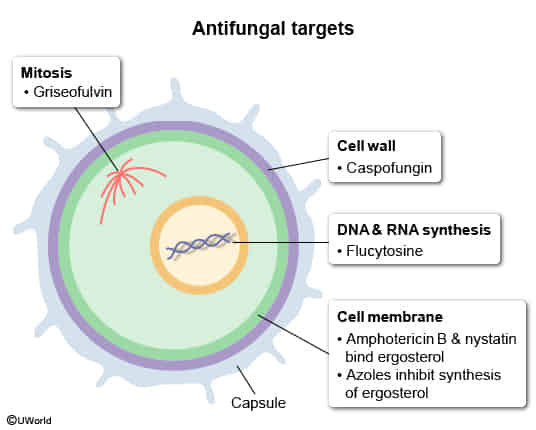
- Cell Membrane: Contains Ergosterol as the major sterol (human membranes contain cholesterol).
- Cell Wall
- Composed of Chitin (polymer of N-acetylglucosamine), β-Glucans, and Mannoproteins.
- Provides rigidity and shape; protects against osmotic pressure.
- Capsule
- Polysaccharide coating found in some fungi.
- Major virulence factor (prevents phagocytosis).
Polyenes
- Bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane → formation of pores in the fungal membrane → disruption of electrolyte balance → cell lysis → cell death
- It binds cholesterol to a degree, which explains a large number of its adverse effects.
Mnemonic
双性霉素B,双理解为一双人,结合麦角固醇——理解为结婚,一双人结婚
Amphotericin B
Mnemonic
“Amphotericin Tears a hole.”
- Ampho-TER-icin TEAR (creates holes in the membrane).
- Think of “Ampho-terrible” because it has severe side effects (nephrotoxicity) due to this aggressive mechanism.
Adverse effects
- Nephrotoxicity: Lipid-based formulations of the drug and IV hydration reduce nephrotoxicity.
- IV phlebitis
- Impaired renal tubule permeability → hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia (restoring K+ and Mg2+ while administering the drug can counter this effect)
- Fever, chills (amphotericin B is sometimes referred to as “shake and bake”)
- Bone marrow suppression, anemia
- Arrhythmias
Nystatin
- Routes of administration (too toxic for intravenous use)
- Topical
- Vaginal candidiasis
- Diaper rash
- Oral (swish and swallow): oropharyngeal candidiasis
- Topical
Azoles
- Mechanism of action (connect with CYP450)
- Inhibition of 14-alpha demethylase, a fungal cytochrome P450 → ↓ fungal synthesis of ergosterol from lanosterol → ↓ levels of ergosterol → membrane instability → cellular death.
Allylamine derivatives (terbinafine)
- Route of administration: oral
- Mechanism of action: inhibition fungal squalene epoxidase → ↓ synthesis of ergosterol → accumulation of squalene → ↑ membrane permeability → cell death
- Clinical use
- Adverse effects
- Hepatotoxicity
- Dysgeusia
- Gastrointestinal upset
- Headache
Mnemonic
A mnemonic i find useful for terbinafine is to imagine a Turban that’s spiraled around the head in Q shaped .. so sQualene epoxidase inhibitor.
Echinocandins
- Drugs
- Caspofungin
- Anidulafungin
- Micafungin
- Route of administration: IV
- Mechanism of action: inhibition of β-glucan synthesis → disruption of fungal cell wall synthesis → ↓ resistance against osmotic forces → cell death t
- Clinical use
- Invasive aspergillosis
- Invasive candidiasis (particularly biofilm-embedded Candida )
- Adverse effects
- Flushing (due to release of histamine)
- Hepatotoxicity
- Gastrointestinal upset
Mnemonic
- Echinocandins has “chino” or China which is famous for Great Wall.
- Echinocandins has “candi” or candy, therefore β-glucan
Benzofurans (griseofulvin)
- Route of administration: oral
- Mechanism of action: griseofulvin binds to keratin precursor cells → accumulation in keratin-rich tissues (e.g., nails, hair) → entry into the fungal cell → interference with microtubule function → disruption of fungal mitosis
- Clinical use: dermatophyte infections (e.g., tinea pedis)
Mnemonic
Griseofulvin (grease=oil, full=food, vino=wine) = sex orgy = reproduction = cell division = mitotic spindle = microtubules.
Antimetabolites (flucytosine)
- Route of administration: oral
- Mechanism of action: converted to 5-fluorouracil by fungal cytosine deaminase, thereby inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis
