Epidemiology
Etiology
- Defect in the interatrial septum allowing communication between left and right atria.
- Ostium Secundum: Most common type (approx 75%). Defect in central septum.
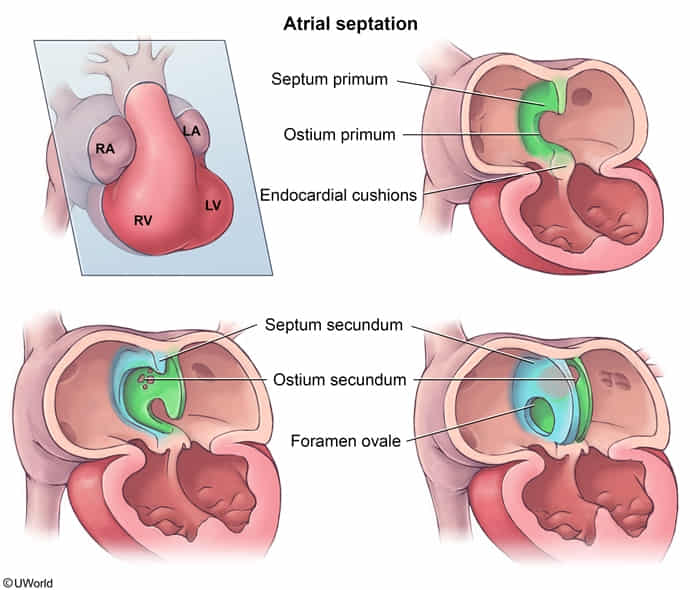
- Ostium Primum: Associated with Down syndrome (endocardial cushion defects). Defect in lower septum.
- Sinus Venosus: Associated with anomalous pulmonary venous return. Defect near SVC/IVC entry.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Auscultation
- Systolic ejection murmur over the second left ICS sternal border
- Relative pulmonary stenosis due to an increase in stroke volume. Not due to the defect! t
- Widely split second heart sound (S2) over the second left ICS, which is fixed (does not change with respiration)
Diagnostics
Treatment
Complications
- Eisenmenger Syndrome: Chronic volume overload → Pulmonary HTN → RV hypertrophy → Shunt reversal (Right-to-Left). Result: Cyanosis, clubbing, polycythemia. Rare in treated ASD.
- Right Heart Failure.
- Atrial Arrhythmias (e.g., Atrial Fibrillation) due to RA dilation.
