Bones, muscles, and joints
- Increased bone resorption and osteoporosis, increased risk of fracture (♀ > ♂)
- Postmenopausal osteoporosis: decreased estrogen levels → increased bone resorption
- Senile osteoporosis (especially in individuals > 70 years): decreased osteoblast activity → decreased osteoid production
- Decreased lean body mass due to atrophy and loss of muscle cells (sarcopenia)
- Degenerative changes in joints: stiffer and less flexible joints, decreased synovial fluid and cartilage, calcification (e.g., in the shoulder), height loss
- Bone marrow: decreased mass, increased percentage of fat, weaker response to stimuli (e.g., ↓ hematopoiesis following blood loss)
Respiratory system
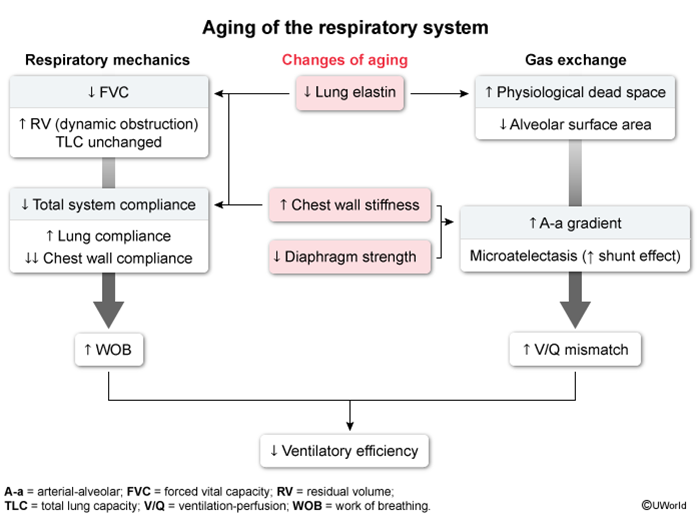
- Mechanical & Structural Changes
- Chest Wall: ↓ Compliance (stiffer) due to calcification & kyphosis.
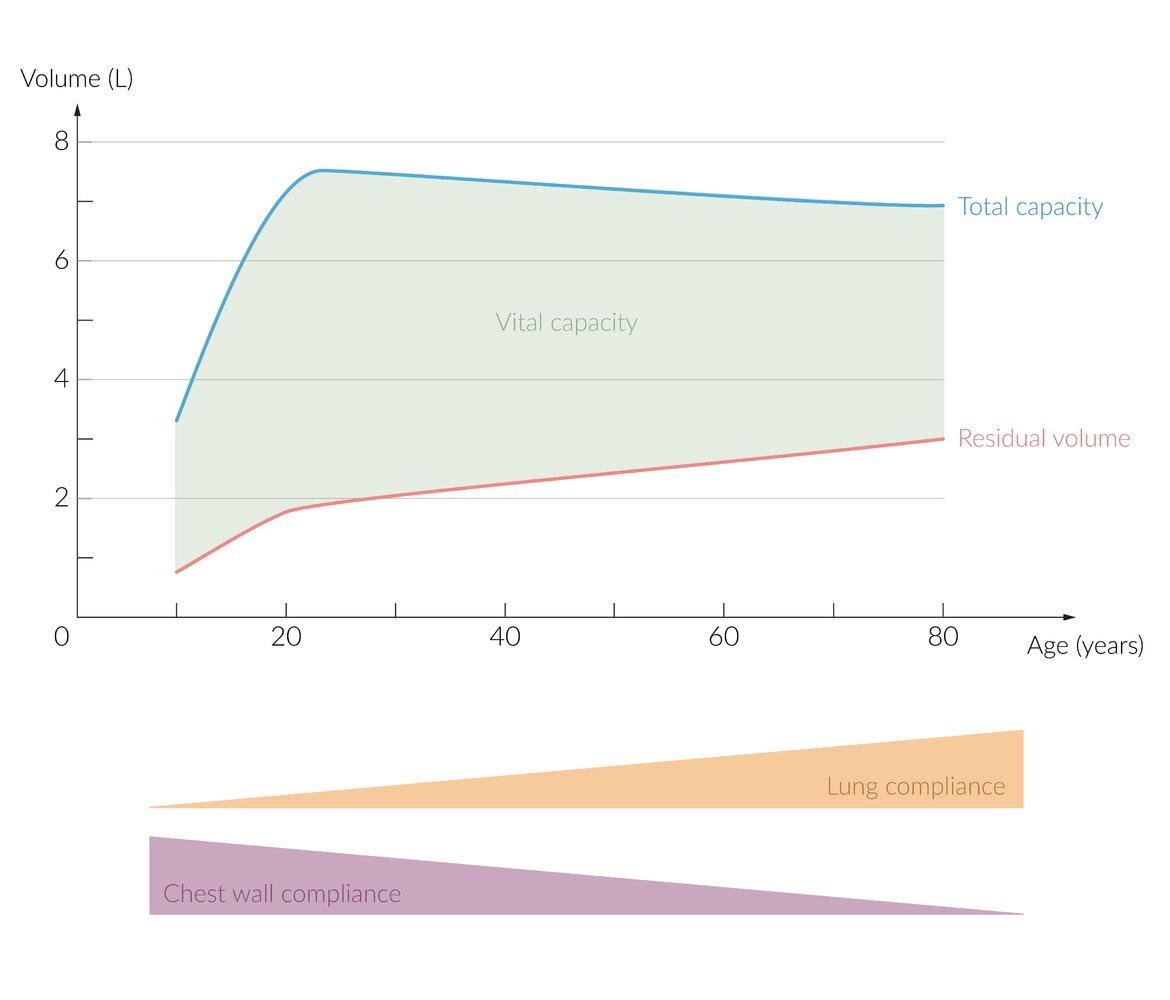
- Lung Parenchyma: ↑ Compliance (floppier) due to loss of elastic recoil.
- Overall System: ↓ Compliance (chest wall effect dominates).
- Means it takes more work to move air into the respiratory system
- Muscles: Weakened diaphragm & intercostals (↓ MIP/MEP) → less effective cough.
- Lung Volumes & Capacities
- ↑ Residual Volume (RV): Due to loss of recoil & early airway closure (air trapping).
- ↓ Vital Capacity (VC): Consequence of increased RV.
- Total Lung Capacity (TLC): Unchanged.
- TLC is not a measure of the work of breathing; it’s the maximum volume achieved at maximal inspiratory effort.
- ↑ Functional Residual Capacity (FRC): Due to loss of elastic recoil.
- ↓ FEV1 & FEV1/FVC ratio.
- Gas Exchange
- ↑ V/Q Mismatch: Leads to an increased A-a gradient.
- ↓ PaO2: Mild, progressive decline with age.
- PaCO2: Unchanged at rest.
- ↓ Diffusing Capacity (DLCO): Due to decreased alveolar surface area.
Cardiovascular system
- Aortic stiffening
- Elastin replacement with collagen
- ↑ Pulse pressure (isolated systolic HTN)
- Mild concentric LVH
- Response to cardiomyocyte dropout & ↑ afterload
- ↓ left ventricular cavity size and sigmoid-shaped interventricular septum
- Resting EF, SV & cardiac output maintained
- ↓ Maximal cardiac output
- Conduction cell degeneration
- Slightly ↓ resting heart rate
- ↓ Maximal heart rate
- Reduced baroreceptor sensitivity & adrenergic responsiveness
- ↑ Orthostasis
- ↓ Heart rate & contractility response
- Formation of lipofuscin deposits within cells. See Cellular adaptations t
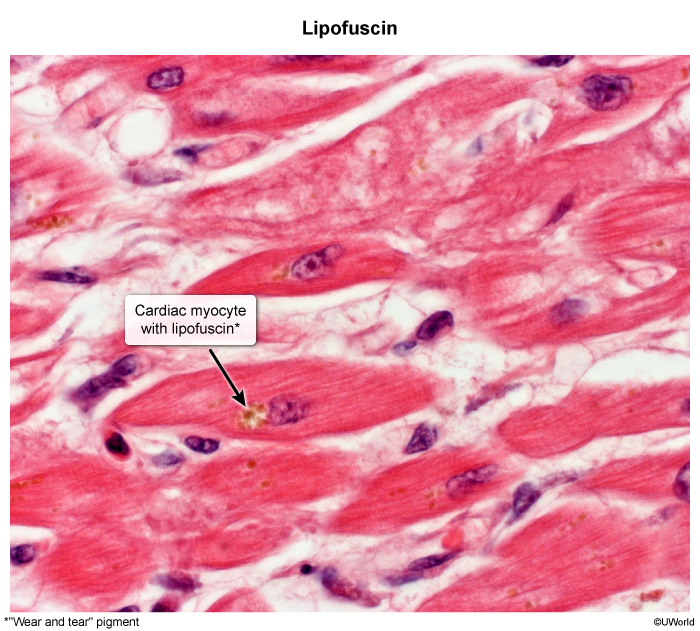
| Feature | Lipofuscin | Heart Failure Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Oxidized lipids/proteins | Hemosiderin (Iron) |
| Origin | Autophagy / “Wear and tear” | Phagocytosed RBCs |
| Organ | Heart, Liver, Brain | Lungs (Alveoli) |
| Prussian Blue Stain | Negative | Positive (Blue) |
| Cause | Aging / Cachexia | Left Heart Failure |
Skin
- Senile purpura: recurrent, irregularly shaped, dark purple macules
- Progressive loss of connective tissue, subcutaneous fat, and blood vessel elasticity → extravasation of blood into the dermis t
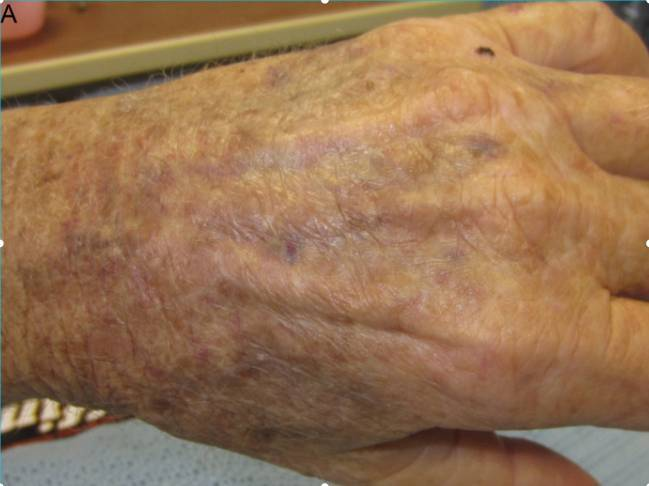
- Progressive loss of connective tissue, subcutaneous fat, and blood vessel elasticity → extravasation of blood into the dermis t
- Heatstroke due to decreased number of sweat glands
- Also due to
- Loss of rete pegs and dermal capillaries, which reduces the effective epidermal area available for heat transfer
- Tonic contraction of the peripheral vasculature, which limits heat transfer to the skin
- Also due to
Nervous system
- Presbyopia
- Pathophysiology: age-related decrease in lens elasticity, strength of ciliary muscle, and lens curvature → decreased lens accommodation (focusing on an object up close)
.png)
Upper aerodigestive tract
- Salivary glands
- Acinar atrophy, fatty infiltration
- Reduced saliva production
- Xerostomia, dental caries
- Oral/oropharyngeal muscles
- Decreased muscle mass & tissue elasticity
- Weakness & dyscoordination of masticatory, tongue & pharyngeal muscles
- Increased transit time, decreased coordination
- Other effects
- Mucosal atrophy
- Decreased taste & smell
- Impaired airway protective reflexes
Beers criteria
Common medications to avoid in older adults
- Anticholinergic (cause urinary retention and constipation)
- First-generation antihistamines
- Also has strong sedative effect
- Gastrointestinal antispasmodics
- First-generation antihistamines
- Cardiovascular (may elevate the risk of orthostatic hypotension)
- Alpha-1 blockers (as antihypertensives)
- Centrally acting alpha-2 agonists
- Many antiarrhythmics
- CNS (can cause sedation, cognitive impairment, and/or delirium → ↑ risk of falls and fractures)
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Antipsychotics
- Barbiturates, benzodiazepines & other hypnotics
- Endocrine (increased risk of hypoglycemia)
- Long-acting sulfonylureas
- Sliding-scale insulin
- Doses are not consistent
- Pain (risk of GI bleeding and AKI)
- Nonselective NSAIDs
- Skeletal muscle relaxants