Phases of Drug Metabolism
The liver is the primary site for drug metabolism, which generally aims to convert lipophilic drugs into more polar (water-soluble) compounds for easier renal excretion.
- Phase I (Functionalization)
- Reactions: Oxidation, reduction, and hydrolysis. These reactions introduce or unmask polar functional groups (e.g., -OH, -NH2, -SH).
- Primary Enzyme System: Cytochrome P450 (CYP450) monooxygenases, a superfamily of enzymes located mainly in the liver.
- Metabolites: Can be active, inactive, or even more toxic than the parent drug.
- Clinical Pearl: Geriatric patients often have reduced Phase I metabolism, which can lead to increased drug half-life and risk of toxicity.
- Phase II (Conjugation)
- Reactions: Glucuronidation, acetylation, and sulfation (“Geriatric Acetylators Sleep”). These are conjugation reactions that add an endogenous substrate to the drug or Phase I metabolite.
- Goal: To significantly increase water solubility for excretion.
- Metabolites: Typically inactive and readily excreted in urine or bile.
- Clinical Pearl: Phase II metabolism is generally preserved in the elderly. “Slow acetylators” due to genetic polymorphisms may have a decreased rate of metabolism for certain drugs, leading to prolonged effects or toxicity. See Drug-induced lupus erythematosus
Cytochrome P450
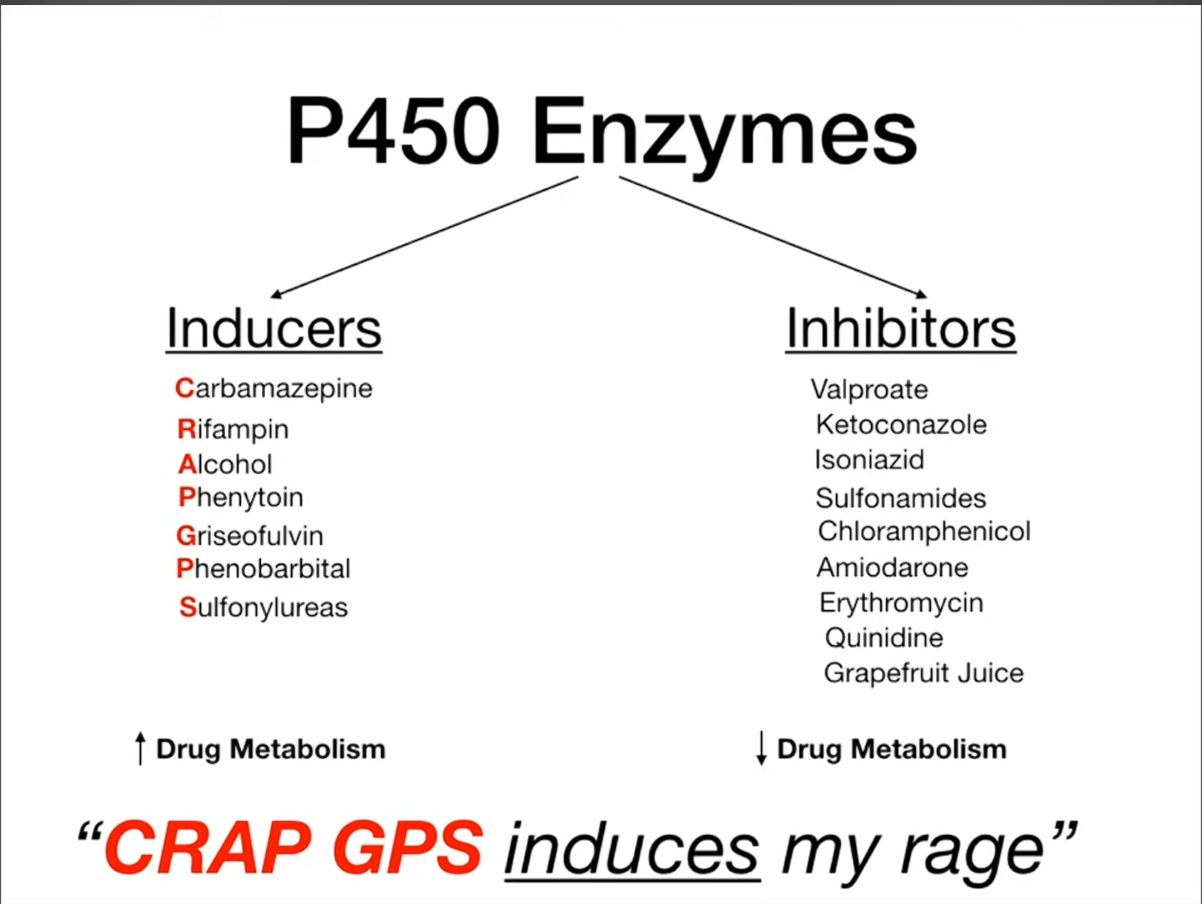
Mnemonic, each has 7 drugs
- 灰黄土地诱惑大,两本就能取一利:灰黄-灰黄霉素,地-地塞米松,诱惑-肝药酶诱导剂,两本-苯巴比妥、苯妥英钠,就-酒精(长期),一利-利福平。
- 铜绿分别多可惜,情绪难免受抑制:铜-酮康唑,绿-氯霉素,分-吩噻嗪类(包括氯丙嗪Chlorpromazine),别-别嘌呤醇(Allopurinol),惜-西咪替丁,抑-异烟肼,抑制-肝药酶抑制剂。
Acetaminophen toxicity
The only drug toxicity caused by induction of CYP
- Metabolism: Most APAP undergoes safe conjugation (glucuronidation/sulfation). A small fraction is metabolized by CYP2E1 into the toxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI).
- Detoxification: At normal doses, NAPQI is safely detoxified by glutathione (GSH).
- Toxicity: In an overdose or with CYP2E1 induction (e.g., chronic alcohol use), excessive NAPQI production depletes GSH stores. Unbound NAPQI then binds to liver proteins, causing hepatocellular injury and centrilobular necrosis.
- Antidote: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) acts as a GSH precursor and substitute, restoring the liver’s ability to detoxify NAPQI. It is nearly 100% effective if given within 8 hours of ingestion.
以下图片中,女性代表肝药酶诱导剂,男性代表肝药酶抑制剂。
1、“异烟肼”和“利福平”。其中利福平担心大家混淆,还特意拿着一个绣着“福”字的帽子。两个人是治疗结核疾病的一对“夫妻”。

2、被追求的女性是“灰黄霉素”。左起第一个古铜色男性是“酮康唑”,第二个红色衣服男性是“红霉素”,第三个黄色衣服男性是“磺胺类”。

3、“西咪替丁”和“卡马西平”是一对情侣。其中“卡马西平”担心大家混淆,手里还特意拿着一个西红柿。

4、“奎尼丁”和“苯妥英”是一对姐妹花。两者具有抗心律失常的作用。
Imagine left is a guy who has big 丁

5、“苯巴比妥”是一个美丽的大小姐。

6、乙醇是最神奇的:短期使用可以抑制肝药酶,长期使用可以诱导肝药酶。就像花木兰一样。
 7、St. John’s wort
7、St. John’s wort
Link to original
Cytochrome P450

Mnemonic, each has 7 drugs
- 灰黄土地诱惑大,两本就能取一利:灰黄-灰黄霉素,地-地塞米松,诱惑-肝药酶诱导剂,两本-苯巴比妥、苯妥英钠,就-酒精(长期),一利-利福平。
- 铜绿分别多可惜,情绪难免受抑制:铜-酮康唑,绿-氯霉素,分-吩噻嗪类(包括氯丙嗪Chlorpromazine),别-别嘌呤醇(Allopurinol),惜-西咪替丁,抑-异烟肼,抑制-肝药酶抑制剂。
Acetaminophen toxicity
The only drug toxicity caused by induction of CYP
- Metabolism: Most APAP undergoes safe conjugation (glucuronidation/sulfation). A small fraction is metabolized by CYP2E1 into the toxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI).
- Detoxification: At normal doses, NAPQI is safely detoxified by glutathione (GSH).
- Toxicity: In an overdose or with CYP2E1 induction (e.g., chronic alcohol use), excessive NAPQI production depletes GSH stores. Unbound NAPQI then binds to liver proteins, causing hepatocellular injury and centrilobular necrosis.
- Antidote: N-acetylcysteine (NAC) acts as a GSH precursor and substitute, restoring the liver’s ability to detoxify NAPQI. It is nearly 100% effective if given within 8 hours of ingestion.
以下图片中,女性代表肝药酶诱导剂,男性代表肝药酶抑制剂。
1、“异烟肼”和“利福平”。其中利福平担心大家混淆,还特意拿着一个绣着“福”字的帽子。两个人是治疗结核疾病的一对“夫妻”。

2、被追求的女性是“灰黄霉素”。左起第一个古铜色男性是“酮康唑”,第二个红色衣服男性是“红霉素”,第三个黄色衣服男性是“磺胺类”。

3、“西咪替丁”和“卡马西平”是一对情侣。其中“卡马西平”担心大家混淆,手里还特意拿着一个西红柿。

4、“奎尼丁”和“苯妥英”是一对姐妹花。两者具有抗心律失常的作用。
Imagine left is a guy who has big 丁

5、“苯巴比妥”是一个美丽的大小姐。

6、乙醇是最神奇的:短期使用可以抑制肝药酶,长期使用可以诱导肝药酶。就像花木兰一样。
 7、St. John’s wort
7、St. John’s wort
Drug clearance
Excretion
- Renal Clearance: Drugs (or active metabolites) excreted by kidneys. Water-soluble (polar, ionized at physiological pH)
- High-Yield Drugs:
- Antibiotics: Aminoglycosides (Gentamicin), Vancomycin, most Penicillins & Cephalosporins (except Nafcillin, Ceftriaxone), Fluoroquinolones (most), TMP-SMX.
- Cardio: Digoxin, Lisinopril (most ACEIs), Atenolol (hydrophilic beta-blockers).
- Other: Lithium, Methotrexate (low dose), Gabapentin, Metformin, H2 blockers (Ranitidine).
- USMLE Pearl: NSAIDs & ACEIs can affect renal clearance. Watch for nephrotoxicity.
- Hepatic Clearance (Metabolism & Biliary Excretion): Drugs metabolized by the liver (often by CYP450 enzymes) and/or excreted in bile. Lipid-soluble (non-polar)
- High-Yield Drugs (Metabolism):
- Warfarin, most Benzodiazepines (safer: Lorazepam, Oxazepam, Temazepam - “LOT”), Statins, Macrolides (not Azithromycin), most Antidepressants & Antipsychotics, Opioids, Acetaminophen, Isoniazid, Rifampin, Phenytoin, Propranolol.
- High-Yield Drugs (Biliary Excretion/Enterohepatic Circulation):
- Ceftriaxone, Nafcillin, Azithromycin, Digoxin, Oral Contraceptives, Rifampin.
- USMLE Pearls:
- CYP Inducers (decrease drug levels): Rifampin, Phenobarbital, Phenytoin, Carbamazepine (“CRAP GPS”).
- CYP Inhibitors (increase drug levels): Macrolides (not Azithro), Azole antifungals, Grapefruit Juice, Cimetidine, Ritonavir (“SICKFACES.COM G”).
- First-pass metabolism: Reduces oral bioavailability (e.g., Lidocaine, Propranolol).
- Pulmonary Clearance: For volatile substances.
- High-Yield Drugs: Volatile anesthetics (e.g., Isoflurane), Ethanol (partially).
- USMLE Pearl: Recovery from anesthesia depends on this.
Metabolism
- Zero order kinetics: The rate of metabolism and/or elimination remains constant and is independent of the plasma concentration of a drug at steady state (Cp decreases linearly over time)
- Zero-order is a capacity-limited elimination.
- Plasma concentration over time:
- Examples include ethanol, phenytoin, aspirin (at high concentrations)
- High-Yield Drugs (“PEA”):
- Phenytoin
- Ethanol
- Aspirin (at high doses/overdose)
- USMLE Pearl: Small dose changes can lead to large changes in plasma concentration and toxicity.
- First order kinetics: The rate of metabolism and/or elimination is directly proportional to the plasma concentration of the drug (Cp decreases exponentially over time)
- First-order is a flow-dependent elimination.
- Plasma concentration over time:
- Half life:
- Applies to most drugs
Link to original
Drug clearance
Excretion
- Renal Clearance: Drugs (or active metabolites) excreted by kidneys. Water-soluble (polar, ionized at physiological pH)
- High-Yield Drugs:
- Antibiotics: Aminoglycosides (Gentamicin), Vancomycin, most Penicillins & Cephalosporins (except Nafcillin, Ceftriaxone), Fluoroquinolones (most), TMP-SMX.
- Cardio: Digoxin, Lisinopril (most ACEIs), Atenolol (hydrophilic beta-blockers).
- Other: Lithium, Methotrexate (low dose), Gabapentin, Metformin, H2 blockers (Ranitidine).
- USMLE Pearl: NSAIDs & ACEIs can affect renal clearance. Watch for nephrotoxicity.
- High-Yield Drugs:
- Hepatic Clearance (Metabolism & Biliary Excretion): Drugs metabolized by the liver (often by CYP450 enzymes) and/or excreted in bile. Lipid-soluble (non-polar)
- High-Yield Drugs (Metabolism):
- Warfarin, most Benzodiazepines (safer: Lorazepam, Oxazepam, Temazepam - “LOT”), Statins, Macrolides (not Azithromycin), most Antidepressants & Antipsychotics, Opioids, Acetaminophen, Isoniazid, Rifampin, Phenytoin, Propranolol.
- High-Yield Drugs (Biliary Excretion/Enterohepatic Circulation):
- Ceftriaxone, Nafcillin, Azithromycin, Digoxin, Oral Contraceptives, Rifampin.
- USMLE Pearls:
- CYP Inducers (decrease drug levels): Rifampin, Phenobarbital, Phenytoin, Carbamazepine (“CRAP GPS”).
- CYP Inhibitors (increase drug levels): Macrolides (not Azithro), Azole antifungals, Grapefruit Juice, Cimetidine, Ritonavir (“SICKFACES.COM G”).
- First-pass metabolism: Reduces oral bioavailability (e.g., Lidocaine, Propranolol).
- High-Yield Drugs (Metabolism):
- Pulmonary Clearance: For volatile substances.
- High-Yield Drugs: Volatile anesthetics (e.g., Isoflurane), Ethanol (partially).
- USMLE Pearl: Recovery from anesthesia depends on this.
Metabolism
- Zero order kinetics: The rate of metabolism and/or elimination remains constant and is independent of the plasma concentration of a drug at steady state (Cp decreases linearly over time)
- Zero-order is a capacity-limited elimination.
- Plasma concentration over time:
- Examples include ethanol, phenytoin, aspirin (at high concentrations)
- High-Yield Drugs (“PEA”):
- Phenytoin
- Ethanol
- Aspirin (at high doses/overdose)
- High-Yield Drugs (“PEA”):
- USMLE Pearl: Small dose changes can lead to large changes in plasma concentration and toxicity.
- First order kinetics: The rate of metabolism and/or elimination is directly proportional to the plasma concentration of the drug (Cp decreases exponentially over time)
- First-order is a flow-dependent elimination.
- Plasma concentration over time:
- Half life:
- Applies to most drugs