Etiology
- IgA nephropathy is the most common primary glomerulonephritis in adults.
- Peak incidence: 20-30 years old
Pathophysiology
An increased number of defective, circulating IgA antibodies are synthesized (often triggered by mucosal infections, i.e., upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections) → IgA antibodies form immune complexes that deposit in the renal mesangium → mesangial cell and complement system activation → glomerulonephritis (type III hypersensitivity reaction)
Clinical features
- Recurring episodes of:
- Gross or microscopic hematuria
- Flank pain
- Low-grade fever
- And/or nephritic syndrome (including hypertension)
- Usually during or immediately following a respiratory or gastrointestinal infection
- Can progress to RPGN and/or nephrotic syndrome (< 10% of patients)
- Up to 50% of patients progress to end-stage renal disease within 20–25 years.
Tip
- IgA Nephropathy and IgA Vasculitis (Henoch-Schönlein Purpura) are considered different clinical presentations of the same biological process. t
- IgA Nephropathy = Renal-limited form.
- IgA Vasculitis = Systemic form involving skin, joints, GI tract, and kidneys.
Diagnostics
- Laboratory tests
- Serum IgA level is elevated in 50% of patients.
- Complement levels (e.g., C3 level) are generally normal.
- Because IgA has weak complement-fixing activity. IgA is mainly in mucosa, where excessive inflammation needs to be avoided.
C3 levels help rule out poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis, membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis, and lupus nephritis.
- Renal biopsy
- Light microscopy: mesangial proliferation
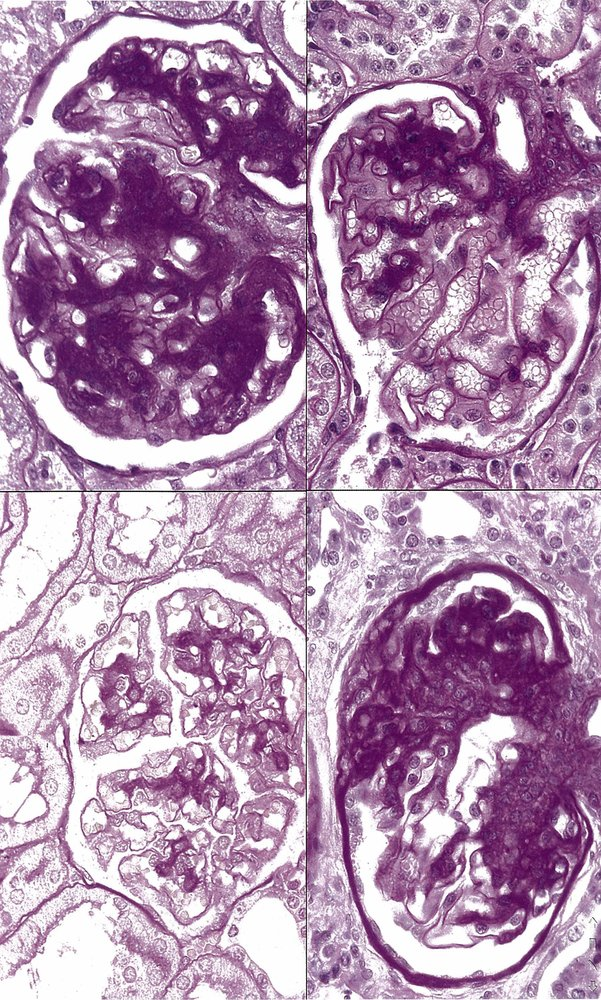
- Immunofluorescent microscopy: mesangial IgA deposits
- Electron microscopy: mesangial immune complex deposits
- Light microscopy: mesangial proliferation
Differential diagnosis
| Feature | IgA Nephropathy | PSGN |
|---|---|---|
| Onset | Days (1–3 days) after infection | Weeks (2–4 weeks) after infection |
| Timing Term | Synpharyngitic (Concurrent) | Post-infectious (Latent) |
| Serum C3 | Normal | Low |
| Recurrence | Common (Episodic) | Rare |
| EM Site | Mesangial deposits | Subepithelial humps |
| IF Pattern | IgA-dominant | ”Starry sky” / Granular (IgG, C3) |
| Prognosis | Variable (Chronic/ESRD risk) | Excellent (Spontaneous resolution) |
Tip
- IgA nephropathy typically occurs immediately following or during a mucosal infection (e.g., upper respiratory tract and gastrointestinal infections), not several weeks after a skin infection in PSGN.
- Most patients also have flank pain and a low-grade fever, which are absent in PSGN.
- Reoccurrence is common in IgA nephropathy, while it’s rare in PSGN.