Epidemiology
Etiology
Causes of impaired vitamin D synthesis
Causes of impaired metabolism of vitamin D
- Conditions
- Liver disease (e.g., cirrhosis)
- Impaired 25-hydroxylation by the liver
- Chronic kidney disease
- Impaired 1α-hydroxylation by the kidneys
- Liver disease (e.g., cirrhosis)
- Medications: cytochrome P450 modulators, e.g.:
- CYP24 inducers can convert vitamin D to inactive forms
- Anticonvulsants: phenytoin, carbamazepine, phenobarbital
- Antimicrobials: rifampin, HAART, antifungals
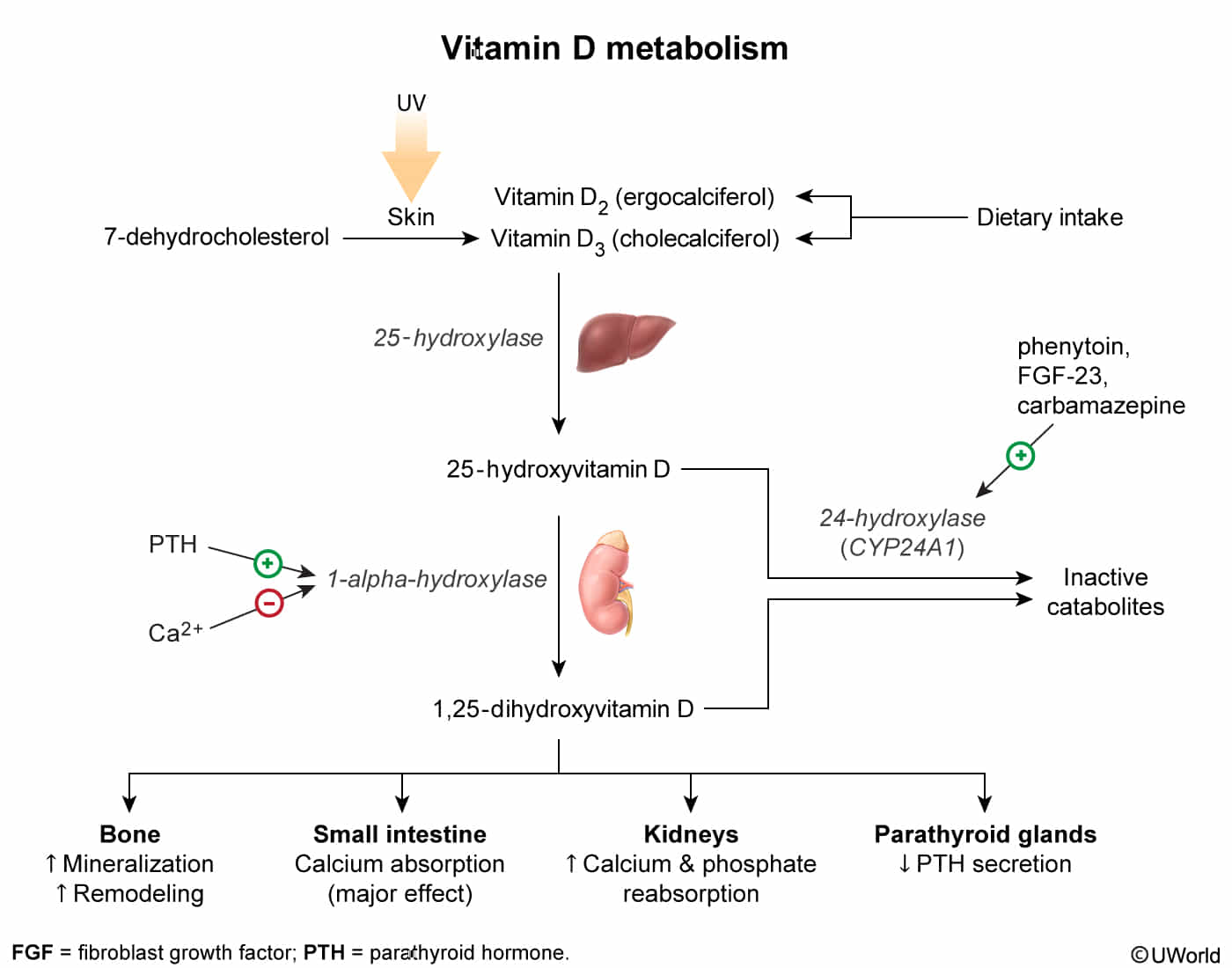
Pathophysiology
-
Sources
- Endogenous: Synthesized in the skin as cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) from 7-dehydrocholesterol upon exposure to UVB sunlight.
- Exogenous (Dietary):
- Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2) from plants, mushrooms, and yeast.
- Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3) from fatty fish, liver, and fortified foods like milk.
-
Activation Pathway (Two-Step Hydroxylation)
- Liver: Vitamin D (both D2 and D3) is transported to the liver and hydroxylated by 25-hydroxylase into 25-hydroxyvitamin D (calcidiol). This is the main circulating and storage form of vitamin D and is what is measured to assess a patient’s vitamin D status.
- Kidney: In the proximal tubules of the kidney, 25-hydroxyvitamin D is hydroxylated by 1α-hydroxylase (CYP27B1) into 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D (calcitriol), which is the biologically active form.
Inactivate catabolites: 24,25-dihydroxycholecalciferol
Clinical features
Rickets
- Skeletal Deformities:
- Craniotabes: Softening of skull bones.
- Frontal bossing and delayed fontanelle closure.
- The body attempts to compensate for the weak bone structure by laying down excess, unmineralized osteoid. This overgrowth of osteoid in the skull leads to a prominent, protruding forehead, known as frontal bossing.
- Rachitic rosary: Enlargement of costochondral junctions.
- Cartilage overgrowth at the costochondral junctions (where ribs meet cartilage), forming palpable “beads.”
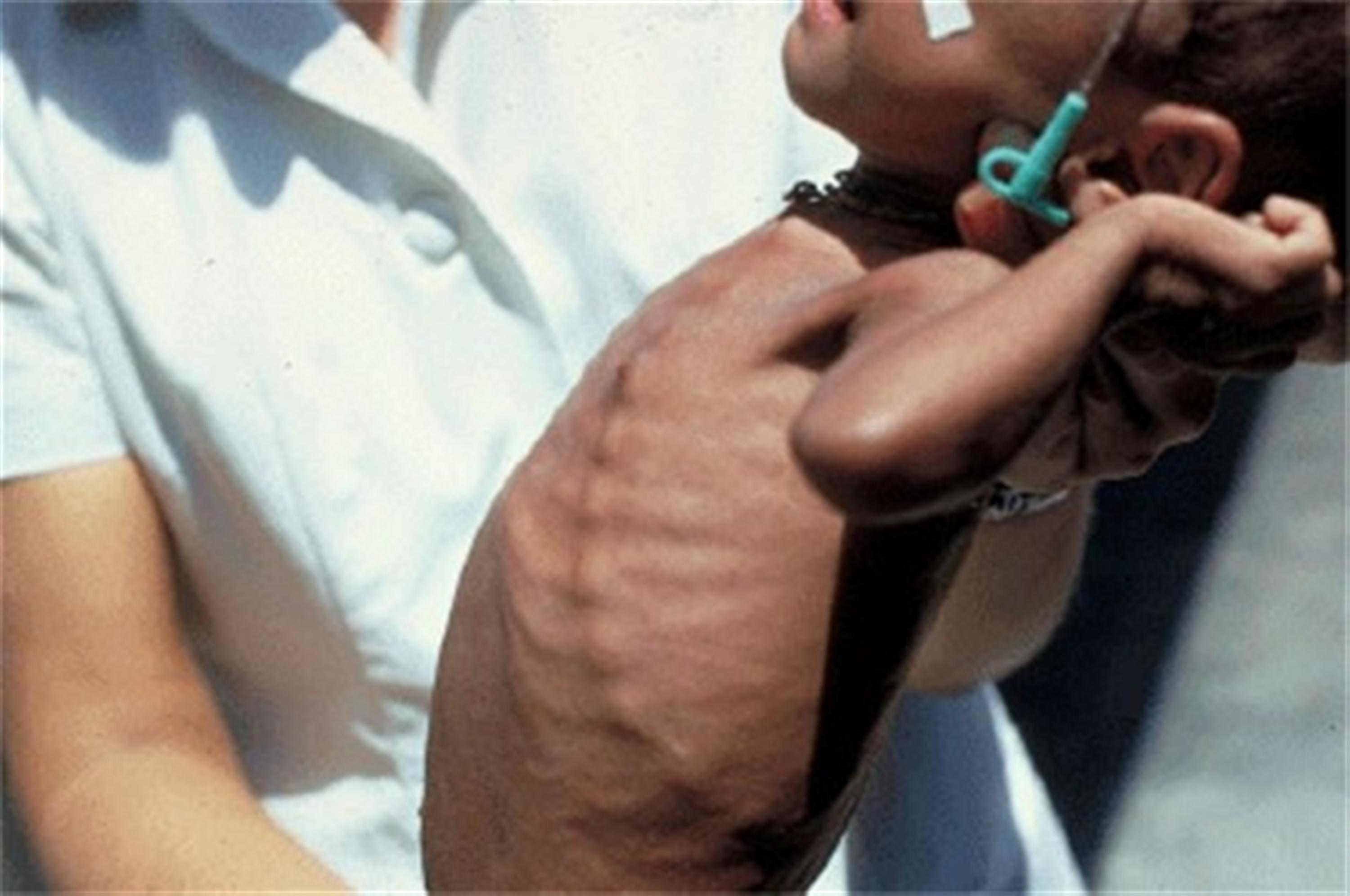
- Cartilage overgrowth at the costochondral junctions (where ribs meet cartilage), forming palpable “beads.”
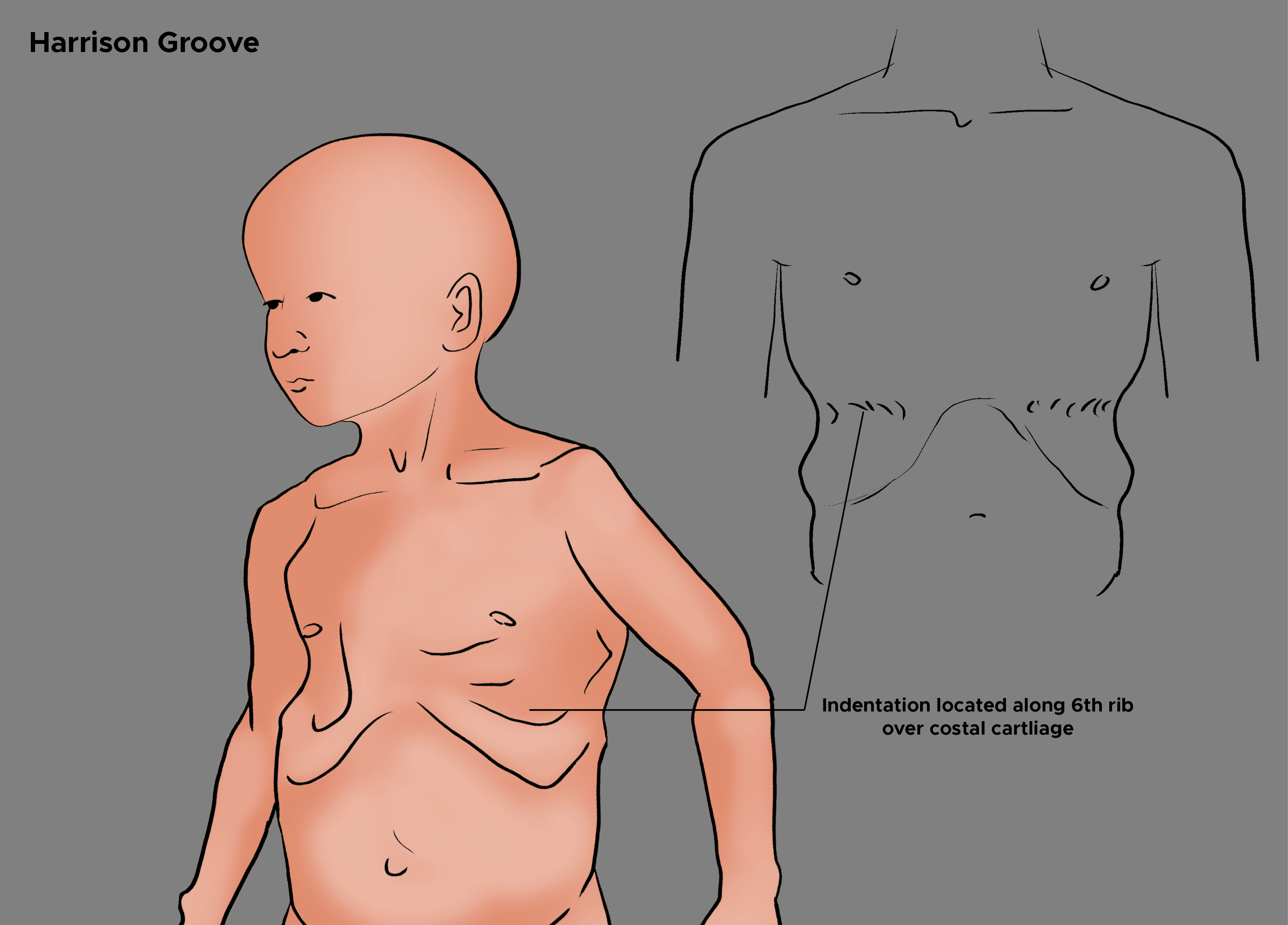
- Harrison’s groove: Indentation of lower ribs at the site of diaphragmatic insertion.
- Genu varum (bowlegs) or genu valgum (knock-knees) after weight-bearing begins.
- Widening of wrists and ankles.
- Other features: Delayed growth, bone pain, muscle weakness (hypotonia), and increased risk of fractures. In severe cases, hypocalcemic seizures may occur.
Mnemonic
- 春夏秋冬,计划放猪
- 春天1-3月,“激”期:神经系统病变
- 夏天4-6月,颅骨软“化”
- 秋天7-9月,“方”颅
- 冬天12月,串“珠”样畸形
- 3-6 个月,头颅生长最快;6-12个月,胸廓和四肢干骺端生长最快;1岁后开始负重,下肢出现异常