Functions

- Vision: component of rhodopsin as 11-cis-retinal
- Gene transcription
- All-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) binds to its nuclear receptors (retinoic acid receptors, RAR; retinoid X receptors, RXR) → receptor dimerization → binding to DNA → uncoiling of chromatin → exposure of promoter regions of genes → binding of transcription factors to promoter → initiation of transcription and cell differentiation
- Regulation of various genes responsible for cell growth, cell differentiation, apoptosis, reproduction (e.g., spermatogenesis), and embryonic development
- Tissue maintenance and cell differentiation
- Mainly retinoic acid
- Promotes differentiation of epithelium into specialized tissue (e.g., pancreatic cells and goblet cells)
- Prevents metaplasia of squamous cells
- Antioxidant
Vitamin A deficiency
Causes
- Disorders associated with fat malabsorption: inflammatory bowel disease (e.g., Crohn disease), celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, pancreatic insufficiency
- Exocrine pancreatic insufficiency → lack of digestive enzymes → malabsorption of carbohydrates, proteins, fats, fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K), and vitamin B12
Clinical features
Triad of
- Night blindness
- Dry eyes, Bitot spots
- Hyperkeratosis
- Ocular manifestations
- Night blindness (nyctalopia)
- Retinopathy
- Xerophthalmia
- Keratomalacia
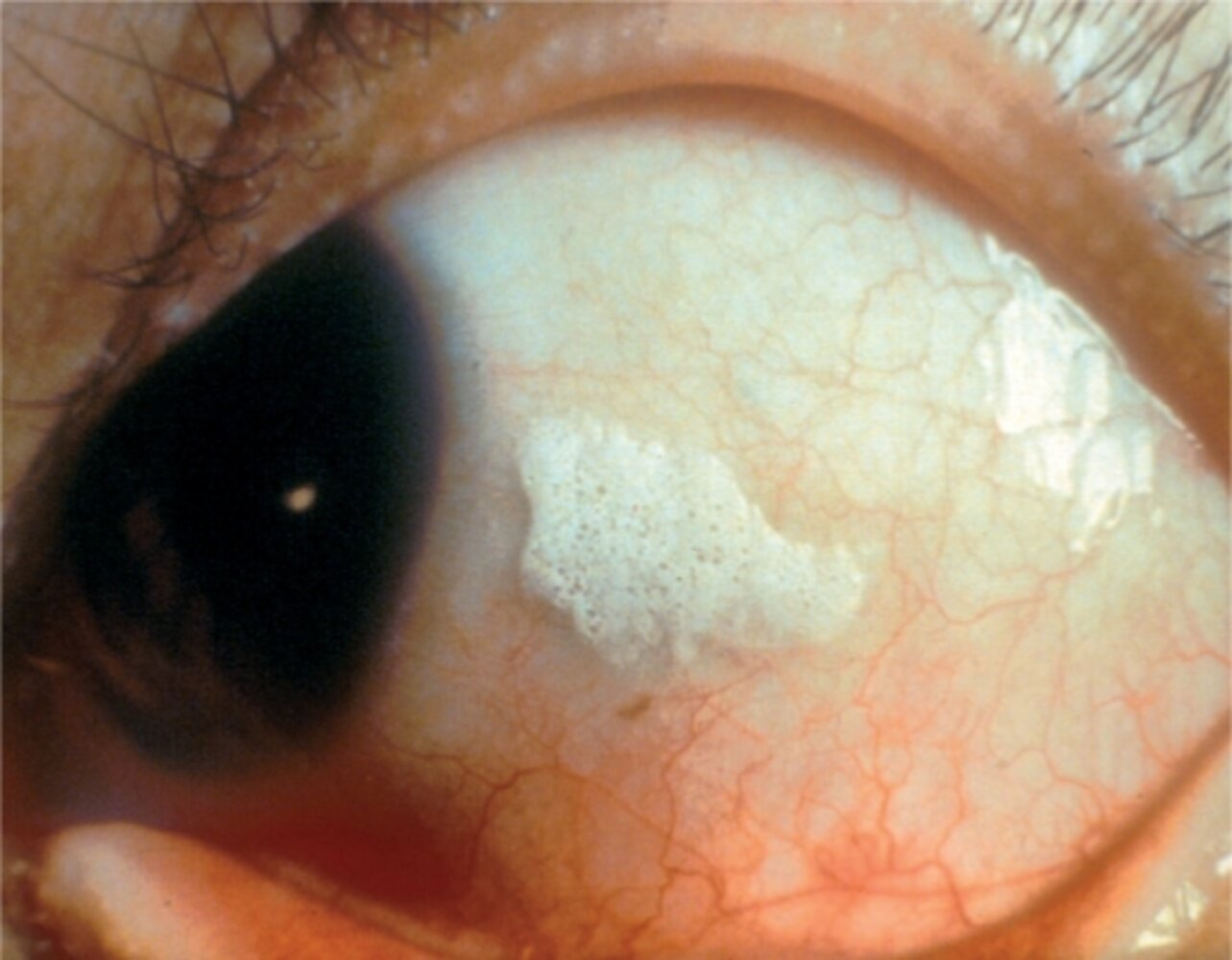
- Bitot spots: gray, triangular, dry patches on the bulbar conjunctiva, covered by a layer with a foamy appearance
- Typical sign of vitamin A deficiency
- Caused by squamous cell metaplasia and keratinization of the conjunctiva
- Keratinizing squamous metaplasia of the bladder (pearl-like plaques on cystoscopy)
- Xerosis cutis (dry skin) t
- Immunosuppression: Vitamin A deficiency increases the risk of a measles infection taking a severe course.
Vitamin A toxicity
- Etiology/Sources
- Excessive preformed vitamin A (retinoids) intake; not from carotenoids
- Sources: Over-supplementation, isotretinoin (acne Tx), animal liver
- Acute Toxicity
- Sx: Nausea, vomiting, vertigo, blurred vision
- Pseudotumor cerebri (↑ ICP): headache, papilledema
- Infants: Bulging fontanelle
- Chronic Toxicity
- Skin: Dry skin, cheilitis, alopecia
- Bone: Arthralgias, bone pain, ↑ fracture risk
- Liver: Hepatotoxicity, hepatomegaly, ↑ LFTs
- Neuro: Headaches, pseudotumor cerebri
- Teratogenicity
- Isotretinoin is highly teratogenic (Category X)
- Defects: Craniofacial (cleft palate), CNS, cardiac abnormalities
- Requires negative pregnancy test + dual contraception
- Dx & Tx
- Dx: Clinical Hx + ↑ serum retinol
- Tx: Discontinue vitamin A; most Sx reversible