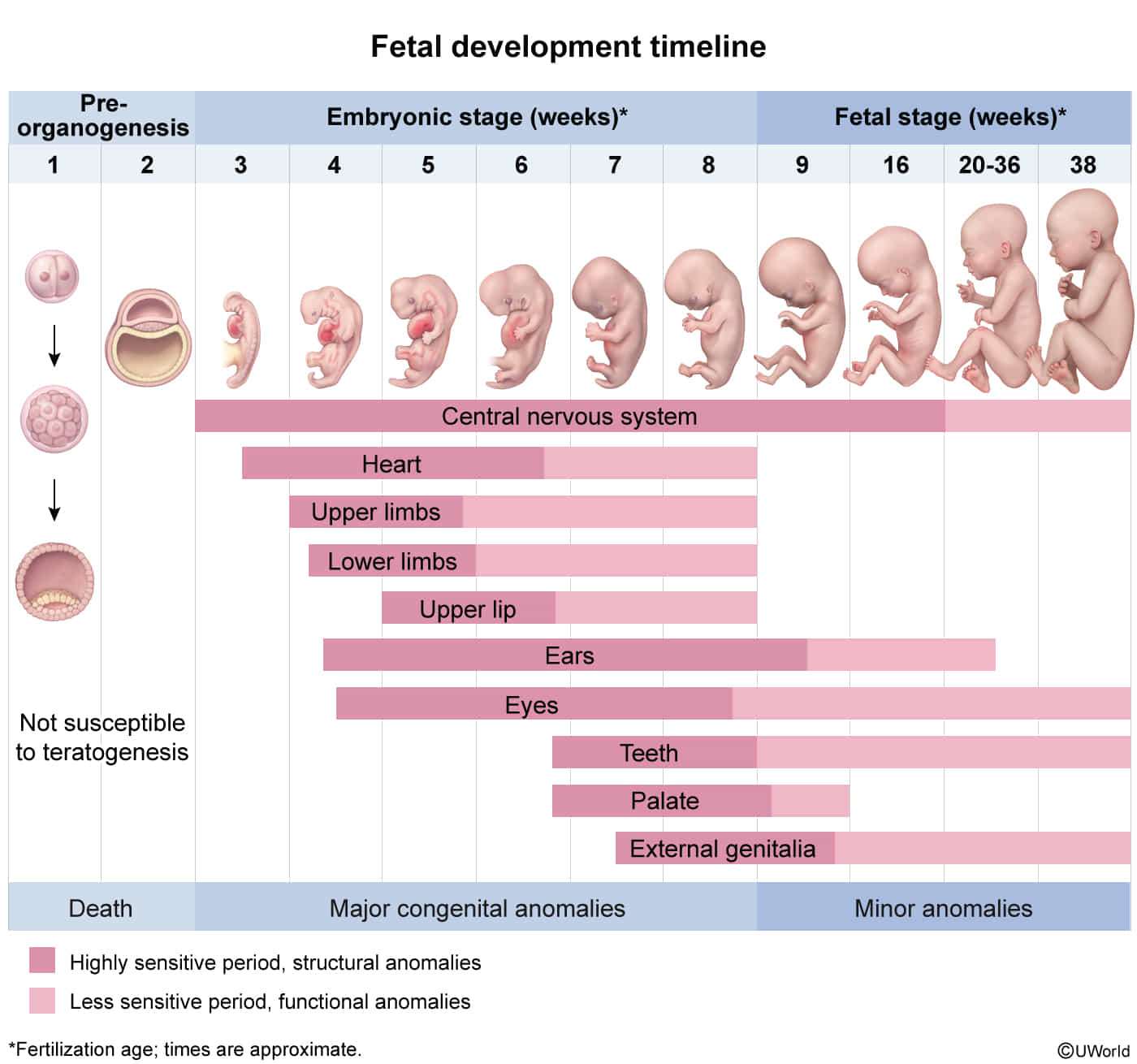
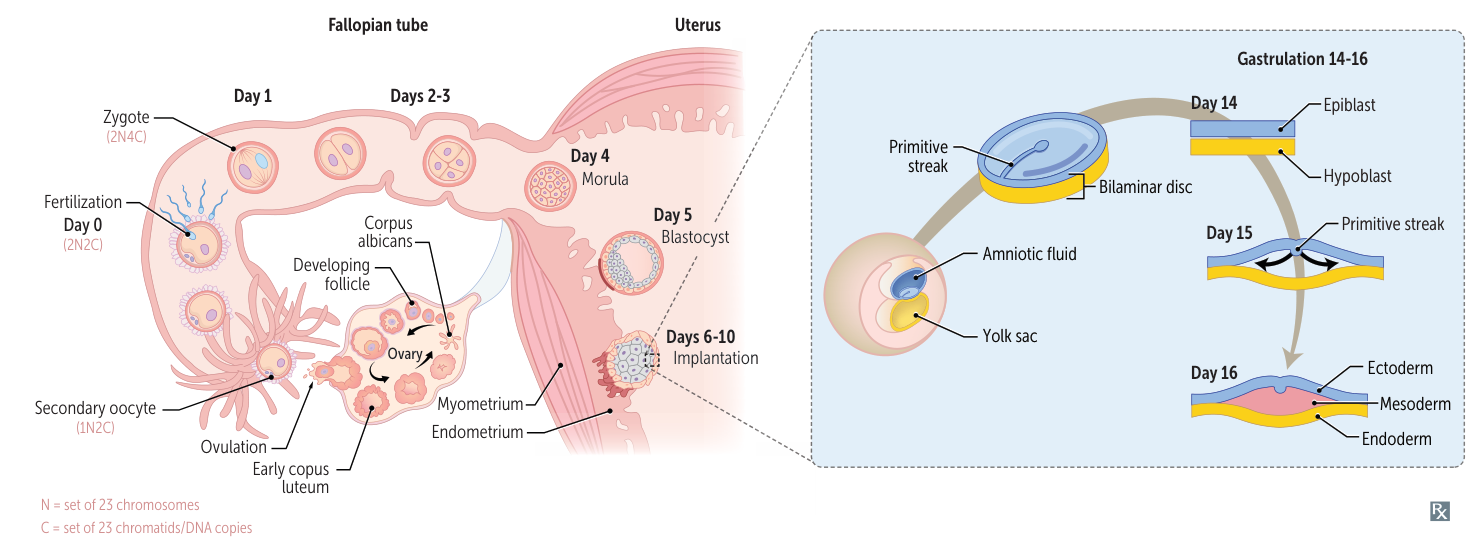
- Overall Timeline
- Pre-embryonic Period (Weeks 1-2): Fertilization to implantation; formation of blastocyst.
- Embryonic Period (Weeks 3-8): Organogenesis. Highest susceptibility to teratogens.
- Fetal Period (Weeks 9-Birth): Growth and maturation of established organs.
- Key Developmental Milestones
- Week 1: Fertilization (in ampulla) → Zygote → Morula → Blastocyst. Implantation begins ~day 6. hCG secretion starts (syncytiotrophoblast).
- Week 2: Implantation complete. Bilaminar disc forms (Epiblast, Hypoblast).
- Clinical Note: hCG detectable in blood ~day 8, in urine ~day 14.
- Week 3: Gastrulation → Trilaminar disc forms (Ectoderm, Mesoderm, Endoderm) from primitive streak. Notochord forms and induces neurulation.
- Mnemonic: Week 3 = 3 layers.
- Week 4: Heart begins to beat. Neural tube closes (failure → neural tube defects). Upper and lower limb buds form.
- Mnemonic: Week 4 = 4 limbs, 4 heart chambers.
- Week 8: End of embryonic period. Fetal movement (“gait at 8”). Embryo has a human-like appearance.
- Week 10: Genitalia begin to show male/female characteristics.
- Weeks 9-12: Red blood cells produced in the liver. Fetus can make a fist.
- Weeks 13-16: Fingernails and toenails develop. Fetal movements can be felt by the mother (quickening).
- Weeks 20-24: Surfactant production begins. Fetus is considered viable.
- Weeks 36-40: Fetus is “full term.” Sufficient surfactant for lung function.
Mnemonic
- Week 1
- hCG secretion begins around the time of blastocyst implantation.
- Blastocyst “sticks” on day six.
- Week 2
- Formation of bilaminar embryonic disc; two layers = epiblast, hypoblast.
- Week 3
- Formation of trilaminar embryonic disc via gastrulation (epiblast cell invagination through primitive streak); three layers = endoderm, mesoderm, ectoderm.
- Notochord arises from midline mesoderm and induces overlying ectoderm (via SHH) to become neural plate, which gives rise to the neural tube via neurulation.
- Week 4
- Heart begins to beat (four chambers). Cardiac activity visible by transvaginal ultrasound.
- Upper and lower limb buds begin to form (four limbs).
- Week 8
- Genitalia have male/female characteristics (pronounce “geneightalia”).
Abnormalities of morphogenesis
- Agenesis: Absent organ due to absent primordial tissue.
- Aplasia: Absent organ despite presence of primordial tissue.
- Association: a collection of malformations that are often seen together and do not have a known, common cause
- Hypoplasia: Incomplete organ development; primordial tissue present.
- Disruption: 2° breakdown of tissue with normal developmental potential (eg, amniotic band syndrome).
- Deformation: Extrinsic mechanical distortion (eg, congenital torticollis); occurs during fetal period.
- Malformation: Intrinsic developmental defect (eg, cleft lip/palate); occurs during embryonic period.
- Arteriovenous malformation (an abnormal, high-flow connection between arteries and veins bypassing capillaries which develops due to disrupted angiogenesis)
- Sequence: Abnormalities result from a single 1° embryologic event (eg, oligohydramnios → Potter sequence).
- Field defect: Disturbance of tissues that develop in a contiguous physical space (eg, holoprosencephaly).
Aortic arches
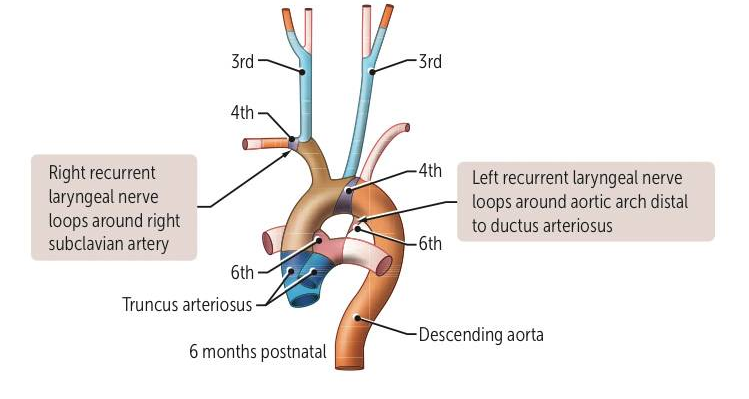
- 1st → “1st is Max” (maxillary artery)
- 2nd → “Second is Stapedial”
- 3rd → “C for Carotid” (C is the 3rd letter)
- 4th → “fOUR rhymes with AORta” + “fouRS” for right subclavian
- 6th → “6 looks like lungs” → pulmonary arteries / PDA