Epidemiology
Etiology
- AIH is commonly associated with other autoimmune conditions
- Type 1 AIH: Hashimoto thyroiditis, Grave disease, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, rheumatoid arthritis
- Type 2 AIH: Hashimoto thyroiditis, type 1 diabetes mellitus, vitiligo
Pathophysiology
Classification
- Type 1 AIH (80% of cases): characteristic autoantibodies include antinuclear antibodies (ANAs), anti-smooth muscle antibodies (ASMAs) anti-soluble liver antigen antibodies (anti-SLA)
- Type 2 AIH: characteristic autoantibodies include anti-liver-kidney microsomal-1 antibodies (anti-LKM-1), anti-liver cytosol antibodies-1 (ALC-1)
Clinical features
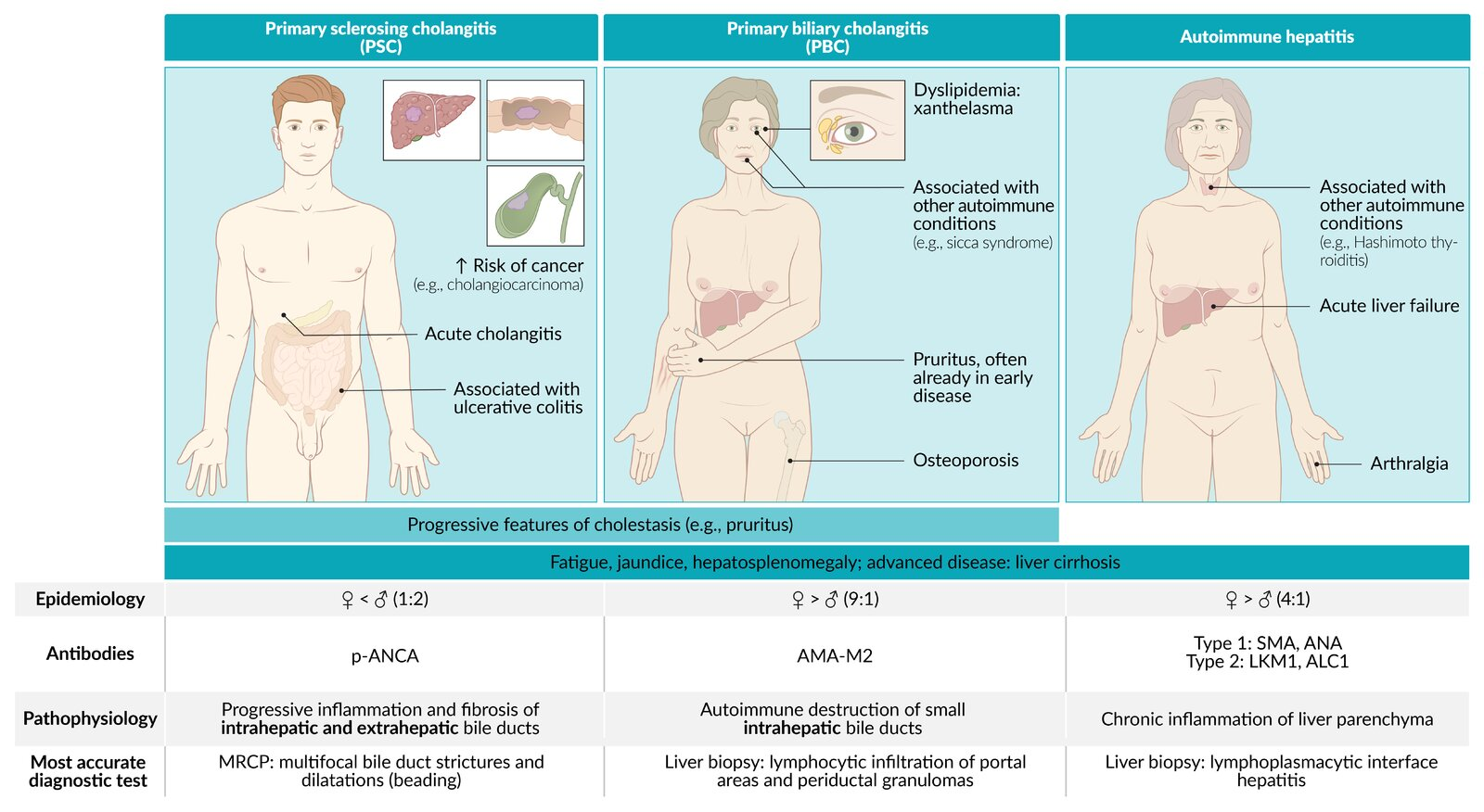
Autoimmune Liver Diseases
Mnemonic
- PBC: Boobs, Women get it (autoimmune + mitochondria from mom) → “Women stay inside” (intrahepatic ducts only).
- PSC: Scrotom, Men get it → “Men go wherever” (intra- and extrahepatic ducts) + p-ANCA (“perineuclear” → crude link to male anatomy).
Feature Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC) Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC) Autoimmune Hepatitis (AIH) Patho Inflammation/fibrosis of intra- & extrahepatic bile ducts Autoimmune destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts Autoimmune destruction of hepatocytes Epi / Assoc. M > F (2:1), <40s
Assoc: Ulcerative Colitis (IBD) (>80%)F >> M (9:1), 40-60s
Assoc: Sjögren’s, other autoimmune dzF > M (3:1), bimodal (young/middle-aged)
Assoc: Other autoimmune dzLabs Cholestatic: ↑↑ ALP, ↑ GGT Cholestatic: ↑↑ ALP, ↑ GGT Hepatocellular: ↑↑↑ AST/ALT (>1000s common), ↑ IgG Serology (+) p-ANCA (+) AMA (Anti-Mitochondrial Ab) (+) ANA, (+) ASMA (Anti-Smooth Muscle Ab) Dx / Histo MRCP/ERCP: “Beads on a string”
Histo: “Onion skinning” periductal fibrosisNormal imaging
Histo: Florid duct lesion (lymphocytic cholangitis, granulomas)Normal/nonspecific imaging
Histo: Interface hepatitis, plasma cellsTx Symptomatic Tx; Liver transplant (definitive) Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) Corticosteroids, Azathioprine Key Risk Cholangiocarcinoma, Colorectal Cancer (w/ UC) Osteoporosis, Cirrhosis, HCC Cirrhosis, Acute Liver Failure Link to original
- Nonspecific symptoms
- Fatigue
- Upper abdominal pain
- Weight loss
- Signs of acute liver failure (∼ ⅓ of patients)
Diagnostics
Laboratory tests
- Liver chemistries: ↑↑↑ ALT and ↑↑ AST, ↑ GGT, normal or ↑ ALP, and ↑ bilirubin
- Serum antibodies
- ANA, ASMA: combination is highly specific for type 1 AIH
- Anti-LKM-1: typically positive in type 2 AIH
- SPEP: hypergammaglobulinemia (↑ IgG)
Liver biopsy
- Histological findings:
- Lymphoplasmacytic interface hepatitis: ongoing inflammatory process with lymphocytic infiltration, bridging or multiacinar necrosis, and fibrotic changes
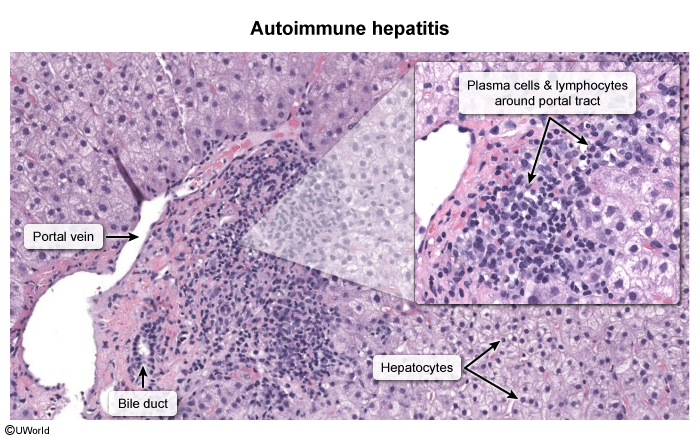
- Bile duct changes (e.g., cholangitis, ductal injury)
- Lymphoplasmacytic interface hepatitis: ongoing inflammatory process with lymphocytic infiltration, bridging or multiacinar necrosis, and fibrotic changes