Microscopic anatomy
- Exocrine Pancreas (approx. 85-99% of mass): Composed of acinar cells and a ductal system.
- Acinar Cells: Synthesize, store, and secrete digestive enzymes (zymogens like trypsinogen, chymotrypsinogen; active enzymes like amylase, lipase). Arranged in clusters (acini).
- Ductal System: Transports pancreatic juice. Lined by ductal cells that secrete bicarbonate-rich fluid to neutralize gastric acid.
- Main Pancreatic Duct (Duct of Wirsung): Runs the length of the pancreas from tail to head. Joins the common bile duct to form the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater), which empties into the 2nd part of the duodenum at the major duodenal papilla. Flow controlled by Sphincter of Oddi.
- Accessory Pancreatic Duct (Duct of Santorini): Variable; when present, typically drains the lower part of the head and empties into the duodenum at the minor duodenal papilla, proximal to the major papilla. May communicate with the main duct.
- Endocrine Pancreas (approx. 1-2% of mass): Consists of Islets of Langerhans, scattered throughout the exocrine tissue (most numerous in the tail). Hormones secreted directly into the bloodstream.
- Alpha (α) cells (approx. 20%): Secrete glucagon (↑ blood glucose).
- Beta (β) cells (approx. 75%): Secrete insulin (↓ blood glucose) and C-peptide.
- Delta (δ) cells (approx. 4-5%): Secrete somatostatin (inhibits insulin, glucagon, growth hormone, and GI hormone secretion).
- PP cells (F cells): Secrete pancreatic polypeptide (regulates pancreatic secretions).
Exocrine Secretions
Acinar Cell Secretions: Digestive Enzymes
The exocrine pancreas secretes digestive enzymes crucial for macronutrient breakdown in the duodenum.
- Amylase: Digests starch and glycogen (carbohydrates) into simple sugars.
- Lipase: Hydrolyzes triglycerides into fatty acids and monoglycerides. Requires bile for optimal function.
- Proteases: Secreted as inactive zymogens to prevent pancreatic autodigestion.
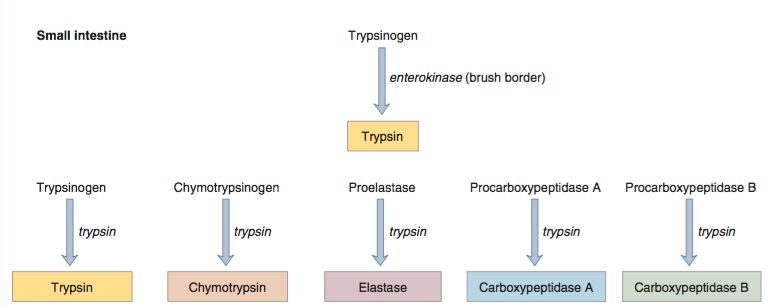
- Trypsinogen: Converted to active trypsin. Trypsin is the primary activator of other pancreatic zymogens.
- Chymotrypsinogen: Converted to active chymotrypsin.
- Procarboxypeptidases: Converted to active carboxypeptidases.
- Proelastase: Converted to active elastase.
Ductal Cell Secretions: Aqueous Bicarbonate (HCO3⁻)
Ductal cells secrete an isotonic, alkaline fluid rich in HCO3⁻. This secretion is vital for neutralizing acidic chyme from the stomach, creating an optimal pH for pancreatic enzyme activity in the duodenum.
- Mechanism:
- HCO3⁻ is secreted into the ductal lumen.
- This process is highly dependent on the Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) channel. The CFTR channel secretes Cl⁻ into the lumen, which is then exchanged for HCO3⁻ via an anion exchanger (e.g., SLC26A6). CFTR may also directly conduct HCO3⁻. t
Regulation of Secretion
Secretion is hormonally and neurally regulated, primarily during the intestinal phase of digestion.
- Cholecystokinin (CCK):
- Stimulus: Presence of fatty acids and amino acids in the duodenum.
- Action: Stimulates acinar cells to secrete enzyme-rich pancreatic juice.
- Secretin:
- Stimulus: High acidity (low pH) of chyme entering the duodenum.
- Action: Stimulates ductal cells to secrete bicarbonate-rich fluid (HCO3⁻), which neutralizes stomach acid and provides an optimal pH for enzymatic activity.
- Vagal stimulation (Ach): Also stimulates acinar cell secretion.
Zymogen Activation Cascade
This is a critical, sequential process that occurs in the duodenal lumen to prevent premature activation within the pancreas.
- Enteropeptidase (formerly enterokinase), a brush border enzyme, converts trypsinogen to trypsin.
- Works best in the slightly alkaline pH (~8.0)
- Trypsin then catalyzes the activation of all other pancreatic zymogens (chymotrypsinogen, procarboxypeptidases, etc.), including more trypsinogen (auto-activation).
- Protective mechanisms to limit premature trypsinogen activation:
- Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1):
- Secreted by pancreatic acinar cells.
- Functions as a trypsin inhibitor, impeding prematurely activated trypsinogen molecules within the pancreas.
- Trypsin self-inhibition:
- Trypsin can cleave active trypsin molecules at a second site, rendering them inactive.
- Serine peptidase inhibitor Kazal-type 1 (SPINK1):
- Hereditary pancreatitis:
- Rare disorder caused by mutations in the trypsinogen or SPINK1 gene.
- Common mutation results in abnormal trypsin that is not susceptible to inactivating cleavage by trypsin.
Embryology
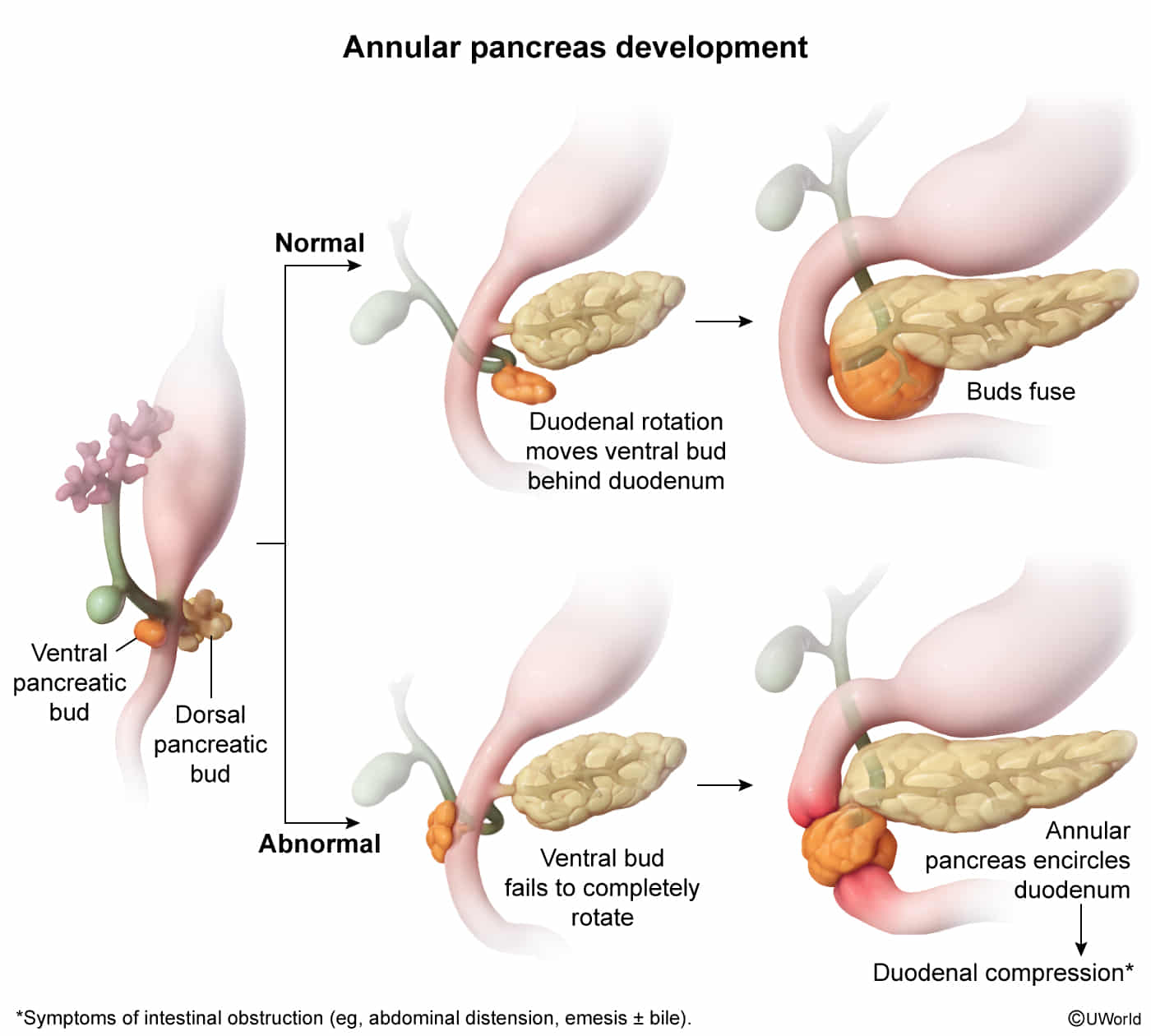
- Origin: Foregut gives rise to dorsal and ventral pancreatic buds.
- Rotation: Duodenum rotates, pulling the ventral bud to fuse with the dorsal bud.
- Derivatives:
- Ventral bud forms uncinate process and main pancreatic duct.
- Dorsal bud forms the head, body, and tail.
- Clinical Correlates:
- Annular Pancreas: Ventral bud abnormally encircles the duodenum, causing obstruction (“double-bubble” sign, see Duodenal atresia). Associated with Down syndrome.
- Pancreas Divisum: Most common. Ventral and dorsal buds fail to fuse. Can cause recurrent pancreatitis due to inadequate drainage through the minor papilla.