Virulence factors and resistances
- Enzymes
- Catalase: protection against ROS
- Coagulase: protection against phagocytosis
- Hyaluronidase
- Lipase
- Penicillinase: a β-lactamase
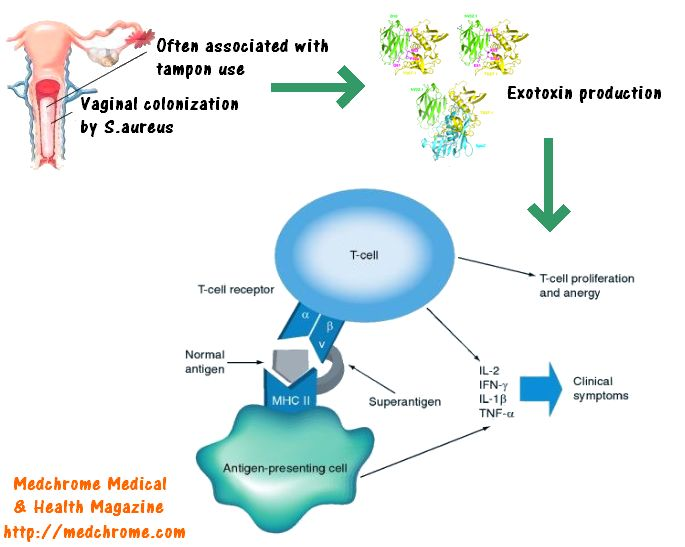
- Toxins
- Superantigens
- Exfoliative toxin
- Leukocidin: creates pores in the membranes of infected cells → necrotic skin and mucosal lesions
- Proteins
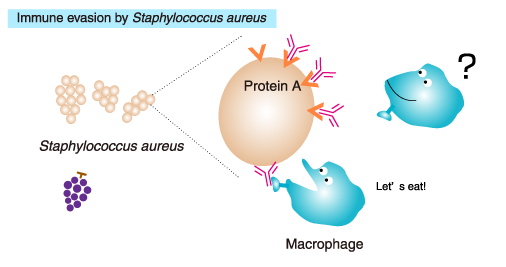
- Protein A (binds to the Fc region of IgG), prevents opsonization and phagocytosis
- Modified penicillin-binding protein (PBP) in MRSA
- Capsular polysaccharides
- Promote colonization and persistence in host tissues
Antibiotics
- Methicillin-Sensitive S. aureus (MSSA)
- First Line: Anti-staphylococcal Penicillins
- Nafcillin, Oxacillin (IV)
- Dicloxacillin (PO)
- Alternative: 1st Generation Cephalosporins
- Cefazolin (IV)
- Cephalexin (PO)
- Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus (MRSA)
- Resistance Mechanism: mecA gene → altered PBP2a → low beta-lactam affinity.
- Severe / Inpatient Treatment:
- Vancomycin: Standard of care. Side effect → Red Man Syndrome.
- Daptomycin: For bacteremia/endocarditis. AVOID in pneumonia (inactivated by surfactant).
- Linezolid: For pneumonia, skin/soft tissue. Side effects → Thrombocytopenia, Serotonin Syndrome.
- Ceftaroline: 5th gen cephalosporin. Only beta-lactam that covers MRSA.
- Community-Acquired / Outpatient Treatment:
- Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMX)
- Clindamycin (Risk of C. difficile colitis)
- Doxycycline