Etiology
Classifications
Three classifications, same as Etiology
- Type I (Anti-GBM Disease, ~10%): Linear IgG & C3 deposits on IF.
- Caused by autoantibodies against the α-3 chain of type IV collagen in the GBM.
- Goodpasture Syndrome: Glomerulonephritis + pulmonary hemorrhage (hemoptysis).
- Type II (Immune-Complex Mediated, ~40%): Granular IF deposits.
- Caused by deposition of antigen-antibody complexes.
- Associated with infections (PSGN), autoimmune diseases (SLE, IgA nephropathy/vasculitis), and cryoglobulinemia.
- Type III (Pauci-Immune, ~50%): No/minimal immune deposits on IF (hence “pauci”).
- Strongly associated with Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibodies (ANCA).
- c-ANCA (anti-PR3): Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener’s).
- p-ANCA (anti-MPO): Microscopic polyangiitis, Eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Churg-Strauss).
Pathophysiology
- Severe glomerular injury leads to breaks in the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), allowing fibrin, inflammatory cells (macrophages), and parietal epithelial cells to proliferate in Bowman’s space, forming a characteristic crescent shape.
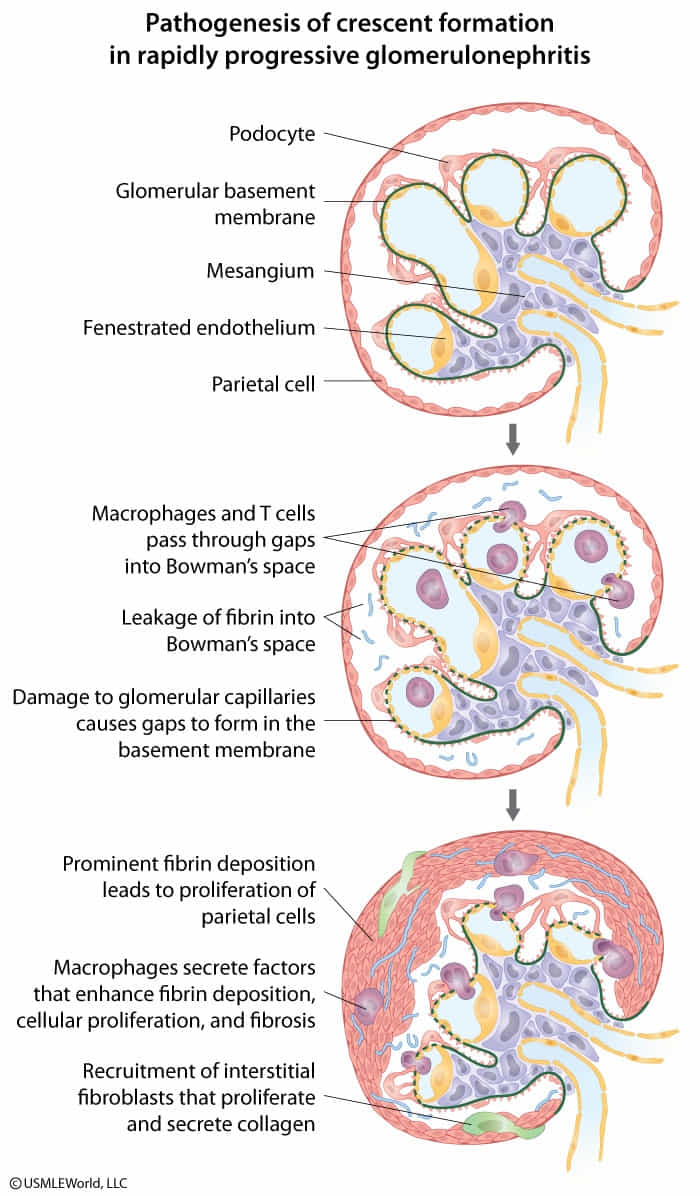
- Release of inflammatory cytokines → damage to the membrane of Bowman space and passage of cells from the interstitium into Bowman space
- This causes the formation of fibrin clots and proliferation of cells (e.g., macrophages, fibroblasts, neutrophils, epithelial cells) → crescent moon formation → compression of the glomerulus → renal dysfunction
Clinical features
Diagnostics
- Serology: Crucial for classification.
- Anti-GBM antibodies: Type I.
- ANA, anti-dsDNA, low complement (C3/C4): Type II (if SLE).
- c-ANCA (anti-PR3) / p-ANCA (anti-MPO): Type III.
Treatment
- Urgent and aggressive immunosuppression is required to prevent irreversible renal failure.
- General approach: High-dose corticosteroids (e.g., pulse methylprednisolone) PLUS another agent.
- Specific therapy depends on type:
- Type I (Anti-GBM): Corticosteroids + Cyclophosphamide + Plasmapheresis (to remove circulating anti-GBM antibodies).
- Type II (Immune-Complex): Treat the underlying disease (e.g., SLE with steroids + cyclophosphamide or mycophenolate).
- Type III (Pauci-Immune/ANCA): Corticosteroids + Cyclophosphamide or Rituximab. Plasmapheresis may be used in severe cases (e.g., pulmonary hemorrhage, dialysis requirement).
Mnemonic
三心二意激素环(II型、III型) 好怕 (Goodpasture) 血浆溢上来(I型、III型)