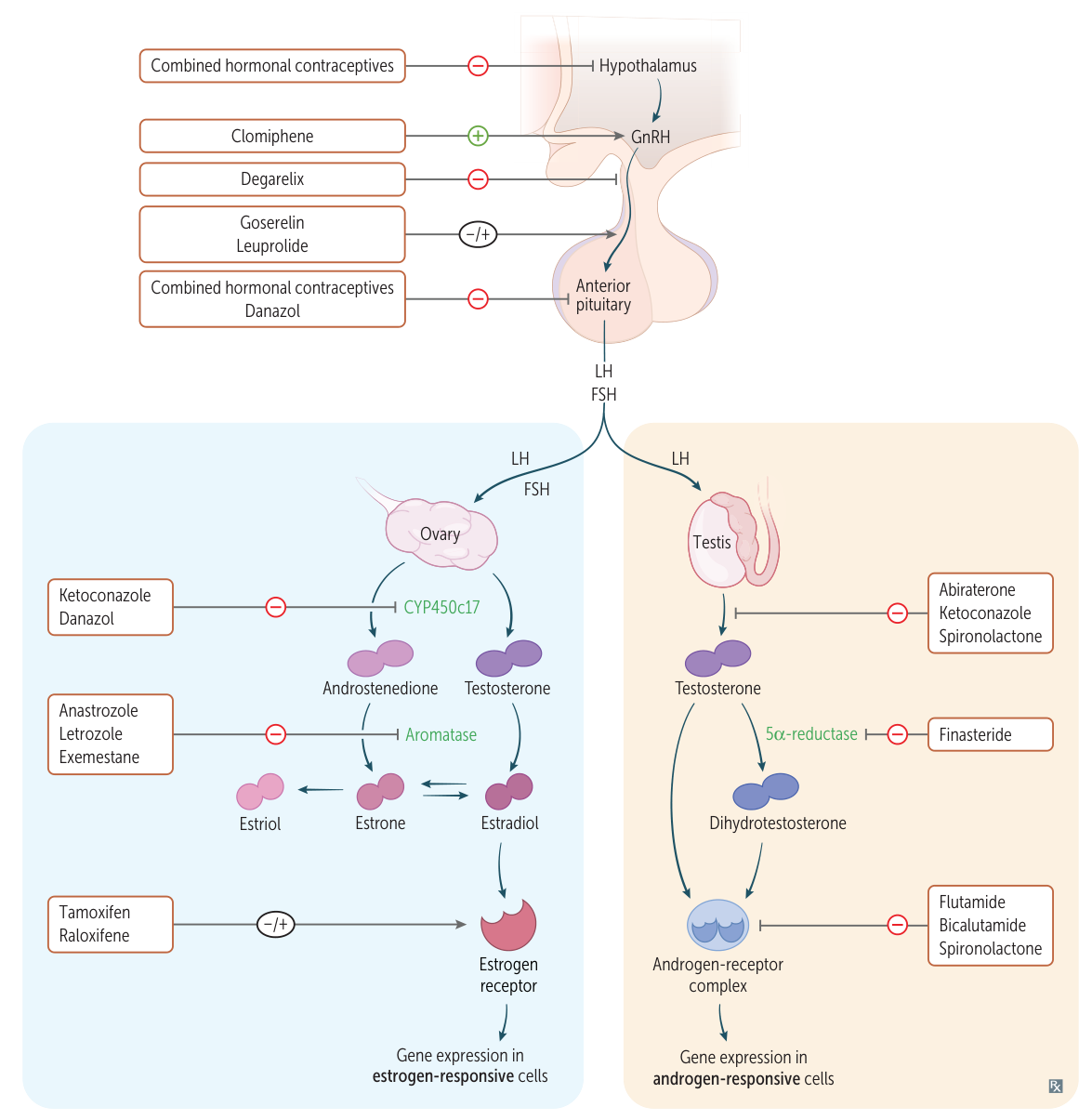
Gonadotropin-Releasing Hormone (GnRH) Analogs & Antagonists
GnRH Agonists
Drugs : Leuprolide Mechanism :
Pulsatile administration: Agonist effect → ↑ FSH, LH release (used for infertility).Continuous administration: Downregulates GnRH receptors on the anterior pituitary → ↓ FSH, LH release → ↓ testosterone (in men) and estrogen (in women).
Clinical Use (Continuous) :
Adverse Effects :
Initial flare-up of symptoms (e.g., bone pain in prostate cancer).
Hypogonadism symptoms: hot flashes, ↓ libido, gynecomastia.
GnRH Antagonists
Drugs : Degarelix, GanirelixMechanism : Directly block GnRH receptors → immediate suppression of FSH, LH.Clinical Use : Prostate cancer (Degarelix), prevent premature LH surge in IVF (Ganirelix).Adverse Effects : Hypogonadism symptoms, injection site reactions. No initial flare-up.
Drugs Affecting Sex Hormones
Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulators (SERMs)
Tissue-specific agonist/antagonist activity.
Common effect
Agonist on liver → ↑ DVT risk Antagonist on hypothalamus/CNS → hot flashes t
Tamoxifen :
Antagonist at breast .Agonist at uterus, bone .Use : ER+ breast cancer.Adverse Effects : ↑ risk of endometrial cancer , thromboembolic events (DVT/PE), hot flashes.
Raloxifene :
Antagonist at breast, uterus .Agonist at bone .Use : Osteoporosis in postmenopausal women, prophylaxis for breast cancer.Adverse Effects : Thromboembolic events, hot flashes. (No increased risk of endometrial cancer).
Clomiphene :
Antagonist at estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus .Mechanism : Prevents normal negative feedback ↑ release of GnRH → ↑ FSH/LH → stimulates ovulation.Use : Infertility (e.g., PCOS).Adverse Effects : Hot flashes, ovarian enlargement, multiple gestation pregnancy.
Aromatase Inhibitors
Drugs : Anastrozole t , Letrozole, ExemestaneMechanism : Inhibit peripheral conversion of androgens to estrogens.Use : ER+ breast cancer in postmenopausal women.Adverse Effects : Osteoporosis, arthralgias.
Antiandrogens
Finasteride :
Mechanism : 5α-reductase inhibitor (blocks conversion of testosterone → DHT).Use : Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), male-pattern baldness.
Flutamide, Bicalutamide :
Mechanism : Competitive inhibitors at androgen receptors.Use : Prostate cancer (often with GnRH agonists to block initial flare).
Spironolactone :
Mechanism : Inhibits steroid binding, acts as an androgen receptor antagonist.Use : Hirsutism in PCOS.Adverse Effects : Hyperkalemia, gynecomastia.
Contraception & Uterine Drugs
Combined Hormonal Contraceptives (Estrogen + Progestin)
Mechanism : Estrogen suppresses FSH release (inhibiting follicle development); Progestin suppresses LH surge (preventing ovulation), thickens cervical mucus, and thins the endometrium.Contraindications (High-Yield) :
Hx of thromboembolism (DVT/PE)
Smoker >35 years old
Migraine with aura
Severe hypertension
History of estrogen-dependent tumor (e.g., breast cancer).
Abortifacients
Mifepristone : Progesterone receptor antagonist → necrosis of decidua.Misoprostol : Prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) analog → induces uterine contractions.Typically used together for medical abortion.
Uterine Stimulants (Oxytocics)
Oxytocin : Used to induce/augment labor; control postpartum hemorrhage.Methylergonovine : Ergot alkaloid used for postpartum hemorrhage. Contraindicated in HTN due to vasoconstrictive effects.
Tocolytics (Relax Uterus)
Use : Delay preterm labor.Terbutaline : Beta-2 agonist.Nifedipine : Calcium channel blocker.Indomethacin : NSAID (prostaglandin inhibitor).
Drugs for Erectile Dysfunction
PDE-5 Inhibitors
Drugs : Sildenafil , Tadalafil, VardenafilMechanism : Inhibit phosphodiesterase-5 → ↑ cGMP → prolonged smooth muscle relaxation in the corpus cavernosum → ↑ blood flow.Adverse Effects : Headache, flushing, dyspepsia, cyanopsia (blue-tinted vision).Contraindication : DO NOT USE WITH NITRATES (e.g., nitroglycerin) → can cause severe, life-threatening hypotension.
Tamoxifen
Mechanism of action
Competitive antagonist on the estrogen receptors of the breast → ↓ breast cancer cell growth
Agonist on estrogen receptors in the following tissues :
Bone tissue → inhibition of osteoclasts → ↓ risk of osteoporosis and fractures
Endometrium → ↑ proliferation
Myometrium → ↑ proliferation
Indications
Side effects
Raloxifene
Mechanism of action
Competitive antagonist on estrogen receptors in the following tissues:
Breast → ↓ breast cancer cell growth
Endometrium and myometrium → ↓ proliferation (in contrast to tamoxifen)
Agonist on estrogen receptor in bone tissue → inhibition of osteoclasts
Indications
Side effects
Clomiphene
Mechanism of action
Blocks hypothalamic estrogen receptors, thereby inhibiting negative feedback and increasing release of FSH and LH to trigger ovulation
Indications
Infertility (for ovulation induction)
Side effects