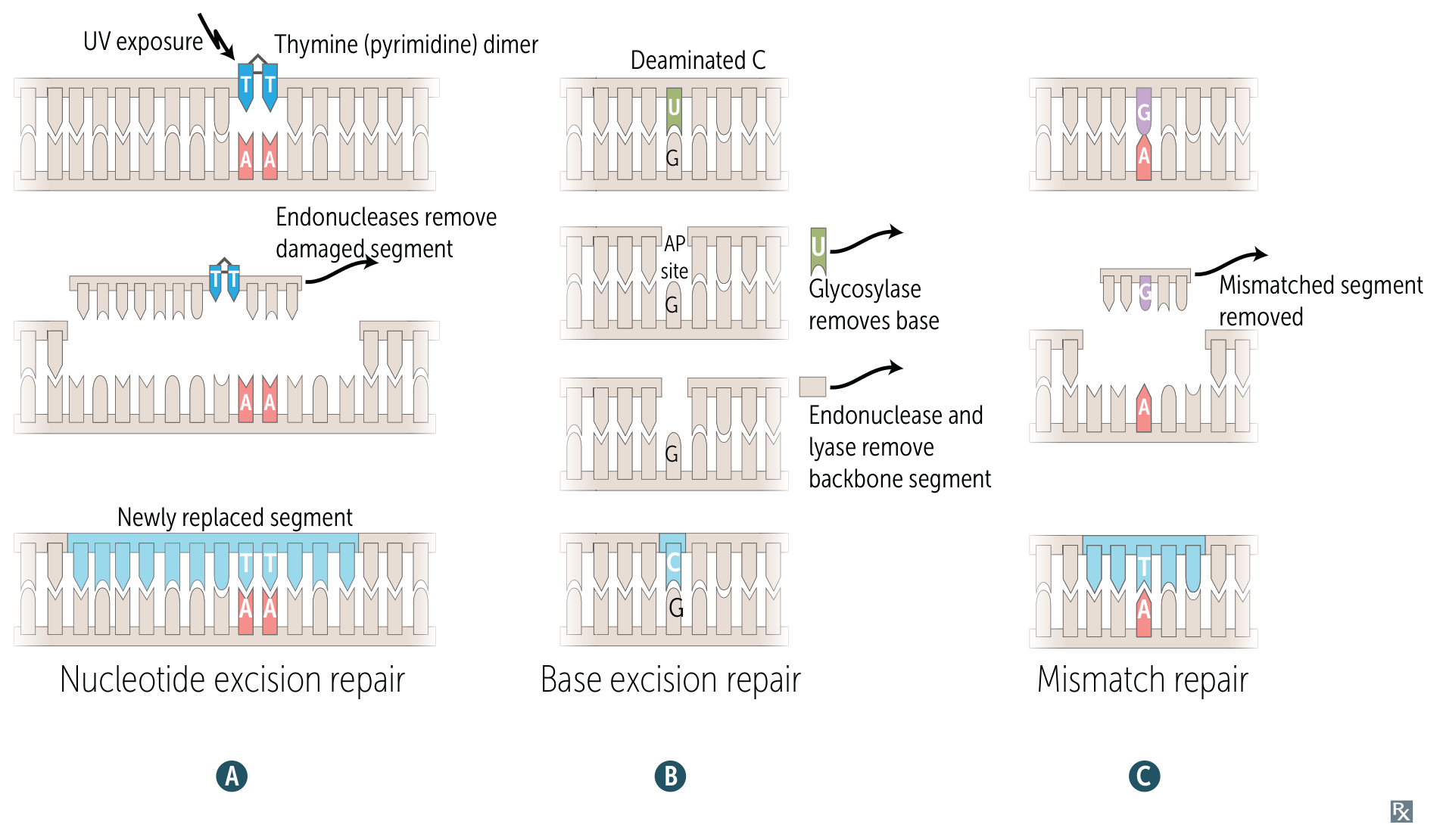
Single-Strand Repair
Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER) t
Fixes: Bulky lesions (thymine dimers from UV light).
Mechanism: An excinuclease complex identifies the distortion, cleaves the phosphodiester backbone on both sides of the lesion, and removes the damaged segment. DNA Polymerase fills the gap, and DNA Ligase seals it.
Defect: Xeroderma Pigmentosum
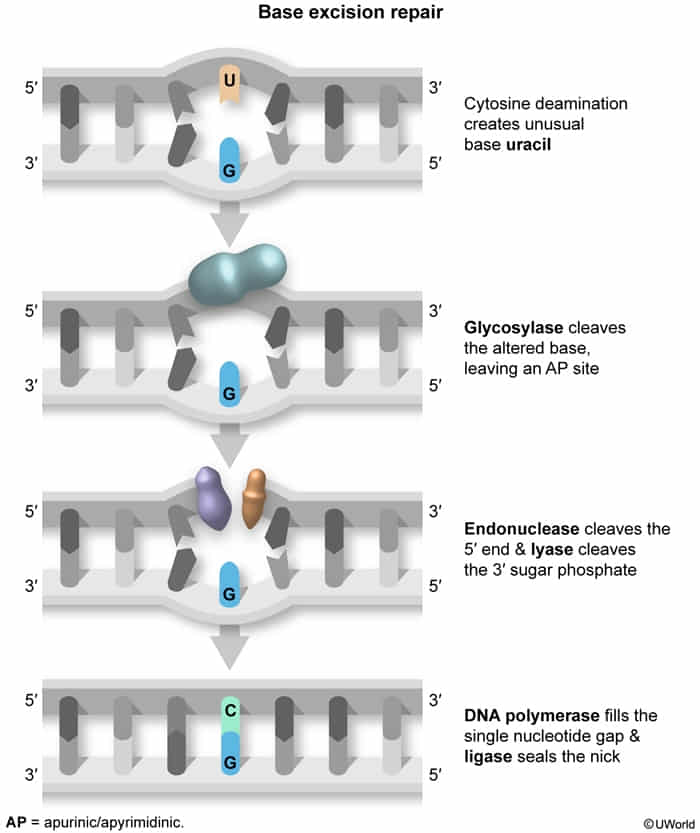
Base Excision Repair (BER)
Fixes: Spontaneous/toxic deamination (e.g., C→U).
Key Enzyme: Glycosylase .
Mechanism:
Base-specific Glycosylase removes the altered base, creating an apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) site.AP-Endonuclease cleaves the 5’ end.AP-Lyase (part of DNA Pol-beta) cleaves the 3’ end.DNA Polymerase fills the gap.DNA Ligase seals the nick.
Mnemonic: “GEL PLease” (Glycosylase, Endonuclease, Lyase, Polymerase, Ligase)
Mismatch Repair (MMR)
Double-Strand Break Repair
Homologous Recombination (HR)
When: S, G2 phases (uses sister chromatid as template).
Quality: Accurate, high-fidelity repair.
Defect: BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations (↑ breast, ovarian, prostate cancer risk).
Non-Homologous End Joining (NHEJ)
When: G1 phase (no template available).
Quality: Error-prone, can cause deletions/insertions.
Defect: Ataxia-Telangiectasia ATM gene ).
Exonuclease vs. Endonuclease
Feature Exonuclease Endonuclease Action Removes nucleotides from the ends (5’ or 3’) of a nucleic acid chain. Cleaves phosphodiester bonds within a nucleic acid chain. Products Single mononucleotides , released one at a time. Oligonucleotide fragments of varying sizes.Specificity Generally not sequence-specific. Can be non-specific (e.g., DNase I) or highly sequence-specific (e.g., restriction enzymes). Key Example DNA Polymerase Proofreading: 3’→5’ exonuclease activity removes mismatched bases during replication.Restriction Enzymes: Recognize and cut specific palindromic DNA sequences (e.g., for RFLP, cloning).Circular DNA Cannot act on circular DNA (no free ends).Can act on circular DNA.
Link to original