Spinal cord
Cross-sectional anatomy
Drawing 2025-07-26 09.26.44.excalidraw
⚠ Switch to EXCALIDRAW VIEW in the MORE OPTIONS menu of this document. ⚠ You can decompress Drawing data with the command palette: ‘Decompress current Excalidraw file’. For more info check in plugin settings under ‘Saving’
Excalidraw Data
Text Elements
Spinothalamic tract
Dorsal column
Corticospinal tract
Embedded Files
0f69b6f90704f2e1846fca80217e793a8633730b: Pasted Image 20250726092659_518.png
Link to original
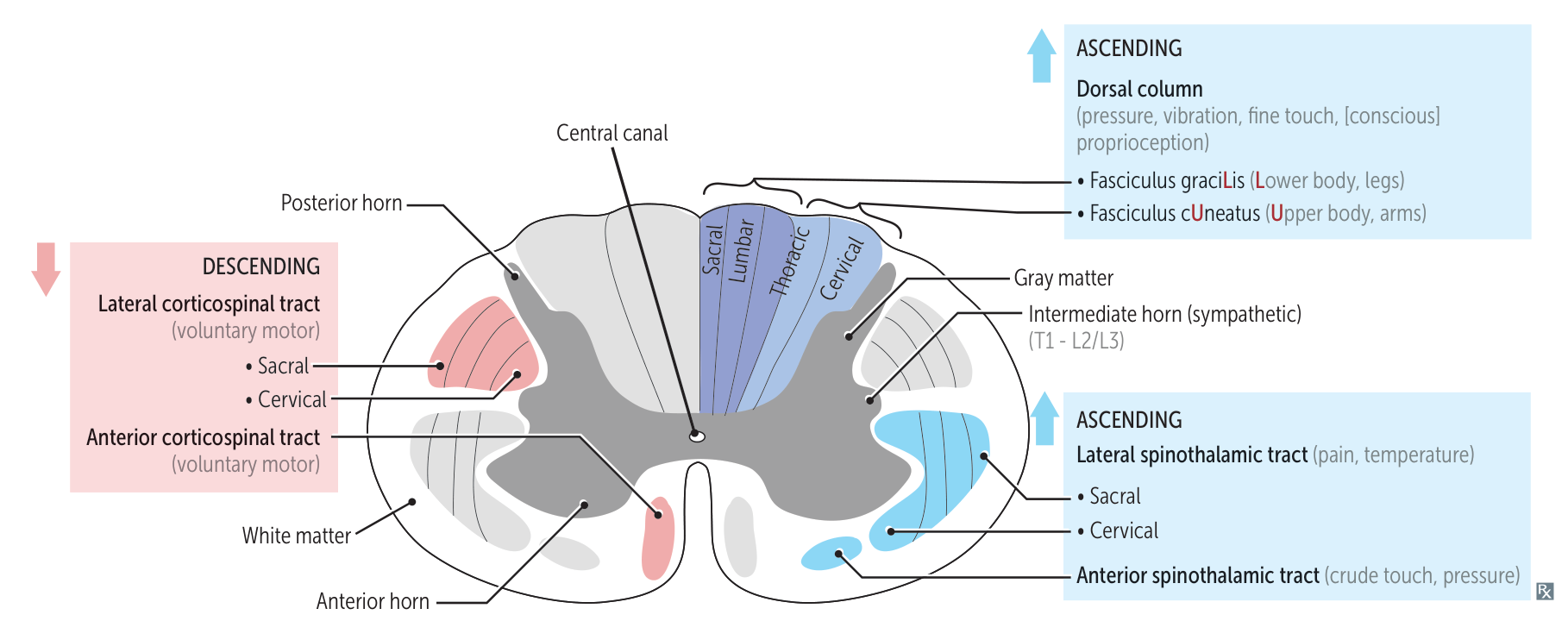
- Gray Matter (Neuron Bodies):
- Dorsal (Posterior) Horn: Sensory input (pain, temp, touch).
- Ventral (Anterior) Horn: Motor output (Lower Motor Neurons - LMNs).
- Lateral (Intermediate) Horn (T1-L2): Sympathetic nervous system.
- White Matter (Axon Tracts):
- Dorsal Columns: Ascending sensory (vibration, proprioception).
- Lateral & Ventral Columns: Corticospinal tract (motor), Spinothalamic tract (pain/temp).
- Anterior White Commissure: Decussation site for spinothalamic tract.
Mnemonic
- If it’s in the back (dorsal), think SENSORY.
- If it’s in the front (ventral), think MOTOR.
Ascending (Sensory) Tracts
- Dorsal Column-Medial Lemniscus (DCML)
- Function: Fine touch, vibration, proprioception, pressure.
- Location: Posterior (dorsal) funiculus.
- Fasciculus Gracilis: Medial; info from lower body (legs).
- Fasciculus Cuneatus: Lateral; info from upper body (arms).
- Decussation: Medulla (as internal arcuate fibers), then ascends as medial lemniscus.
- Path: 1° neuron (DRG) → ascends ipsilaterally in dorsal column → synapses in nucleus gracilis/cuneatus (medulla) → 2° neuron decussates → ascends to VPL of thalamus → 3° neuron to somatosensory cortex.
- Somatotopy: Fibers are added laterally. Sacral/leg fibers are most medial (Fasciculus Gracilis), and cervical/arm fibers are most lateral (Fasciculus Cuneatus). “Legs are in the middle.” t
- Spinothalamic Tract (Anterolateral System)
- Function: Pain, temperature, crude touch.
- Location: Anterolateral funiculus.
- Decussation: Anterior white commissure at/near the level of entry into the spinal cord.
- Entry & Lissauer’s Tract: The primary pain/temperature neurons (1st order) enter the spinal cord and travel within the Tract of Lissauer, where they can ascend or descend 1-2 spinal segments before synapsing.
- Synapse: They then synapse on the second-order neuron in the dorsal horn (substantia gelatinosa).
- Decussation: The axon of this second-order neuron is what immediately crosses to the contralateral side via the anterior white commissure to form the spinothalamic tract.
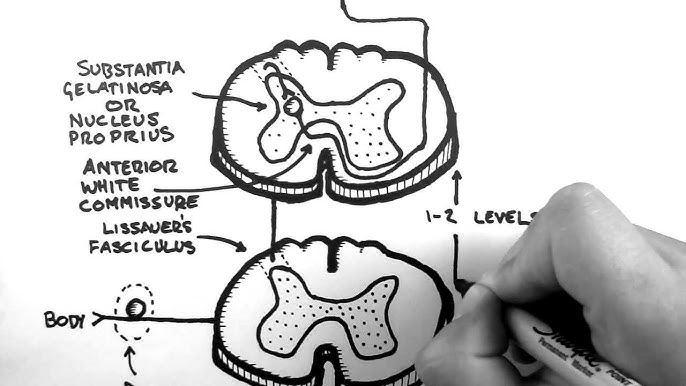
- Path: 1° neuron (DRG) → synapses in dorsal horn → 2° neuron decussates → ascends contralaterally → synapses in VPL of thalamus → 3° neuron to somatosensory cortex.
- Somatotopy: Cervical/arm fibers are most medial, and sacral/leg fibers are most lateral. “Pain in the ass is on the outside.”
Descending (Motor) Tracts
- Lateral Corticospinal Tract
- Function: Voluntary motor control of limbs (distal muscles).
- Location: Lateral funiculus.
- Decussation: Pyramidal decussation in the caudal medulla.
- Path: Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) in primary motor cortex → descends ipsilaterally through internal capsule → decussates in medulla → descends contralaterally in lateral corticospinal tract → synapses on LMN in ventral horn.
- Somatotopy: Cervical/arm fibers are most medial, and sacral/leg fibers are most lateral.
- Hypothalamospinal Tract (Sympathetic)
- Function: Provides sympathetic innervation to the body.
- Location: Lateral funiculus.
- Decussation: None (descends ipsilaterally).
- Path: Hypothalamus → descends through brainstem and lateral funiculus of spinal cord → synapses on preganglionic neurons in the lateral horn (T1-L2).
- Clinical Pearl: A lesion anywhere along this path (e.g., lateral medulla, cervical spinal cord) causes ipsilateral Horner’s Syndrome (Ptosis, Miosis, Anhidrosis).
| Tract | Organization | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Dorsal Column | Legs Medial, Arms Lateral | Ascends before crossing; new fibers are added laterally. |
| Spinothalamic | Arms Medial, Legs Lateral | Crosses then ascends; existing fibers are pushed laterally. |
| Corticospinal | Arms Medial, Legs Lateral | Fibers exiting soonest (arms) are medial; long-traveling fibers (legs) are lateral. (“exit” is on the inside, not the outside.) |
Nerve roots
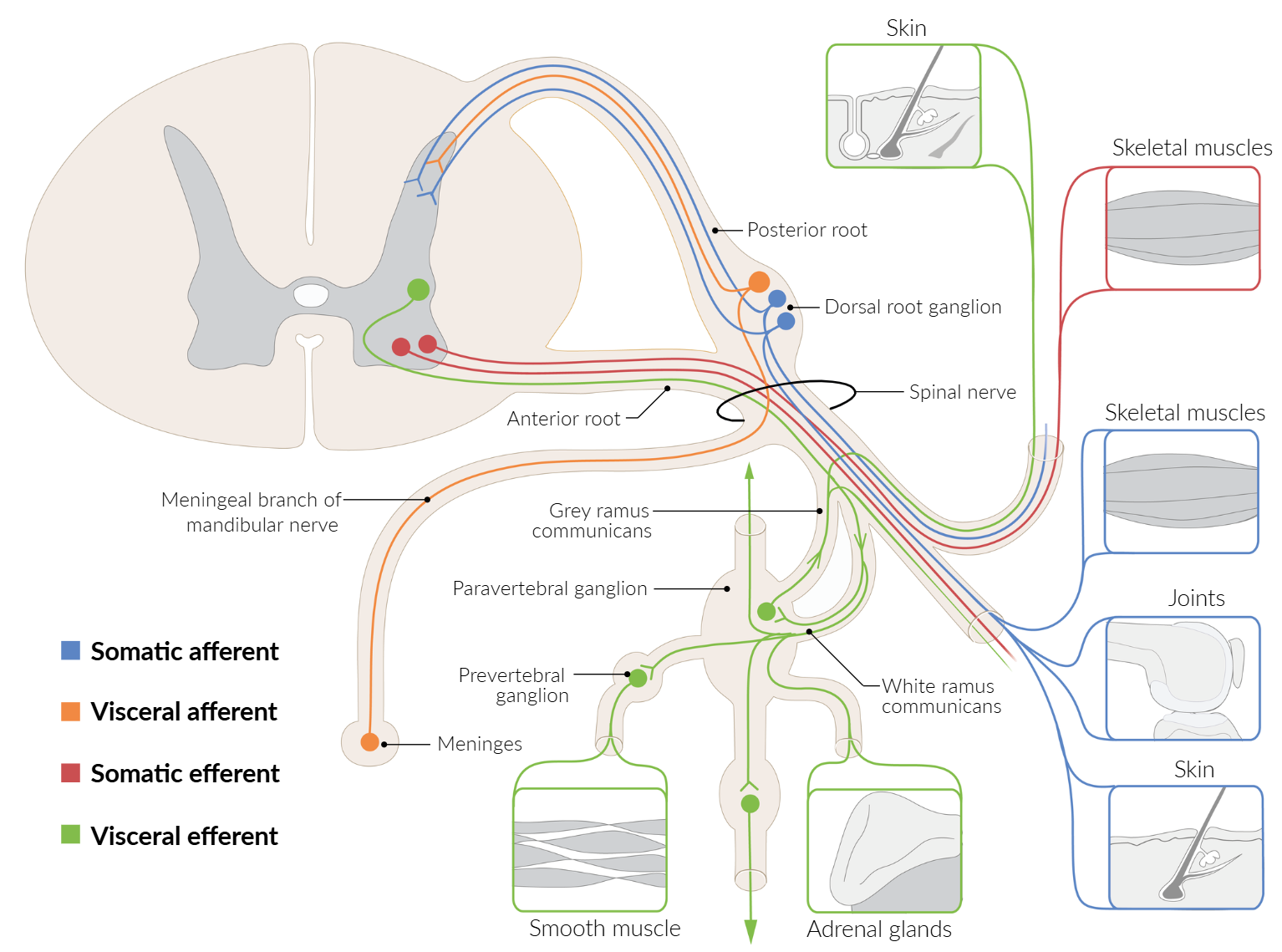
- Anterior roots carry motor (efferent) fibers that control skeletal and smooth muscle.
- Dorsal roots carry sensor (afferent) fibers that transmit somatosensory information.
Muscle proprioceptors
- Muscle Stretch Receptors (Muscle Spindles)
- Primary function: to regulate muscle tension and prevent damage from excessive force.
- Pathway (Myotatic Reflex)
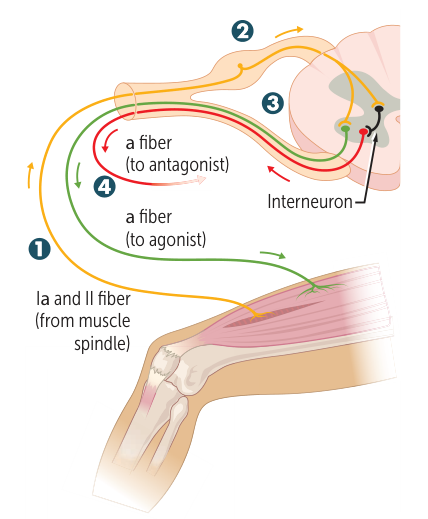
- Senses an ↑ in muscle length and the speed of the stretch.
- The signal travels via Type Ia/II sensory axons to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG).
- In the spinal cord, there is direct activation of the α-motor neuron (for the agonist) and an inhibitory interneuron (for the antagonist).
- This leads to the simultaneous contraction of the agonist muscle and the inhibition of the antagonist muscle, which prevents overstretching.
- Location/Innervation
- Found in the body of the muscle.
- Innervated by Type Ia and II sensory axons.
- Activated By
- ↑ muscle stretch.
- This mechanism is responsible for Deep Tendon Reflexes (DTRs).
- Example: The Knee-Jerk Reflex (deep tendon reflex). Tapping the patellar tendon stretches the quadriceps, causing it to contract and the leg to extend.
- Golgi Tendon Organ (GTO)
- Primary Function: to resist changes in muscle length; maintains muscle tone and posture.
- Pathway (Inverse Myotatic Reflex)
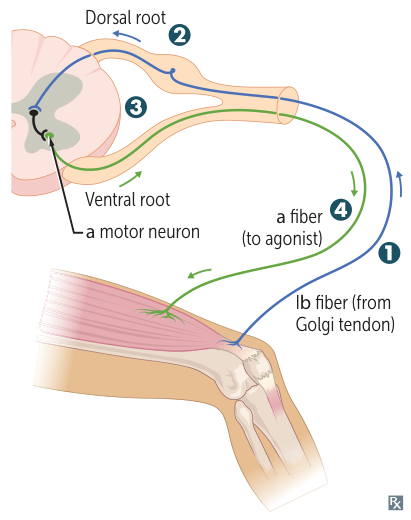
- Senses an ↑ in muscle tension.
- The signal travels via Type Ib sensory axons to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG).
- In the spinal cord, it activates an inhibitory interneuron.
- This interneuron leads to the inhibition of the agonist muscle, causing it to relax and producing a reduction in tension.
- Location/Innervation
- Found in tendons.
- Innervated by Type Ib sensory axons.
- Activated By
- ↑ muscle tension.
- This is a protective reflex to prevent damage from excessive force.
- Example: A weightlifter suddenly dropping a very heavy weight when the tension becomes excessive, overriding the voluntary command to lift.
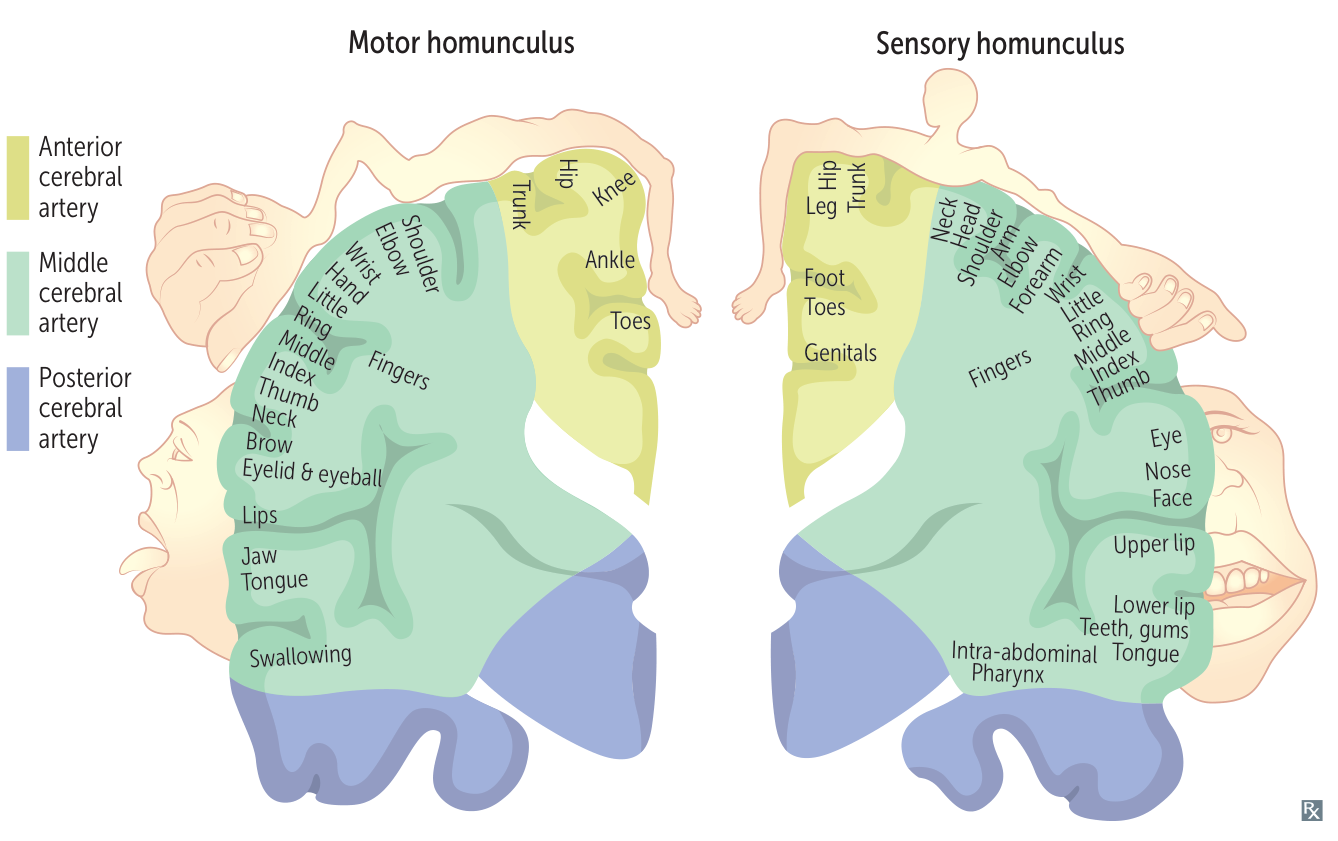
Homunculus