Sjogren syndrome is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that most commonly occurs in middle-aged women.
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Primary Sjogren syndrome: idiopathic (association with HLA-DR52)
- Secondary Sjogren syndrome: associated with another autoimmune disease, e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, polymyositis, or primary biliary cirrhosis
Pathophysiology
- Systemic autoimmune disease characterized by lymphocytic infiltration of exocrine glands, particularly salivary and lacrimal glands.
- Pathogenesis involves both humoral (autoantibodies) and cell-mediated (CD4+ T cells) destruction of glandular tissue.
Clinical features
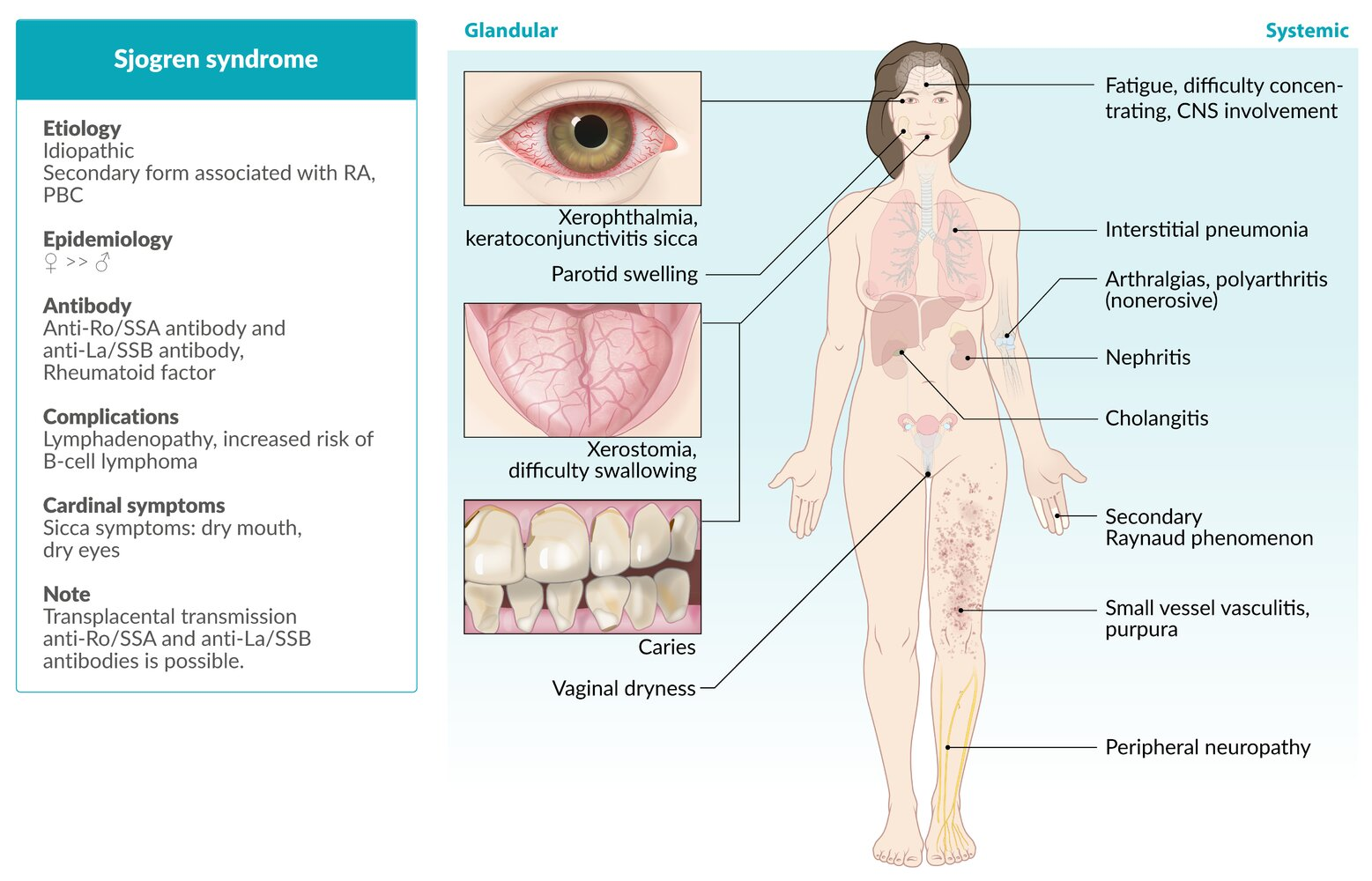
- Predominantly affects middle-aged women (9:1 female-to-male ratio).
- Sicca Symptoms (Dryness)
- Xerophthalmia (dry eyes): Pt c/o gritty sensation, corneal ulcers, “sand in my eyes.”
- Xerostomia (dry mouth): Pt c/o dysphagia for dry foods, dental caries, “lipstick sign” (lipstick adheres to teeth).
- Glandular Enlargement: Firm, non-tender enlargement of parotid or submandibular glands is common.
- Extraglandular Manifestations:
- Systemic: Fatigue, low-grade fever.
- MSK: Arthralgias, non-erosive arthritis.
- Skin: Raynaud phenomenon, cutaneous vasculitis (palpable purpura).
- Pulmonary: Interstitial lung disease.
- Renal: Interstitial nephritis (Type 1 RTA).
- Neuro: Peripheral neuropathy.
Diagnostics
- Serology:
- Anti-Ro (SSA) and Anti-La (SSB) antibodies: Highly specific, especially anti-La.
- Sjogren syndrome → Anti-SSA and anti-SSB
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA): Positive in >95% of cases, making it a sensitive but non-specific test.
- Rheumatoid Factor (RF): Often positive even without concomitant RA.
- Anti-Ro (SSA) and Anti-La (SSB) antibodies: Highly specific, especially anti-La.
- Ophthalmologic Tests:
- Schirmer test: Measures tear production by placing filter paper in the lower eyelid; <5 mm of wetting in 5 minutes is abnormal.
- Rose bengal stain: Stains devitalized cornea and conjunctiva, revealing damage from dryness.
- Biopsy: Lip (minor salivary gland) biopsy is the most accurate test, showing focal lymphocytic infiltration.
Treatment
Complications
- Development of associated conditions
- Autoimmune diseases, e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis
- B-cell lymphomas, e.g., MALT lymphoma
- Prevalence ∼ 5%
- Frequently manifests as unilateral, persistent parotid enlargement
- Predictors of lymphoma include lymphadenopathy, palpable purpura, and cryoglobulinemia.
- Renal tubular acidosis type 1
- Corneal scarring, ulcer, rupture, and infection
- Pregnancy: fetal loss, infant with neonatal lupus syndrome and associated complete heart block