Epidemiology
Etiology
Risk factors
- Increased uric acid production
- Dietary sources
- Purine-rich foods (eg, seafood, red meat)
- Fructose-containing & alcoholic beverages (particularly beer)
- ↑ Cell turnover (eg, tumor lysis syndrome)
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome (deficiency of HGPRT)
- ↑ Phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate activity
- Dietary sources
- Decreased uric acid clearance
- Chronic kidney disease
- Volume depletion
- Diuretics (eg, thiazide)
- Niacin
- Cyclosporine & tacrolimus
- Rapid decline in uric acid levels
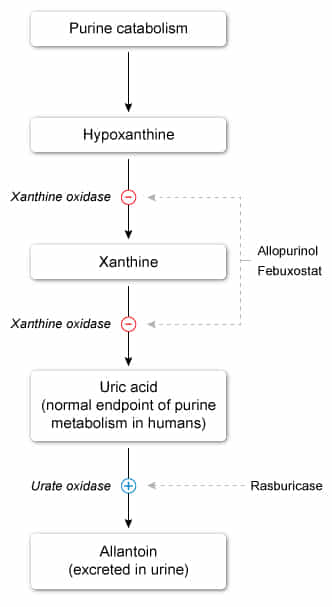
- Xanthine oxidase inhibitors (eg, allopurinol)
- Uricosuric drugs (eg, probenecid)
Pathophysiology
- Gout
- An inflammatory crystal arthropathy that is caused by the precipitation and deposition of uric acid crystals in synovial fluid and tissues.
- It is typically associated with hyperuricemia, but can also occur if uric acid levels are normal.
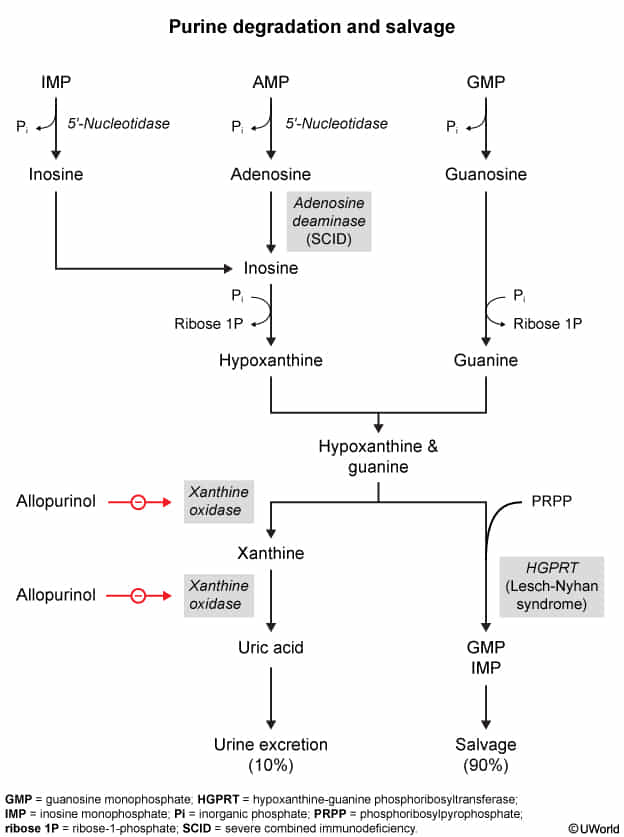
- Uric acid
- An end-product of purine metabolism that is excreted by the kidneys
- Has somewhat poor water solubility
- Predisposes to gout
- Triggers of urate crystal deposition
- ↑ Uric acid levels (due to insufficient excretion or increased production of purines)
- Acidosis
- Low temperature (e.g., cool peripheral joints)
- Crystalline arthritis: supersaturation of uric acid in extracellular fluid → intraarticular uric crystal precipitation (coated by IgGs) → phagocytosis by polymorphonuclear cells → release of inflammatory mediators and enzymes → local joint inflammation
- Chronic effects: repeated attacks → aggregations of urate crystals and giant cells (tophi) → deformities and arthritis
Clinical features
- Most common manifestation
- Acute severe pain with overlying erythema, decreased range of motion, swelling, warmth
- Possibly fever
- Symptoms are more likely to occur at night, typically waking the patient.
- Symptoms peak after 12–24 hours and regress over days to weeks.
- Desquamation of the skin overlying the joint may be seen during the recovery from an acute gout flare.
- Location
- Usually monoarthritis during first attacks
- In < 20% of cases, patients present with polyarthritis during first attacks.
- Asymmetrical distribution is common if more than one joint is affected
- Usually monoarthritis during first attacks
Diagnostics
- Synovial fluid leukocyte count
- Gout: >2,000/mm3
- Septic arthritis: > 50,000/mm3
Treatment
Tip
- NSAIDs (e.g., naproxen, indomethacin) preferred if no contraindications
- Colchicine used as second-line therapy
Acute gout flare
NSAIDs
- Naproxen or an alternative (e.g., indomethacin, ibuprofen)
- Contraindicated in PUD
Colchicine
- Mechanism of action: binds and stabilizes tubulin subunits → inhibits microtubule polymerization → inhibits phagocytosis of urate crystals, neutrophil activation, migration, and degranulation
- Adverse effects
- Gastrointestinal symptoms, e.g., diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain, are the most common.
- Rhabdomyolysis , myopathy
- Polyneuropathy
- Cardiac toxicity, arrhythmias
- Nephrotoxicity
- Myelosuppression
- CNS symptoms (e.g., fatigue, headache)
Tip
Chronic gout
- Urate-lowering therapy (ULT) is recommended for chronic gout.
- First-line: xanthine-oxidase inhibitors (allopurinol)
- Second-line: uricosurics (probenecid)
- Third-line: recombinant uricase (pegloticase, rasburicase)
- Also used in Tumor lysis syndrome
- Administer anti-inflammatory prophylaxis before initiating ULT as ULT may trigger, prolong, or worsen an acute gout flare.
- Lowering of serum urate levels likely causes preexisting urate crystal deposits to dissolve and become mobile.
Uricosurics
- Probenecid
- Mechanism of action
- Inhibition of uric acid reabsorption along renal proximal convoluted tubules → increased renal elimination
- Side effects
- Uric acid stones
- Hypersensitivity reactions (sulfa allergy due to being a sulfonamide derivative)