stimulates vagal afferent fibers (5-HT3 receptors) in the bowel wall, which project to the brainstem and stimulate the vomiting reflex. Therefore, serotonin receptor antagonists (eg, ondansetron) can be used for treatment.
- Delayed-phase CINV (1-5 days after chemotherapy) is mediated primarily by increased levels of substance P in the brainstem due to chemotherapy-associated emetic stimuli in the cerebrospinal fluid and bloodstream. Substance P binds to and activates the neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor in areas of the brainstem that mediate vomiting (eg, nucleus tractus solitarius, area postrema). Therefore, NK1 receptor antagonists (eg, aprepitant, fosaprepitant) are often used for treatment.