Functions
- Cofactor for enzymes:
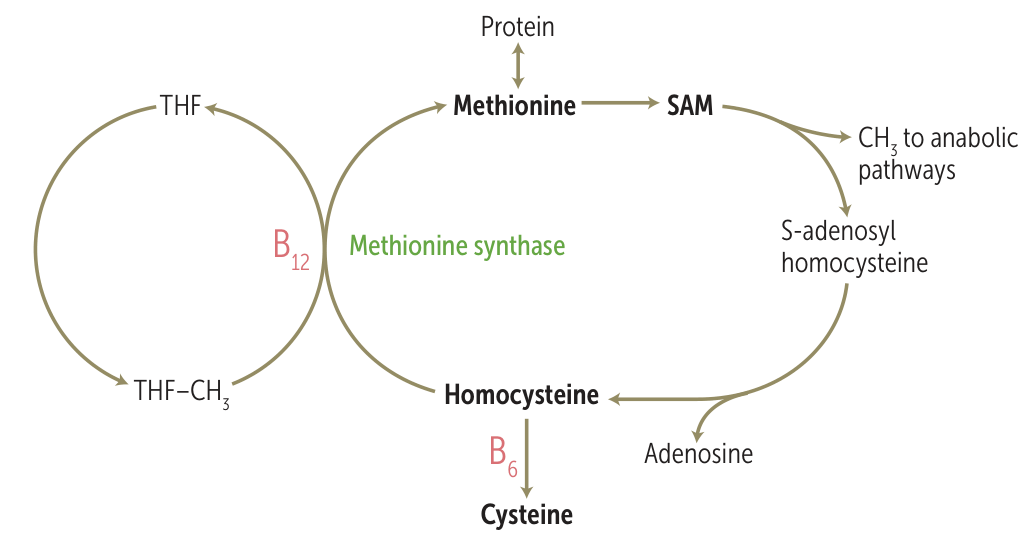
- Methionine synthase: Converts homocysteine to methionine (requires folate). Deficiency leads to ↑ homocysteine and traps folate as methyl-THF, impairing DNA synthesis.
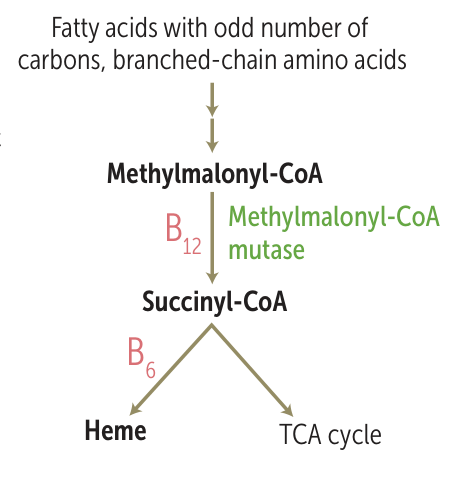
- Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase: Converts methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA. Deficiency leads to ↑ methylmalonic acid (MMA), which is neurotoxic and impairs myelin synthesis.
- Deficiency leads to impaired myelin synthesis: the buildup of Methylmalonyl-CoA disrupts myelin
- Deficiency leads to impaired myelin synthesis: the buildup of Methylmalonyl-CoA disrupts myelin
- Hydroxocobalamin (precursor of vitamin B12) is used to treat Cyanide poisoning
- Methionine synthase: Converts homocysteine to methionine (requires folate). Deficiency leads to ↑ homocysteine and traps folate as methyl-THF, impairing DNA synthesis.
Epidemiology
Etiology
Attention
The liver can store approximately 1,000 times the daily vitamin B12 requirement; deficiency develops only after the complete absence of intake or absorption for 3-4 year
- Decreased Intake
- Strict Veganism (takes years to develop).
- Gastric Causes (↓ Intrinsic Factor)
- Pernicious Anemia (Anti-parietal cell/IF antibodies).
- Gastrectomy / Bypass surgery.
- Atrophic gastritis (H. pylori).
- Intestinal Causes (Terminal Ileum Issues)
- Crohn Disease (affects terminal ileum).
- Ileal Resection. t
- Diphyllobothrium latum (Fish tapeworm).
- Bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
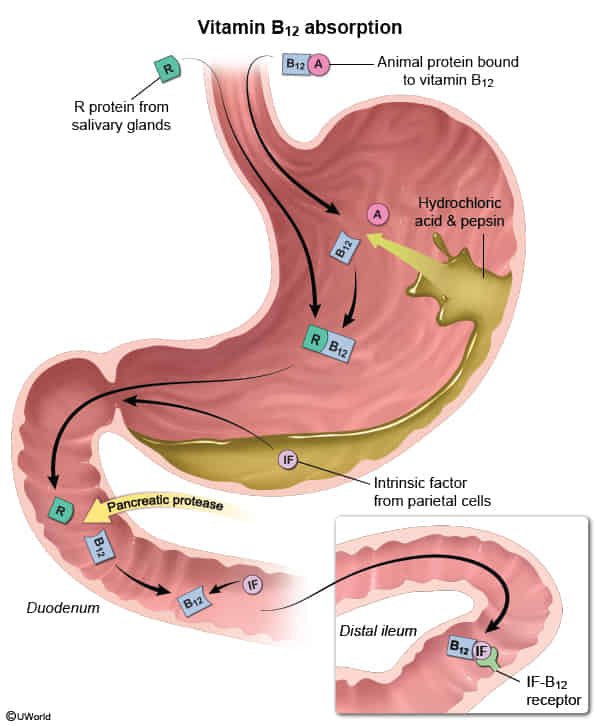
- Pancreatic insufficiency (cannot cleave R-binder).
- Pancreatic proteolytic enzymes are needed to release vitamin B12 from the vitamin B12–R protein complex (R protein is also known as transcobalamin I or haptocorrin), a necessary step that enables vitamin B12 to bind intrinsic factor, which ultimately facilitates terminal ileal absorption.
- Drugs
- Metformin.
- PPIs.
- Nitrous Oxide.
Pathophysiology
Dysfunctional biochemical reactions
- Dysfunctional methionine synthase (normally converts homocysteine to methionine, thereby demethylating N5-methyl-THF to THF)
- ↓ Tetrahydrofolate (THF; cofactor in purine synthesis) → ↓ DNA synthesis → large, nucleated hematopoietic cells, including megaloblasts → megaloblastic precursors undergo apoptosis or are phagocytosed by macrophages → pancytopenia (including megaloblastic anemia)
- ↓ Methionine → neuropathy
- ↑ Homocysteine → endothelial damage → predisposes to cardiovascular disease
- Can also cause secondary folate deficiency
- Dysfunctional methylmalonyl CoA mutase
- Methylmalonyl CoA cannot be converted to succinyl CoA → accumulation of methylmalonyl CoA and its precursor propionyl CoA, as well as their associated odd-chain fatty acids, which cannot be completely metabolized
- Propionyl CoA replaces acetyl CoA in neuronal membranes → demyelination → neurological manifestations
Pernicious anemia
- A type of vitamin B12 deficiency caused by autoantibodies against intrinsic factor and/or gastric parietal cells (type II hypersensitivity reaction)
- Antiparietal cell antibodies: target gastric parietal cells
- Causes ↓ acid production and atrophic gastritis
- In turn increases gastrin level
- ↓ Intrinsic factor production → ↓ vitamin B12 absorption in terminal ileum
- Causes ↓ acid production and atrophic gastritis
- Anti-IF antibodies: bind intrinsic factor and block the vitamin B12 binding site
- Antiparietal cell antibodies: target gastric parietal cells
- Associated with other autoimmune diseases (e.g., hypothyroidism, vitiligo)
- Increases the risk of gastric cancer
Clinical features
- Signs of anemia (e.g., fatigue, pallor)
- Subacute combined degeneration
- Glossitis
Tip
Always consider vitamin B12 deficiency when evaluating patients with dementia.
Folate deficiency
Link to original
Feature Vitamin B12 (Cobalamin) Deficiency Folate (Vitamin B9) Deficiency Primary Unique Role Neurological function (myelin sheath) Neural tube development (in fetus) Primary Sources Animal products Leafy greens, legumes, fortified foods Body Stores Large (Years) Small (Months) Absorption Terminal Ileum (Requires Intrinsic Factor) Duodenum/Jejunum (No Intrinsic Factor) Key Unique Causes Pernicious anemia, vegan diet, gastric surgery Poor diet, alcoholism, pregnancy needs Neurologic Symptoms PRESENT (Paresthesias, gait issues, cognitive changes) ABSENT Key Lab Marker Elevated Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) Normal Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) Treatment Danger Folate alone masks anemia, allows neuro damage to progress Less critical interaction (though diagnosis is key)
Diagnostics
- If vitamin B12 serum levels are normal:
- Measure homocysteine: elevated in both vitamin B12 deficiency and folate deficiency
- Measure methylmalonic acid (MMA) to help rule out folate deficiency (MMA is normal in folate deficiency and elevated in vitamin B12 deficiency)
- Without vitamin B12, methylmalonyl CoA mutase cannot break down methylmalonyl CoA, which leads to the accumulation of MMA.

- Without vitamin B12, methylmalonyl CoA mutase cannot break down methylmalonyl CoA, which leads to the accumulation of MMA.