 Consistent with 交大附小
Consistent with 交大附小
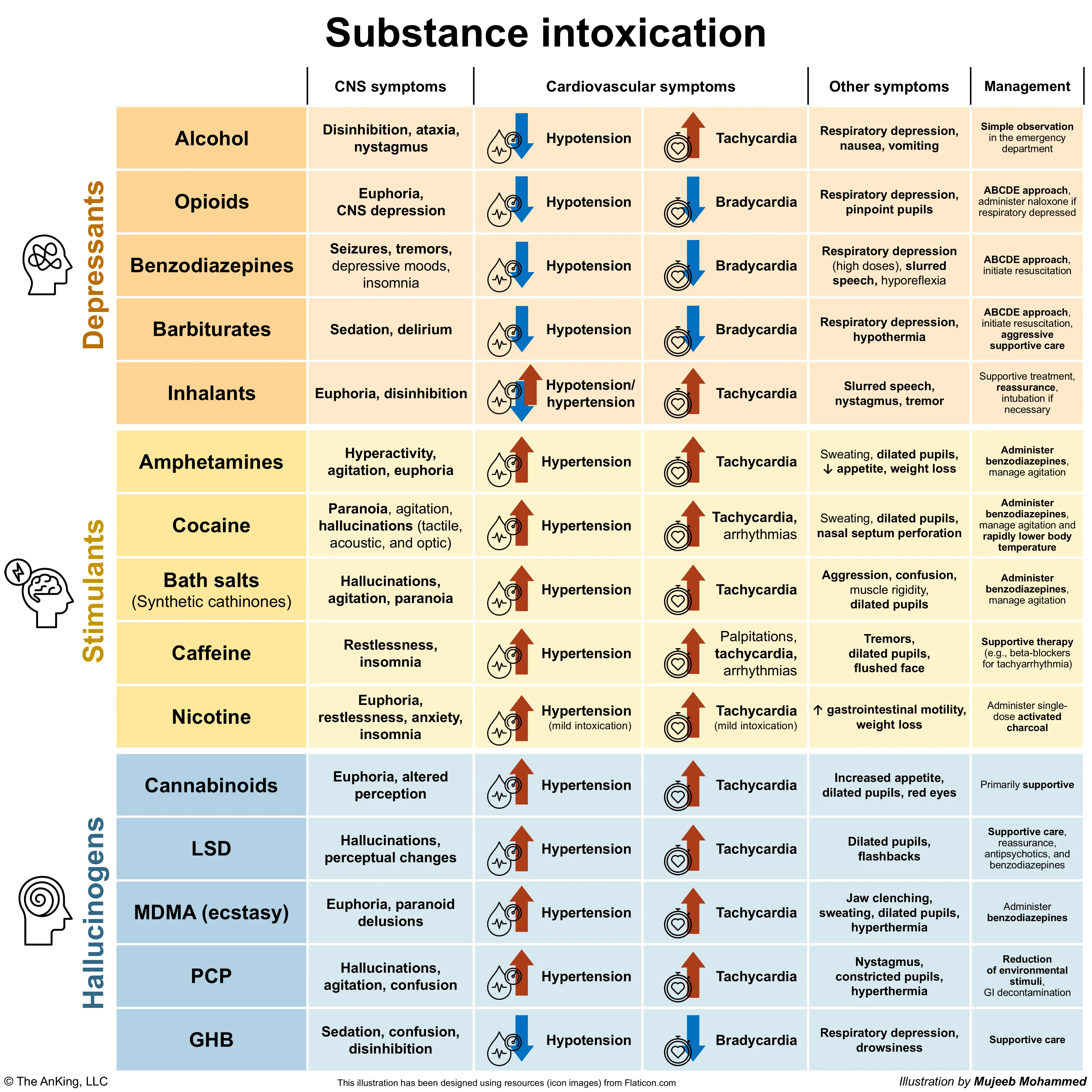
- Depressants (Opioids, Benzodiazepines)
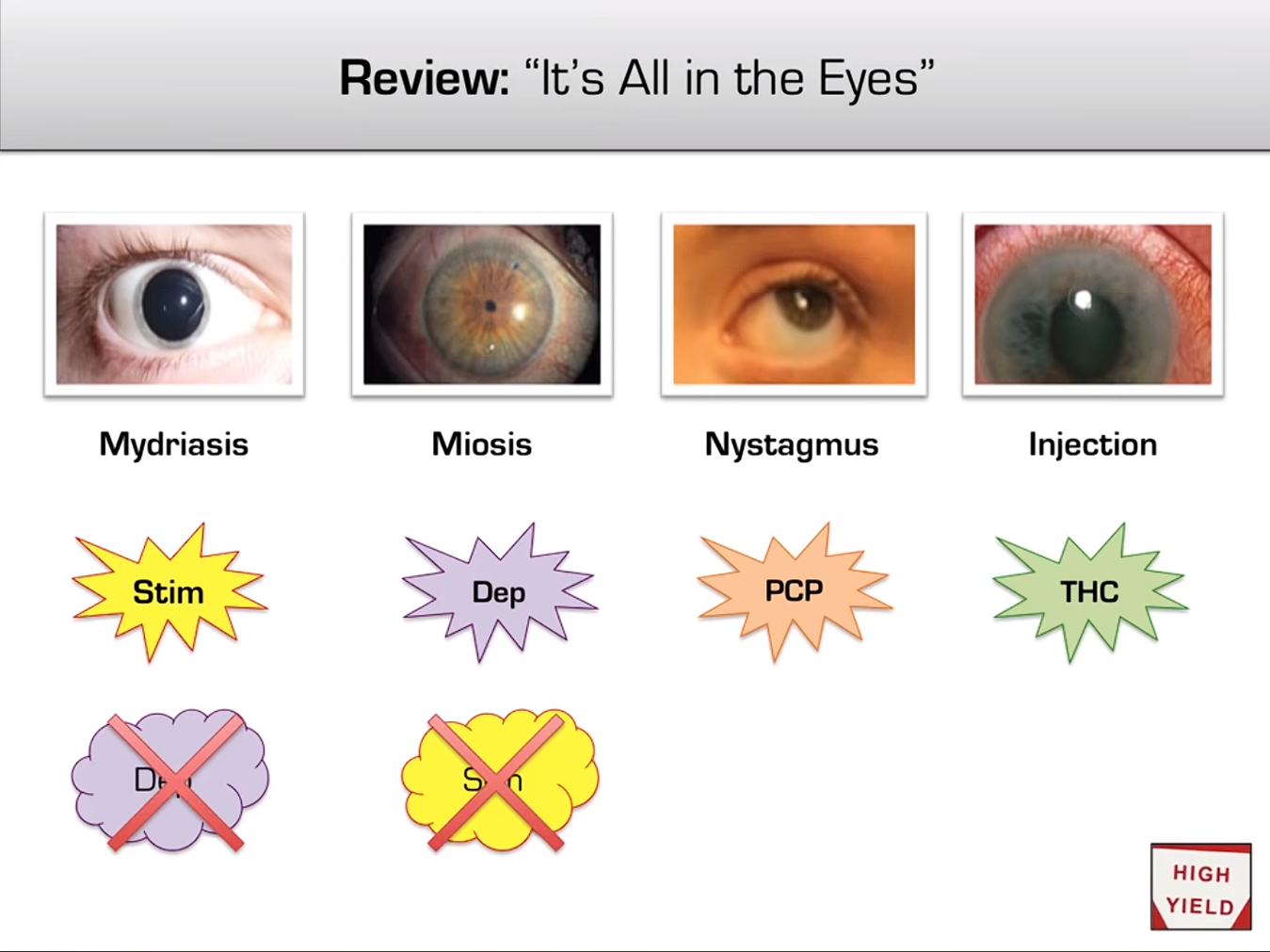
- Key Sign: Miosis (pinpoint pupils) is the hallmark of opioid (e.g., heroin, fentanyl) overdose.
- Mechanism: Potent stimulation of the parasympathetic nervous system.
- Other: Benzodiazepines are less consistent; pupils may be normal or dilated.
- Stimulants (Cocaine, Amphetamines)
- Key Sign: Mydriasis (dilated, poorly reactive pupils).
- Mechanism: Sympathetic nervous system activation (“fight-or-flight” response).
- Hallucinogens (LSD, PCP, Psilocybin)
- LSD/Psilocybin: Mydriasis (dilated pupils) due to sympathomimetic effects.
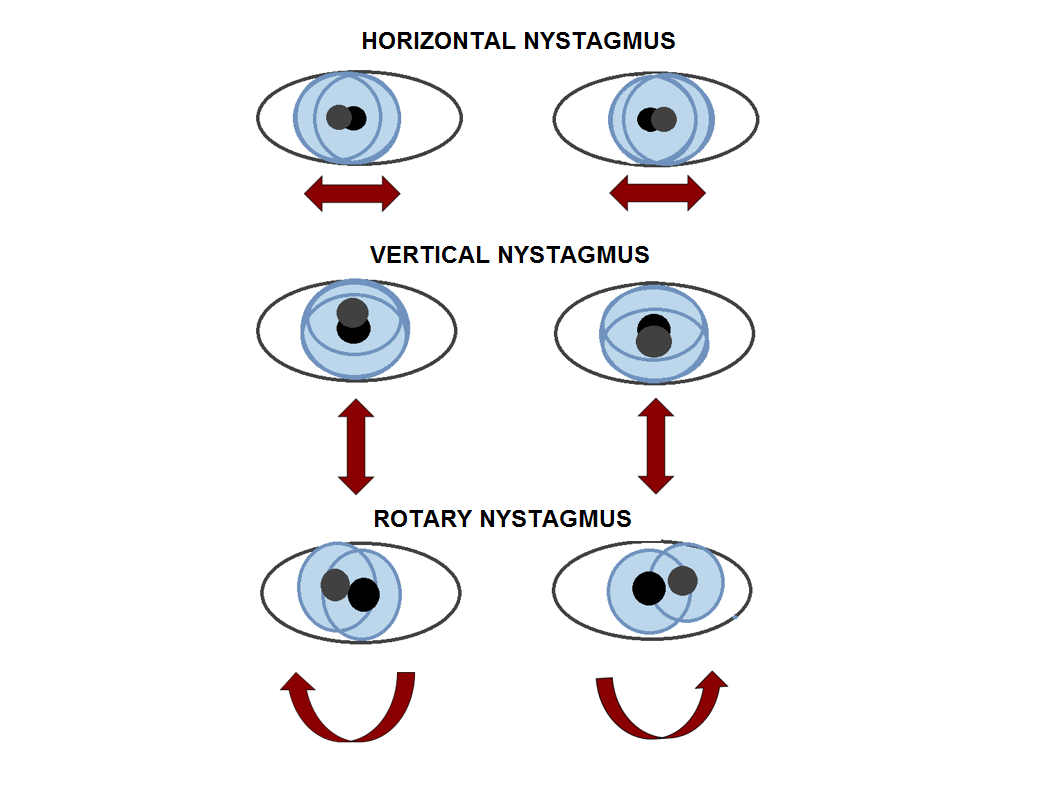
- PCP (Phencyclidine): Nystagmus (horizontal, vertical, or rotatory) is the classic and most specific sign. Pupils can be of any size.
Tip
- Depressants:
- Alcohol: Enhances GABA-A receptor activity; inhibits glutamate.
- Opioids: Activate mu, kappa, delta opioid receptors.
- Benzodiazepines: Enhance GABA-A (increase frequency of Cl- channel opening).
- Barbiturates: Enhance GABA-A (increase duration of Cl- channel opening); direct Cl- channel opening.
- Inhalants: General CNS depression (often via GABA enhancement/NMDA inhibition).
- Stimulants:
- Amphetamines: Increase release & block reuptake of dopamine (DA), norepinephrine (NE), serotonin (5-HT).
- Cocaine: Block reuptake of DA, NE, 5-HT; Na+ channel blockade.
- Bath Salts: Inhibit reuptake of DA, NE, 5-HT (variable).
- Caffeine: Adenosine receptor antagonist.
- Nicotine: Activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs).
- Hallucinogens:
- Cannabinoids (THC): Partial agonist at CB1 & CB2 receptors.
- LSD: Agonist at 5-HT2A serotonin receptors.
- MDMA (Ecstasy): Increases release & blocks reuptake of 5-HT >> DA, NE.
- PCP: NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist.
- GHB: Agonist at GHB receptors & weak GABA-B agonist.
Stimulants
Warning
Stimulants can trigger substance-induced psychosis, especially in individuals with high-dose, daily use, and/or other risk factors for psychosis.
Decreased appetite and insomnia are the most common adverse effects of stimulant medications
Caffeine
- Has MAOI effects → ↑ levels of epinephrine, norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine
Nicotine
- Effects of caffeine + opioids receptor
Smoking cessation
- Varenicline
- Nicotine receptor (alpha-4-beta-2 nACHR) partial agonist
- Reduces positive symptoms, cravings, and withdrawal symptoms
- Bupropion
- Reduces craving and withdrawal symptoms
Mnemonic
Varenicline helps to quit nicotine.
Amphetamines
- Substances
- Alpha-methylphenethylamine (“speed”)
- Methamphetamine (“meth,” “crank”)
- 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (“MDMA,” “ecstasy,” “molly”)
- Cathinone (“bath salts”)
- Mechanism of action: ↑ release and ↓ reuptake of presynaptic monoamine neurotransmitters (e.g., adrenaline, norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine)
- Central effect: CNS sympathetic stimulation and hallucinogenic effectsPeter trying meth
- Peter trying meth

- Indication: ADHD
Cocaine
- Famously was the “Coca” in Coca-Cola
- Clinical features
- Clinical features of stimulant intoxication, e.g., sympathomimetic toxidrome, euphoria
- Chest pain and/or angina due to cocaine-induced coronary vasospasm
- Complications
- Nasal pathology
- Nasal inhalation can damage nasal blood vessels and result in epistaxis.
- Chronic local vasoconstriction may cause ischemic necrosis and perforation of the nasal septum.
- Nasal pathology
Tip
Withdrawal from stimulants will not cause morbidity or morality. However, withdrawal from depressants like benzodiazepines or alcohol will. Common withdrawal symptoms:
- Increased appetite, hypersomnia, fatigue, intense psychomotor retardation, severe depression (“crash”)
Depressants
Alcohol
Alcohol use disorder Alcohol withdrawal
Opioids
Opioid Intoxication, Withdrawal, and Use Disorder
Benzodiazepines
- Benzos increase the FREQUENCY of chloride channel opening
- Barbiturates increase the DURATION of chloride channel opening
Mnemonic
Ben wants it to happen more often (frequency) Barbie wants it to last longer (duration)
Inhalants
Hallucinogens
Cannabis
Phencyclidine (PCP)
- Street names: angel dust, peace pill, elephant tranquilizer, hog
- Mechanism of action
- Inhibits dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine reuptake
- Antagonizes NMDA receptors → stimulant or depressive neurological effects (dose dependent)
- Clinical features
Mnemonic
Phencyclidine → Rotary nystagmus