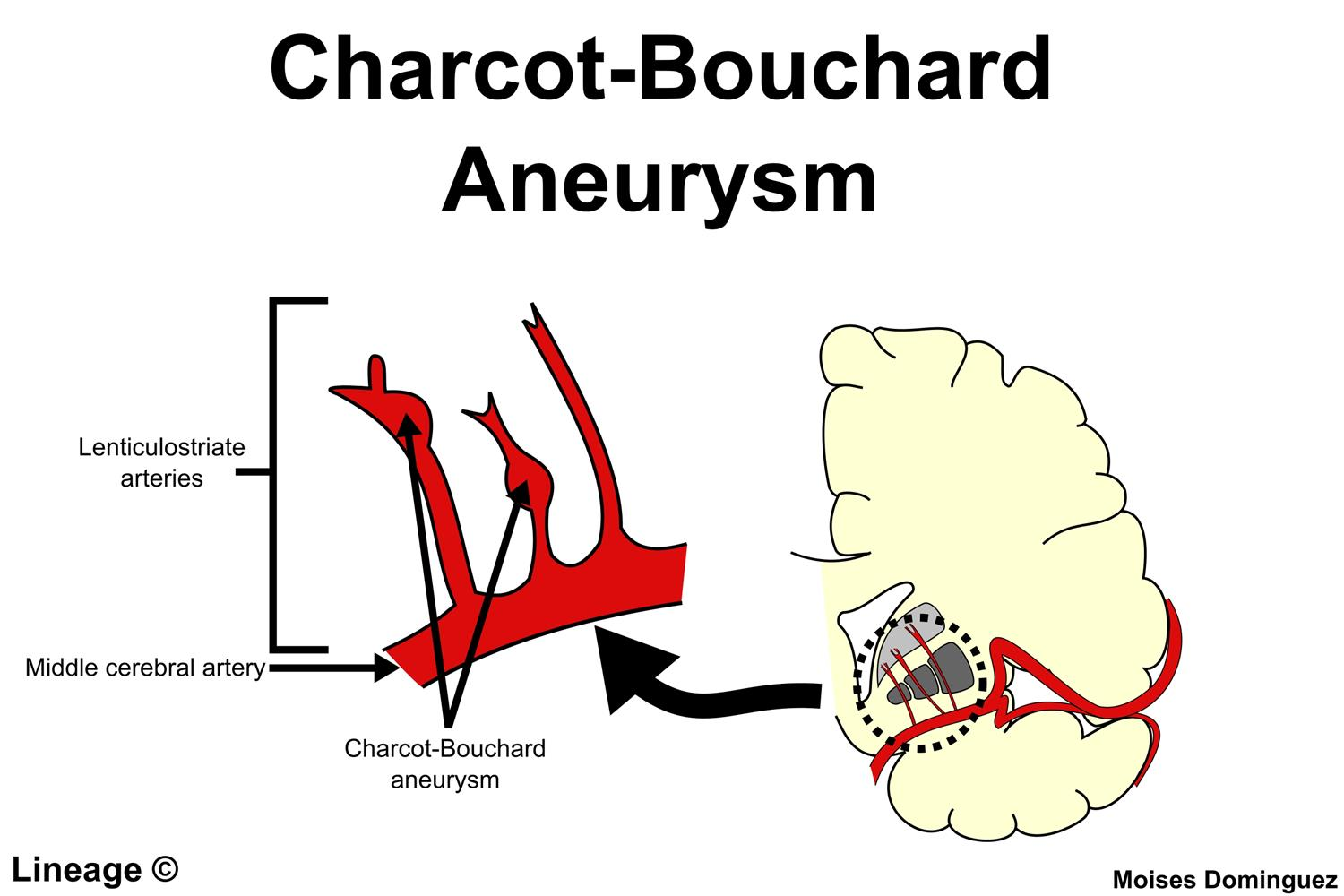
| Feature | Charcot-Bouchard | Saccular (Berry) |
|---|---|---|
| Etiology | Chronic HTN | Congenital weakness + Hemodynamics |
| Pathology | Lipohyalinosis of microvessels | Lacking Internal Elastic Lamina & Media |
| Location | Deep Brain (Basal Ganglia, Thalamus) | Circle of Willis Bifurcations (ACom > PCom) |
| Vessels | Lenticulostriate arteries | Medium-sized arteries |
| Rupture | Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage | Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
| Symptoms | Focal deficits (Hemiparesis) | “Thunderclap” Headache, Meningismus |
| Associations | Lacunar strokes | ADPKD, Ehlers-Danlos, Marfan |
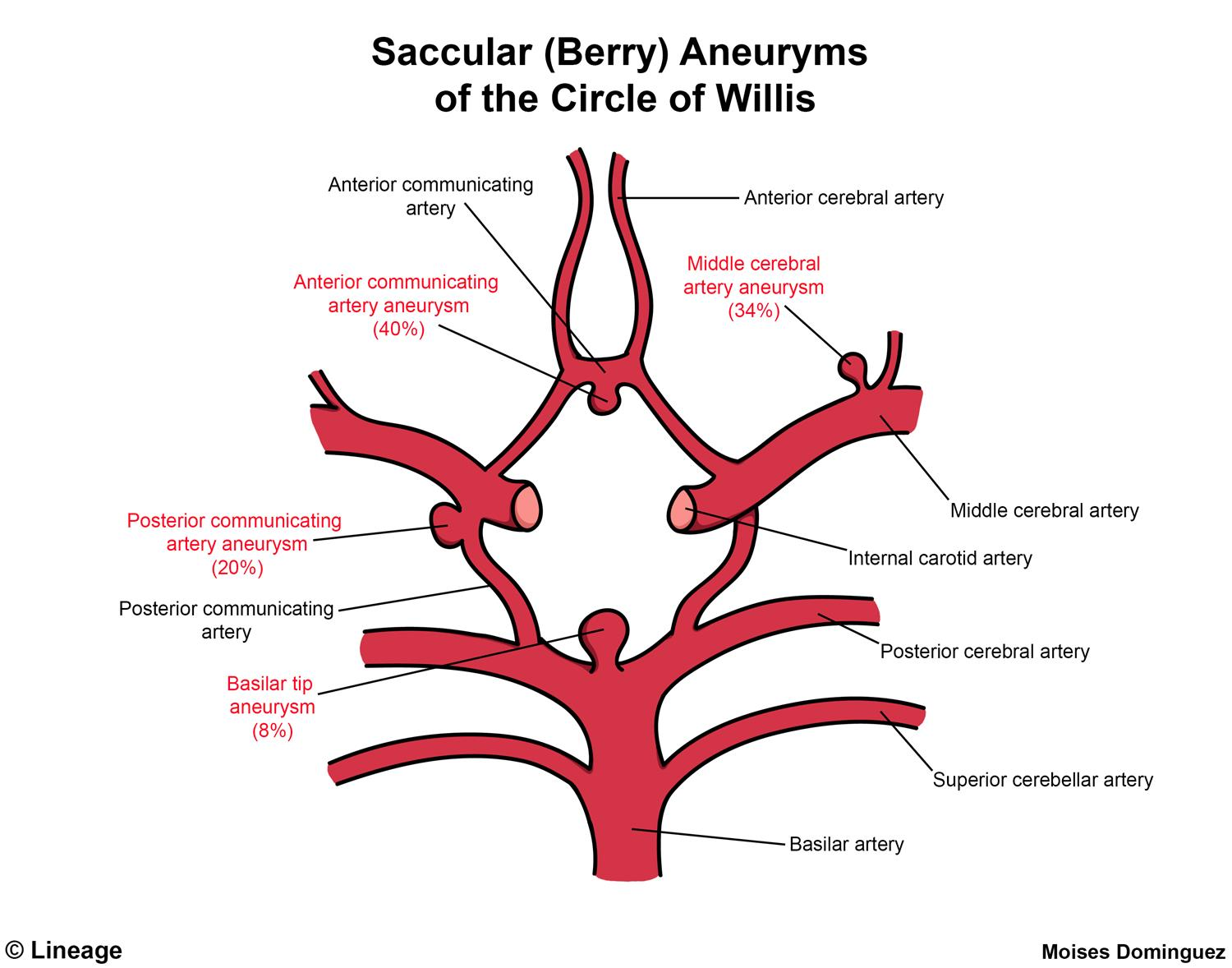
- Saccular: This term means “resembling a sac.” Saccular aneurysms are outpouchings or bulges on one side of a blood vessel wall.
- Berry: The “berry” description refers to the characteristic round shape of these aneurysms. They look like a berry connected to the main artery.