Epidemiology
Etiology
- Primary (Essential) HTN: 90% of cases. Risk factors: Age, obesity, diabetes, smoking, genetics (2x risk if parents have HTN), African American ancestry, high Na+ intake, alcohol.
- Secondary HTN: 10% of cases. Suspect if resistant to 3+ meds or young patient (<30 yo).
- Renal: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS). t
- Fibromuscular dysplasia: Young females (“string of beads” on angiogram).
- Atherosclerosis: Older males.
- Mechanism: ↓ renal perfusion → ↑ Renin → ↑ Angiotensin II/Aldosterone.
- Endocrine:
- Primary Hyperaldosteronism (Conn syndrome): HTN + Hypokalemia + ↓ Renin.
- Cushing syndrome: Weight gain, striae, buffalo hump.
- Pheochromocytoma: Episodic HA, sweating, tachycardia (5 P’s).
- Other: Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA), Coarctation of the Aorta (BP arms > legs, rib notching).
- Renal: Renal Artery Stenosis (RAS). t
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
- Core Principles
- Goal: BP <130/80 mmHg for most patients.
- First-Line Agents: Thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors (ACEi)/ARBs, and Dihydropyridine CCBs.
- Foundation: Lifestyle modifications (DASH diet, Na+ restriction, exercise) are critical.
- Compelling Indications
- Heart Failure (HFrEF) & Post-MI: β-blockers + ACEi/ARB are essential for mortality benefit.
- CKD & Diabetes: ACEi or ARBs are first-line for their renoprotective effects.
- Osteoporosis: Thiazide diuretics are beneficial because they decrease Ca2+ excretion.
- BPH: α1-blockers (e.g., doxazosin) treat both conditions.
- Special Populations
- African Americans: Thiazides or CCBs are preferred initial therapy.
- Pregnancy: Use Hydralazine, Methyldopa, Labetalol, Nifedipine (“He Makes Life Nice”).
- CI in Pregnancy: ACEi, ARBs, and renin inhibitors are teratogenic.
- High-Yield Adverse Effects
- ACEi: Dry cough, hyperkalemia, angioedema.
- Thiazides: Hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, hyperuricemia, hypercalcemia.
- Dihydro-CCBs: Peripheral edema, flushing, headache.
- β-blockers: Bradycardia, bronchoconstriction, sexual dysfunction.
- Spironolactone: Hyperkalemia, gynecomastia.
- Hypertensive Emergency
- Definition: SBP >180 or DBP >120 mmHg with acute end-organ damage.
- Tx: Use IV agents (e.g., labetalol, nicardipine). Lower Mean Arterial Pressure (MAP) by ≤25% in the first hour.
- Aortic Dissection Exception: Rapidly lower SBP to <120 mmHg with IV β-blockers (e.g., esmolol, labetalol).
Warning
In patients with long-standing hypertension, a chronic autoregulatory shift in the blood pressure–flow relationship occurs, affording less perfusion (flow) at any given pressure. Therefore, excessively rapid correction of blood pressure toward normal may induce relative ischemia.
Complications
Eyes
- Hypertensive retinopathy
- Arteriosclerotic and hypertension-related changes of the retinal vessels
- Initial reactive vasoconstriction (vasospasm), followed by sclerosis with breakdown of blood-retinal barrier and subsequent hemorrhage and exudation
- Fundoscopic examination
- Cotton wool spots
- Retinal hemorrhages (i.e., flame-shaped hemorrhages)
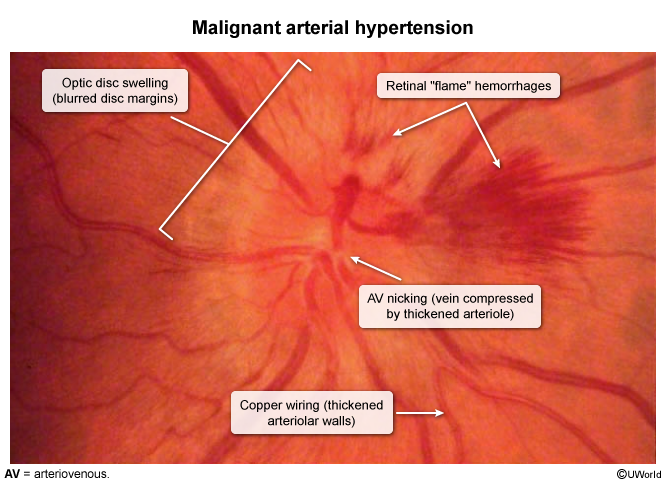
- Microaneurysms
- Macular star (results from exudation into the macula)
- Hard exudates
- Arteriovenous nicking: a tapering of a retinal venule at the point where a retinal arteriole crosses the retinal venule
- Marked swelling and prominence of the optic disk with indistinct borders due to papilledema and optic atrophy (end-stage disease)
- The presence of papilledema in a hypertensive patient may indicate a hypertensive crisis and warrants urgent lowering of blood pressure