Tip
- Hydatidiform mole: need sperm + oocyte.
- Teratoma: just oocyte.
Epidemiology
Etiology
Tip
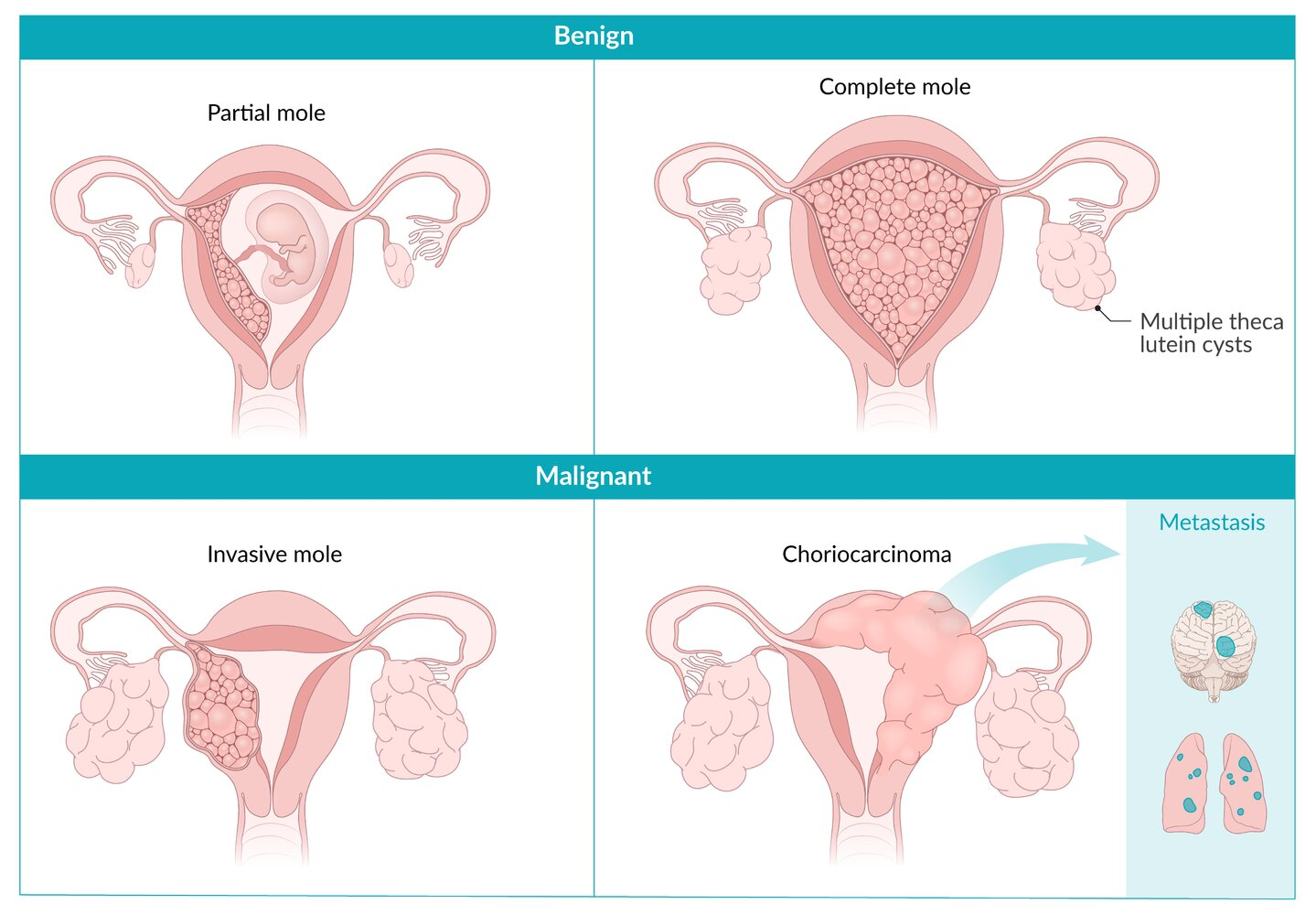
The terms “partial” and “complete” refer to the extent of abnormal tissue growth and the presence or absence of fetal tissue. In a complete mole, no normal tissue is present, whereas in a partial mole, there may be some but it’s still non-viable.
- Complete Mole
- Karyotype: 46,XX (most common) or 46,XY.
- Mechanism: Empty egg (no maternal DNA) + 1 sperm (duplicates DNA) OR + 2 sperm. All genetic material is paternal (Androgenesis). t
- Fetal Parts: Absent.
- Uterine Size: > Dates (enlarged).
- -hCG: Extremely high (>100,000 mIU/mL).
- Risk of Malignancy: 15–20% (Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia/Choriocarcinoma).
- Immunostain: p57 negative (p57 is maternally expressed; no maternal DNA = no expression).
- Partial Mole
- Karyotype: 69,XXX, 69,XXY, or 69,XYY.
- Mechanism: Normal egg + 2 sperm (or 1 sperm that duplicates).
- Fetal Parts: Present (fetal tissue often seen).
- Uterine Size: Normal or Small for dates.
- -hCG: Normal or slightly elevated.
- Risk of Malignancy: Low (<5%).
- Immunostain: p57 positive (contains maternal DNA).
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Vaginal bleeding during the first trimester
- Uterus size greater than normal for gestational age
- Pelvic pressure or pain
- Passage of vesicles with grape-like appearance
- β-hCG-mediated endocrine conditions
- Theca lutein cysts t
- Preeclampsia (before the 20th week of gestation)
- Hyperemesis gravidarum
- Hyperthyroidism: Very high amounts of hCG may lead to hyperthyroidism because the α-subunit of hCG structurally resembles TSH.
Diagnostics
DDx
Comparison of choriocarcinoma, hydatidiform mole, and teratoma
Link to original
Feature Choriocarcinoma Hydatidiform Mole Teratoma Nature Malignant Premalignant Benign (usually) Origin Trophoblasts (often from molar pregnancy) Trophoblasts (from abnormal fertilization) Germ cells Karyotype Aneuploid (often derived from mole) 46,XX (Complete) or 69,XXX/XXY (Partial) 46,XX Key Histo Anaplastic trophoblasts, NO villi Hydropic (swollen) villi Mature tissue (hair, teeth, etc.) β-hCG Massively ↑ (>100k) Massively ↑ (>100k, Complete) Normal Key Sx Lung mets (hemoptysis, dyspnea) Uterine size > dates, preeclampsia <20wks Asymptomatic or ovarian torsion Ultrasound Solid uterine mass ”Snowstorm” appearance (Complete) Cyst with calcifications/fat Treatment Chemotherapy (Methotrexate) Suction Curettage Surgical Removal (Cystectomy)