- Tissue factor pathway inhibitor: inhibits tissue factor
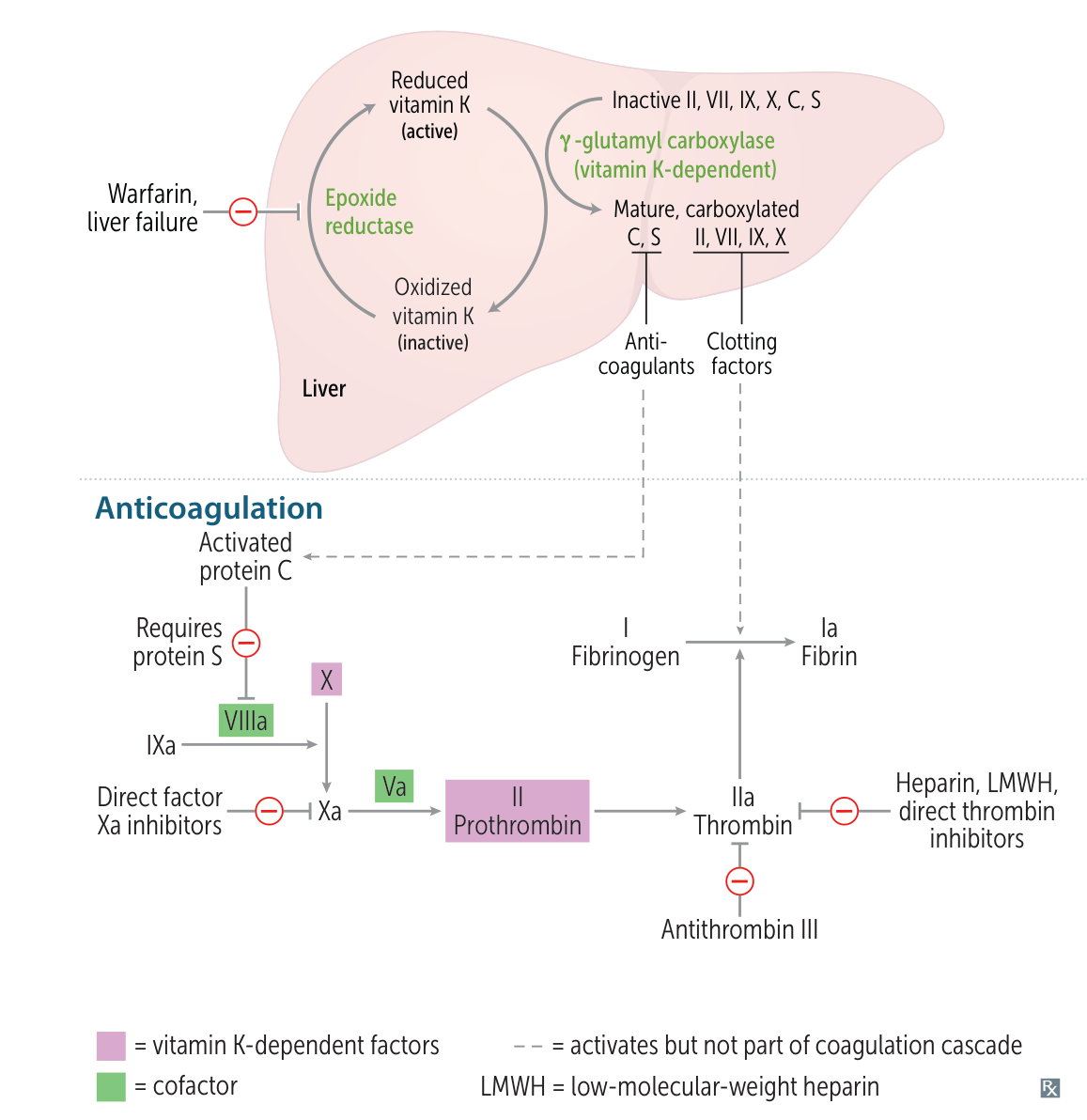
- Protein C and protein S: Activated protein C and its cofactor protein S form the activated protein-C complex (APC complex), which inhibits factors Va and VIIIa.
- Vitamin K-dependent synthesis in the liver
- Shorter half-life than vitamin K-dependent coagulation factors (relevant for treatment with vitamin K antagonists, e.g., warfarin)
- Clotting risk will increase during the initial administration of warfarin, because protein C and S will break down faster.
- Clinical relevance
- Antithrombin
- Degrades thrombin and factors IXa and Xa
- Activates tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)
