- Phosphodiesterase (PDE) inhibitors are a heterogenic class of drugs that target various isoforms of PDE enzymes.
- Normally, the PDE decreases cAMP or cGMP in target cells by catalyzing the hydrolysis of these second messengers.
- By inhibiting PDE, these drugs ↑ intracellular levels of cAMP and/or cGMP, leading to smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation.
- Different PDE isoenzymes (PDE1-11) are located in different tissues, allowing for selective drug targeting.
| Feature | Nonspecific PDE Inhibitor | PDE5 Inhibitor | PDE4 Inhibitor | PDE3 Inhibitor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Second Messenger Increased | cAMP & cGMP | cGMP | cAMP | cAMP |
| Primary Mechanism | ↑cAMP & ↑cGMP → Broad effects | ↑cGMP → Smooth muscle relaxation | ↑cAMP → ↓Inflammation, Bronchodilation | ↑cAMP → ↑Cardiac contractility, Vasodilation, ↓Platelet aggregation |
| Key System/Tissue Focus | Broad (Airways, CNS) | Vasculature (Penile, Pulmonary) | Inflammatory Cells, Airways | Cardiovascular System, Platelets |
| Core Clinical Application(s) | Asthma/COPD (older) | Erectile Dysfunction, PAH | COPD, Psoriasis/Psoriatic Arthritis | Acute Heart Failure (IV), Claudication |
| Defining Side Effect Concern(s) | Narrow Therapeutic Index (Toxicity) | Hypotension (esp. w/ Nitrates - Contraindicated), Visual changes | GI Upset (N/D), Weight Loss, Psychiatric Effects | Arrhythmias, Hypotension |
| Representative Drug | Theophylline | Sildenafil (Viagra) | Roflumilast (Daliresp), Apremilast (Otezla) | Milrinone (Primacor), Cilostazol (Pletal) |
Nonspecific phosphodiesterase inhibitors (inhibitors of PDE3, 4, and 5)
- Theophylline
Indications
Adverse effects
- General considerations
- Close drug monitoring due to narrow therapeutic index (high risk of overdose).
- Metabolized in the liver by the cytochrome P450 oxidase system.
- ↑ Risk of drug interactions (e.g., ciprofloxacin can increase theophylline serum levels).
- Cardiotoxicity
- Tachycardia, arrhythmias
- Neurotoxicity (dosage-dependent)
- At low levels of overdose: dizziness, lightheadedness, headache
- At high levels of overdose: seizures
- Gastrointestinal (GI) toxicity
- Severe refractory nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal pain
Phosphodiesterase type 3 inhibitor (PDE3 inhibitor)
Antiplatelets
- Agents
- Cilostazol
- Dipyridamole
- Indications
- Intermittent vascular claudication
- Antiplatelet (antianginal, TIA/stroke prevention)
- Coronary stent restenosis prophylaxis
Heart failure drugs
- Agent: Milrinone
- Indications
- Acute treatment of decompensated cardiac failure with cardiogenic shock
- Mechanisms
- Inhibition of smooth muscle proliferation
- PDE3 inhibition → ↑ cAMP
- In the myocardium: ↑ cAMP → activation of calcium channels → cardiostimulatory effects → ↑ inotropy and ↑ chronotropy
- In peripheral vessels: ↑ cAMP → inhibition of myosin light chain kinase → smooth muscle relaxation → vasodilation with reduced cardiovascular preload and afterload
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor (PDE5 inhibitor)
Tip
Vasodilators, see cGMP
- Sildenafil
- Tadalafil
- Avanafil
Mechanism (MOA)
- Inhibit phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) → ↓ breakdown of cGMP
- ↑ cGMP → smooth muscle relaxation via ↓ intracellular Ca2+
- Sites: Corpus cavernosum (↑ penile blood flow → erection); pulmonary vasculature (↓ PVR)
- Require endogenous NO (i.e., sexual stimulation) for effect
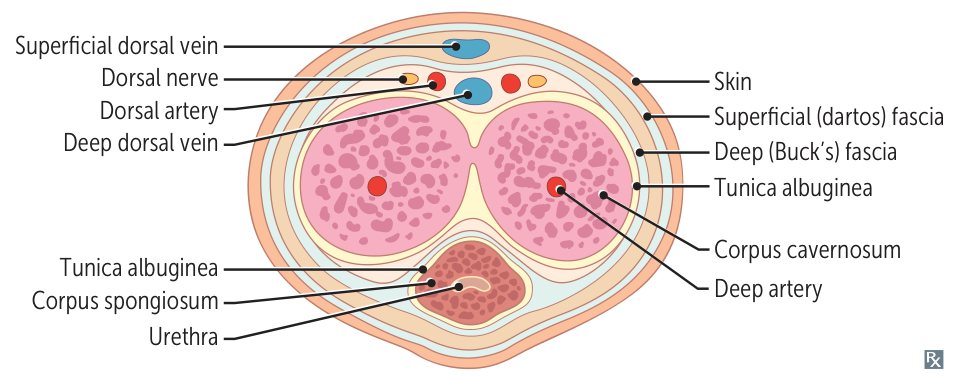
Erection
- Smooth muscle relaxation → dilation of cavernosal arteries → rapid ↑ arterial inflow.
- Engorged corpora cavernosa compress the subtunical venules against the rigid tunica albuginea.
- This veno-occlusive mechanism traps blood in the penis, increasing intracavernosal pressure and leading to tumescence and rigidity.
Indications
- Erectile dysfunction
- Pulmonary hypertension
- Benign prostatic hyperplasia (tadalafil only)
Adverse effects
- Headache
- Lightheadedness
- Exanthema, flushing
- Visual changes: photophobia, optic neuropathy, visual deficits (cyanopsia)
- Due to concomitant PDE 6 (photoreceptor) inhibition by PDE5 inhibitor in the retina.
- GI symptoms (e.g., dyspepsia)
- Runny nose, nasal congestion