Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
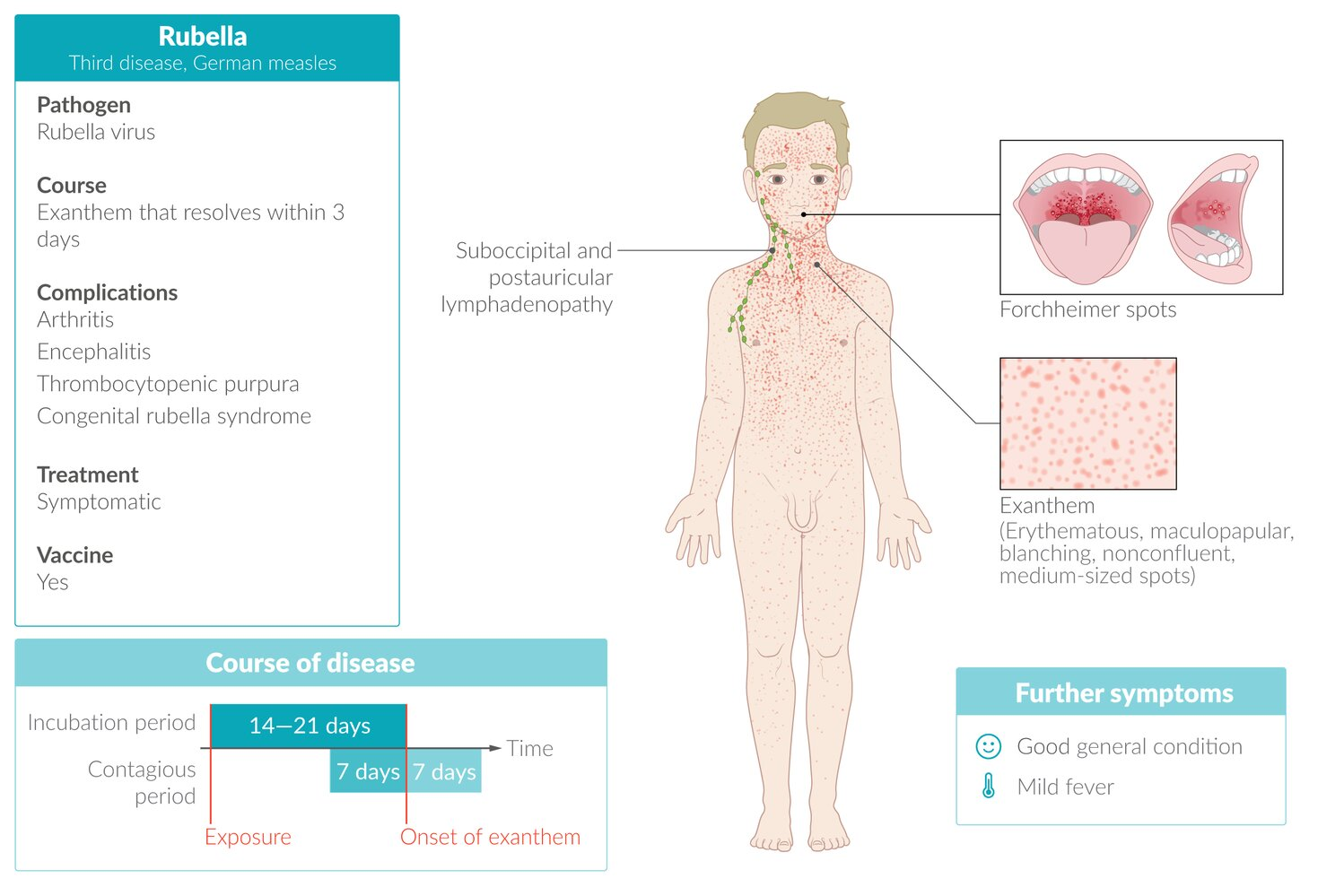
Clinical features
 See Congenital rubella infection
See Congenital rubella infection
| Characteristic | Rubella | Measles |
|---|---|---|
| Severity of Illness | Generally milder disease | More severe with higher complication rates |
| Rash Characteristics | Fine, pink maculopapular rash starting on face; lasts ~3 days | Erythematous maculopapular rash starting at hairline; more confluent; lasts 5-7 days |
| Prodromal Symptoms | Minimal; mild fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy | Prominent with high fever, cough, coryza, conjunctivitis (“3 Cs”) |
| Pathognomonic Signs | Posterior auricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy | Koplik’s spots (white spots on buccal mucosa) |
| Congenital Effects | Significant risk of congenital rubella syndrome | No specific congenital syndrome; may cause pregnancy complications |
| Infectivity | Moderately contagious | Highly contagious (one of the most contagious diseases) |
| Complications | Rare in children; arthritis in adults; congenital defects | Pneumonia, encephalitis, SSPE, high mortality in malnourished children |
Diagnostics
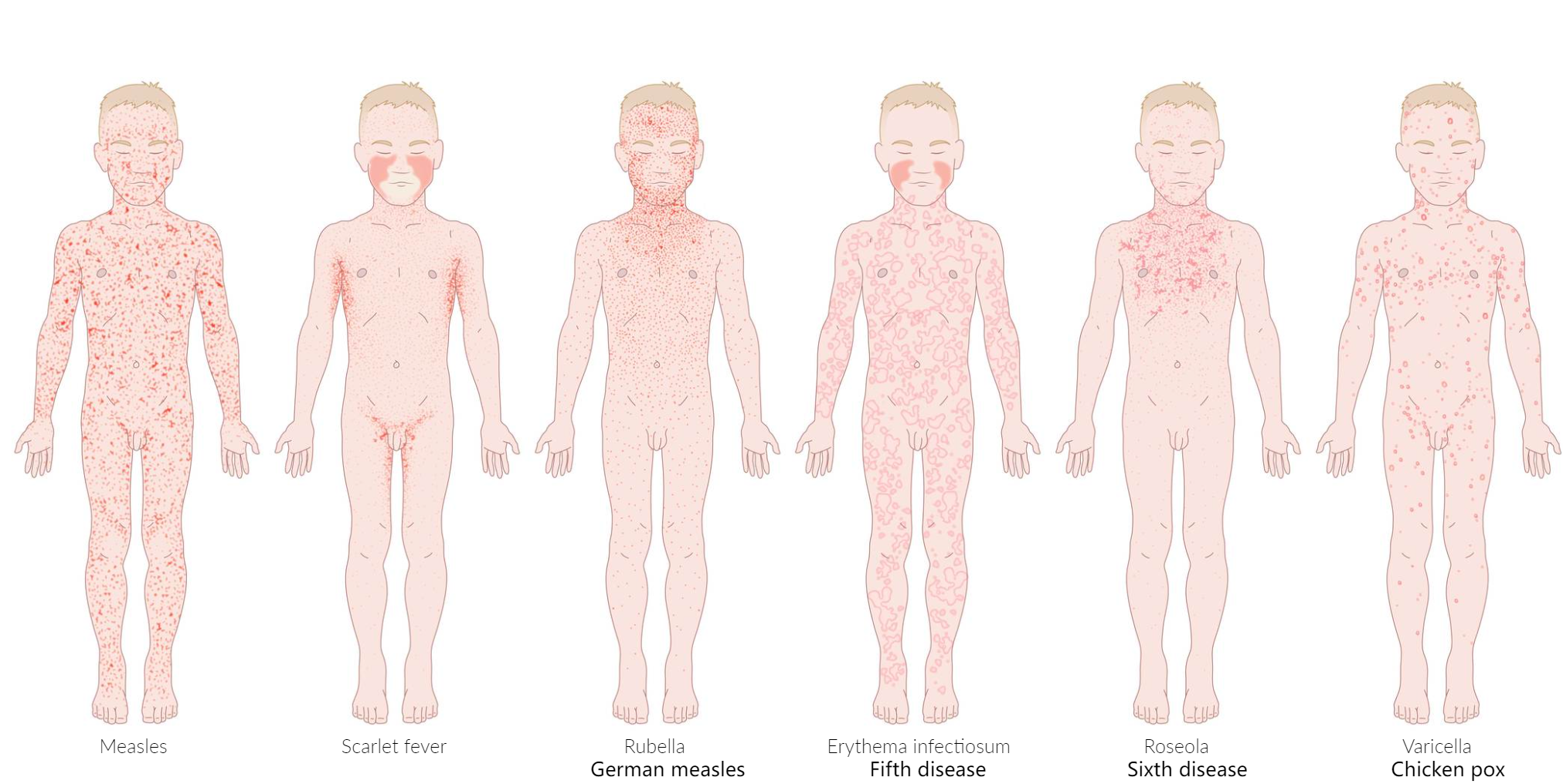
Childhood exanthems
Disease Pathogen Classic Presentation & Buzzwords Measles Measles virus 4 C’s (Cough, Coryza, Conjunctivitis, Koplik spots).
Rash: Face Body (Confluent).
Assoc: Vitamin A deficiency.Rubella Rubella virus Post-auricular LAD.
Rash: Face Body (spares 3 days, non-confluent).
Assoc: Congenital (PDA, cataracts, deaf), Adult arthritis.Roseola HHV-6 High fever breaks Rash appears.
Rash: Trunk Face.
Assoc: Febrile seizures.Fifth Disease Parvovirus B19 ”Slapped Cheek” Lacy/Reticular body rash.
Assoc: Aplastic crisis (Sickle Cell), Hydrops fetalis.Varicella VZV ”Dewdrop on a rose petal”.
Lesions in different stages of healing. t
Rash: Trunk Extremities.Scarlet Fever Strep pyogenes Sandpaper rash, Strawberry tongue, Circumoral pallor.
Assoc: Strep throat, Desquamation (palms/soles).
Fever-rash relationship
Link to original
- Measles (Rubeola): Fever first (with cough, coryza, conjunctivitis) → Rash appears 3-5 days later, spreading from head to toe.
- Rubella (German Measles): Low-grade fever → Rash appears 1-2 days later, spreading quickly from head to toe.
- Scarlet Fever: Fever and sore throat begin together → “Sandpaper” rash appears 1-2 days later.
- Erythema Infectiosum (Fifth): Low-grade fever/prodrome resolves → “Slapped cheek” rash appears days later.
- Roseola Infantum (Sixth): High fever for 3-5 days → Fever breaks → Rash appears after the fever is gone.
- Varicella (Chickenpox): Fever and vesicular rash appear at the same time (lesions in various stages).