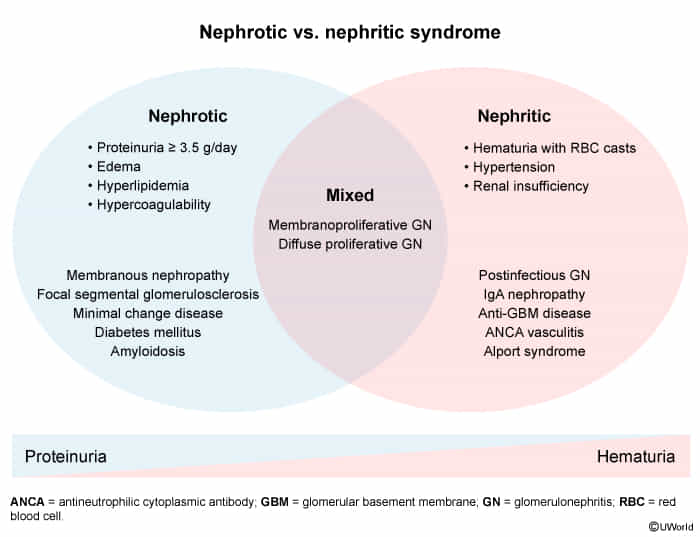
| Feature | Minimal Change (MCD) | Focal Segmental (FSGS) | Membranous (MN) | Diabetic Nephropathy | Amyloidosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Classic Patient | Children; assoc. w/ lymphoma | African American; assoc. w/ HIV, heroin | Caucasian Adult; assoc. w/ tumors, anti-PLA2R | Long-standing DM | Multiple Myeloma, RA |
| Patho | T-cell cytokines damage podocytes | Primary podocyte injury & scarring | Immune complex deposition (anti-PLA2R) | Non-enzymatic glycosylation of GBM | Misfolded protein deposition |
| Light Micro (LM) | Normal glomeruli | Sclerosis in some parts of some glomeruli | Thick GBM | Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules | Congo Red stain → apple-green birefringence |
| Electron Micro (EM) | Podocyte foot process effacement | Effacement (like MCD) + sclerosis | ”Spike & Dome” subepithelial deposits | Thickened GBM | Random fibrils |
| Key Fact | Excellent response to steroids | Poor prognosis; progresses to ESRD | Most common cause of primary nephrotic syndrome in adults | Manage with ACE-inhibitors | Poor prognosis |
  |
Diagnostics
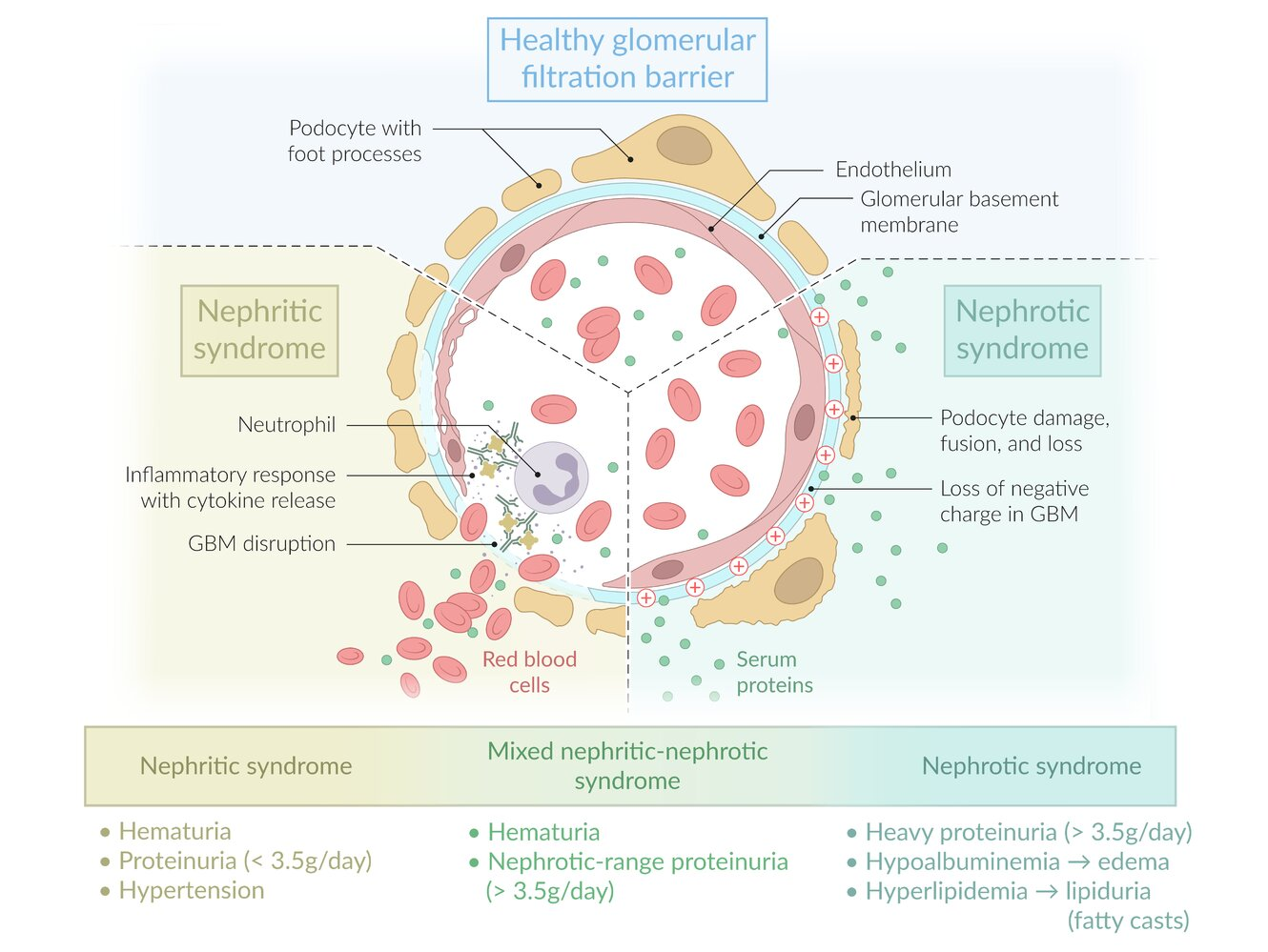
Confirmation of nephrotic-range proteinuria
- Qualitative assessment by urine dipstick (commonly used for screening)
- Usually shows ≥ 3+ proteins
- Hematuria may indicate concomitant glomerulonephritis.
- Quantitative assessment of urine protein excretion
- 24-hour urine protein (test of choice): > 3.5 g/24 hours
- Spot urine protein/creatinine ratio: > 3.5 g/g
Immune deposition
Mnemonic
- Membranous nephropathy: subepithelial & ‘spike and dome’
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Type II: intramembranous & ‘tram track’
- Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis Type I: subendothelial & ‘tram track’
Warning
podocyte = visceral epithelial cell
Classifications
Complications
Thrombotic complications
- Venous thromboembolism (e.g., deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism)
- Renal vein thrombosis: thrombus formation in the renal veins or their branches
- Cause: hypercoagulable state (e.g., malignancies, antiphospholipid syndrome, nephrotic syndrome)
- Manifestations
- Flank pain
- Hematuria
- ↑ LDH
- Anuria/renal failure in bilateral thrombosis
- Scrotal edema
- Diagnostics
- CT angiography or MR venography (preferred modality in patients with renal injury or failure)
- Doppler ultrasonography if no other diagnostic modality is available
- Treatment
- Anticoagulation
- Thrombolysis or thrombectomy in selected patients
- Complications: rupture of renal capsule, pulmonary embolism, kidney injury