- Key Teratogenic Medications
- ACE Inhibitors & ARBs (e.g., lisinopril, losartan)
- Defects: Renal dysplasia/failure, oligohydramnios, hypoplastic calvaria (Potter sequence).
- Timing: Primarily 2nd and 3rd trimesters, but increasing evidence suggests risk of cardiovascular and CNS malformations with 1st-trimester exposure.
- Antiepileptic Drugs
- Isotretinoin (Vitamin A analog)
- Defects: Extremely high risk of multiple, severe birth defects. Includes craniofacial (microtia/anotia, small jaw), CNS (hydrocephalus), cardiovascular, and thymic abnormalities.
- Mechanism: Affects cell signaling crucial for development.
- Warfarin (Coumadin)
- Defects: Fetal warfarin syndrome. Characterized by nasal hypoplasia and stippled epiphyses (bone/cartilage abnormalities). CNS and eye abnormalities can occur with later exposure.
- Timing: Critical risk period is 6-12 weeks gestation.
- Thalidomide
- Defects: Classic teratogen causing phocomelia (limb defects, “flipper limbs”). Can also cause cardiac, ear, and internal organ defects.
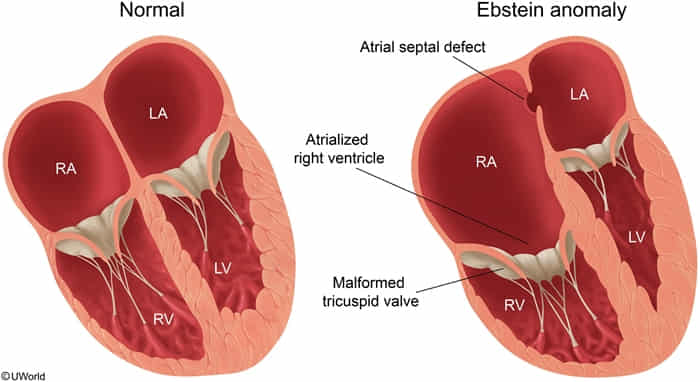
- Lithium
- Defects: Associated with Ebstein anomaly, a malformation of the tricuspid valve leading to an “atrialized” right ventricle.
- Tetracyclines
- Defects: Deposition in fetal bones and teeth, leading to discolored teeth and inhibited bone growth.
- Timing: Primarily after the 1st trimester.
- Recreational Drugs & Other Substances
- Alcohol
- Defects: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) is the most severe presentation. Features include a smooth philtrum, thin upper lip, small palpebral fissures, microcephaly, and neurodevelopmental deficits (intellectual disability, ADHD). Alcohol is a leading preventable cause of intellectual disability.
- Cocaine
- Maternal Diabetes
