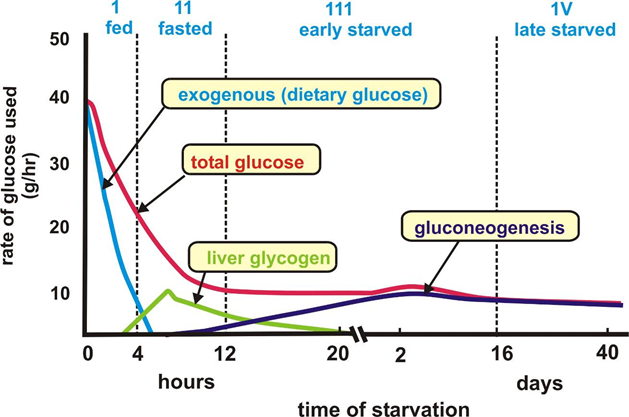
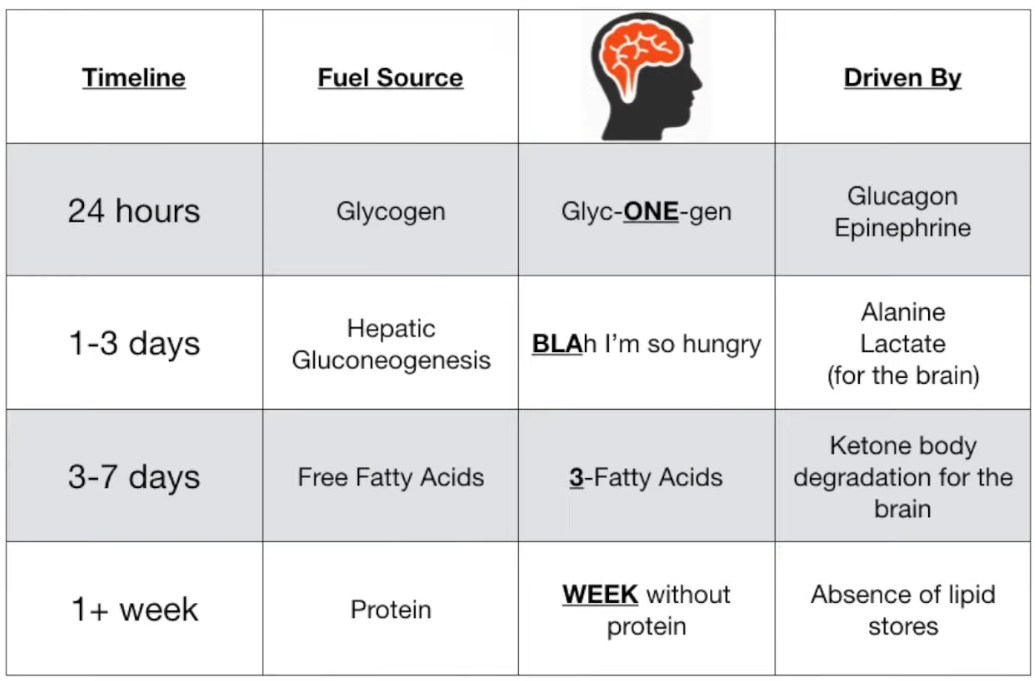
- Glycogenolysis: Primary source of blood glucose in the first ~12-24 hours of fasting. Liver glycogen is depleted after ~24 hours.
- Gluconeogenesis: Becomes the main source of glucose after glycogen stores are depleted.
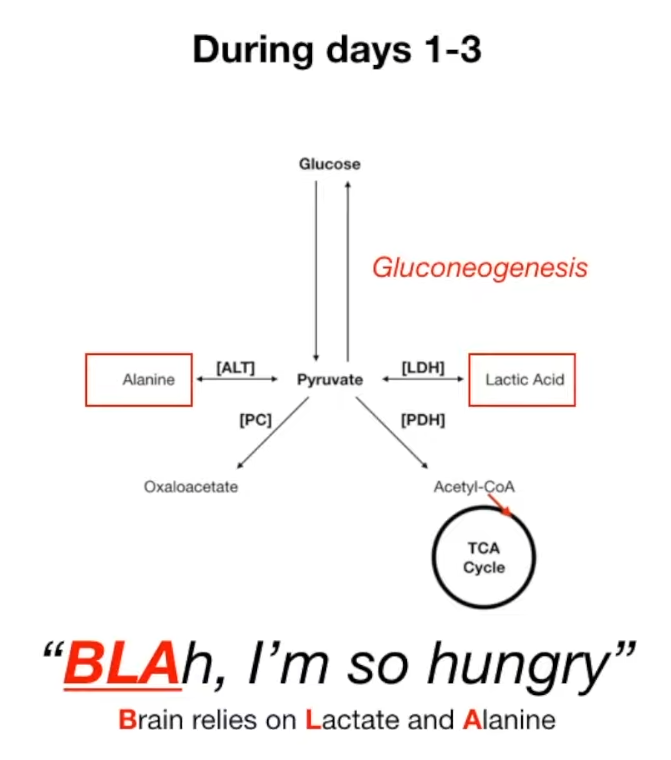
- Substrates: Lactate & Alanine (from muscle), Glycerol (from fat), Propionyl-CoA (from odd-chain FAs).
- Initially occurs primarily in the liver; kidneys contribute significantly in prolonged starvation.
- Ketogenesis: Occurs in the liver mitochondria when acetyl-CoA (from β-oxidation) exceeds the oxidative capacity of the TCA cycle.
- Because oxaloacetate are all used for gluconeogenesis, making TCA cycle less available.
- Ketone bodies (acetoacetate & β-hydroxybutyrate) are used by the brain, heart, and skeletal muscle, sparing glucose and reducing protein catabolism.
- “The brain adapts to ketones to spare protein.”
- Exercise Fuel Use:
- Short burst (<10 sec): Stored ATP, Creatine Phosphate.
- Intense exercise (~1 min): Anaerobic glycolysis.
- Endurance exercise: Aerobic metabolism. Starts with muscle glycogen, then blood glucose and FFAs. The contribution from FFAs increases with duration.
| State | Brain | RBCs | Heart & Muscle | Liver | Adipose Tissue |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well-Fed State (~0-4 hrs) | Glucose (GLUT1/3, insulin-independent). | Glucose only (anaerobic glycolysis; no mitochondria). | Glucose (GLUT4, insulin-dependent). | Glucose; processes excess for glycogen synthesis & lipogenesis. | Glucose (for glycerol-3-P) & chylomicron remnants for TG storage. |
| Fasting State (~4-24 hrs) | Glucose (from hepatic glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis). | Glucose only. | Fatty Acids (primary), Ketones. Spares glucose for brain/RBCs. | Fatty Acids for its own energy; performs glycogenolysis & gluconeogenesis to export glucose. | Lipolysis: breaks down TGs into FFAs & glycerol for release into blood. |
| Starvation (>24-48 hrs) | Glucose initially, then adapts to use Ketone Bodies as primary fuel (~day 3+). Spares protein. | Glucose only. | Ketone Bodies, Fatty Acids. | Fatty Acids for its own energy; performs gluconeogenesis (from lactate, alanine, glycerol) & ketogenesis. | Continues Lipolysis until fat stores are depleted. |
| Prolonged Starvation (> 3 days) | Ketone bodies become the main fuel source. | Glucose only. | Ketone bodies, Fatty acids. | Gluconeogenesis slows to conserve protein; ketogenesis is maximal. | Fat stores depleted; leads to muscle proteolysis. |
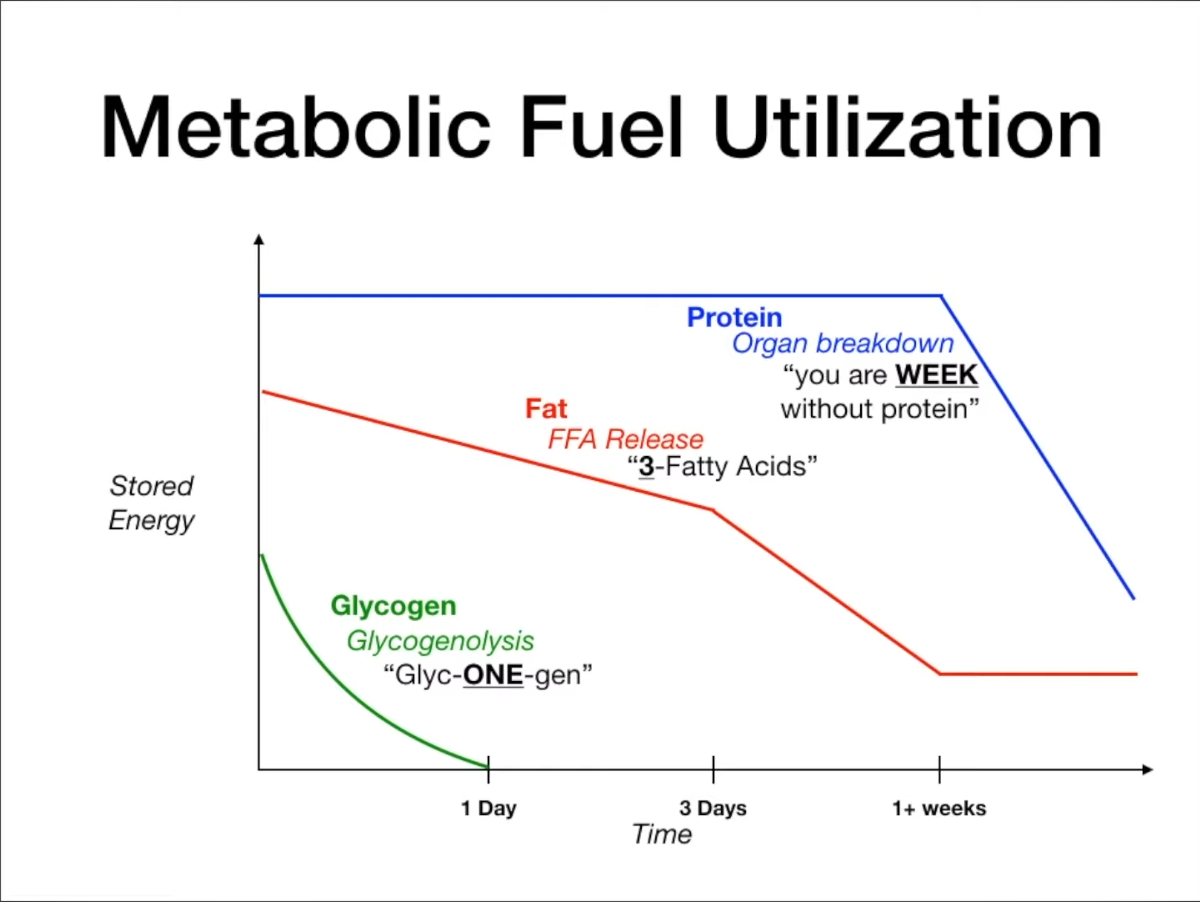 2. Free fatty acids → three fatty acids
2. Free fatty acids → three fatty acids
 Hormone-sensitive lipase is activated in response to stress hormones (eg, catecholamines, glucagon, ACTH), whereas it is inhibited by the release of insulin.
Hormone-sensitive lipase is activated in response to stress hormones (eg, catecholamines, glucagon, ACTH), whereas it is inhibited by the release of insulin.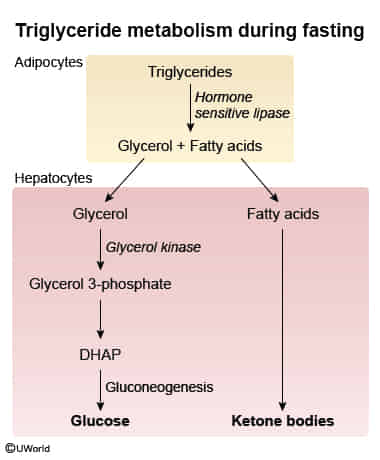
Tip
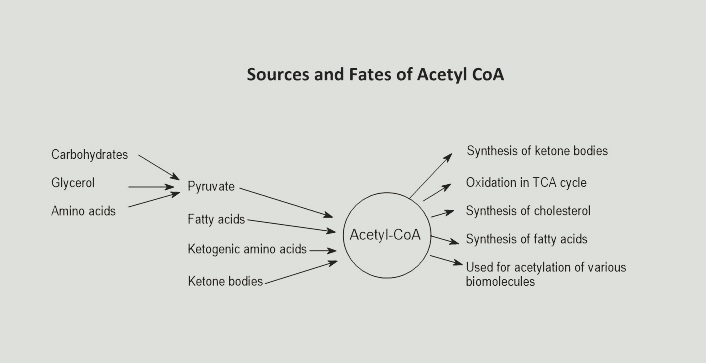
When lack of glucose, the body need new ways to generate acetyl-CoA, which then can be used in TCA cycle
- Fatty acid oxidation
- ketone body metabolism: Ketone bodies are synthesized in liver, then transported in blood to other organs for ketogenolysis, to acetyl-CoA
Regulation by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate
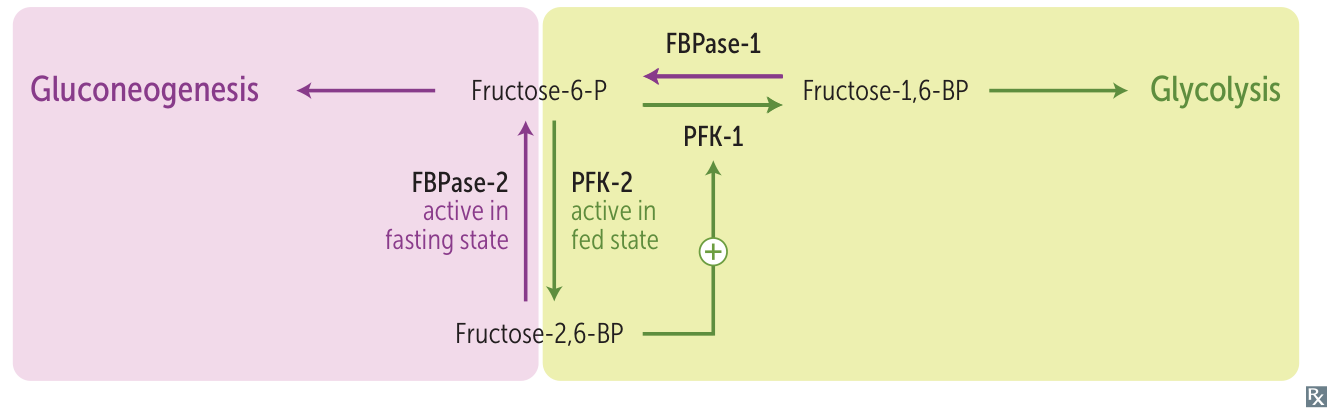
- Goal: Prevent a futile cycle of making and breaking glucose simultaneously. Regulation occurs at irreversible steps.
- Primary Control Point: The Fructose-2,6-Bisphosphate Switch
- This is the most important regulatory step.
- Fructose-2,6-BP is the master regulator.
- Activates: PFK-1 (Glycolysis)
- Inhibits: FBPase-1 (Gluconeogenesis)
- Hormones control the level of F-2,6-BP via the bifunctional enzyme PFK-2/FBPase-2.
- Fed State (↑ Insulin): DEphosphorylation → PFK-2 is active → ↑ F-2,6-BP → Glycolysis ON. t
- Fasting State (↑ Glucagon): PHOSPHORYLATION → FBPase-2 is active → ↓ F-2,6-BP → Gluconeogenesis ON.
- Allosteric Regulation (Energy State)
- High Energy (↑ ATP, ↑ Citrate): Inhibits glycolysis (PFK-1).
- Low Energy (↑ AMP): Activates glycolysis (PFK-1), inhibits gluconeogenesis (FBPase-1).
- Pyruvate Fate Regulation
- Pyruvate Kinase (Glycolysis)
- Inhibited by ATP and Alanine.
- Activated by Fructose-1,6-BP (feed-forward).
- Pyruvate Carboxylase (Gluconeogenesis)
- Activated by Acetyl-CoA (signals abundant energy from fat breakdown, shunts pyruvate to glucose production).
- Pyruvate Kinase (Glycolysis)
Main idea: Insulin & glucagon control PFK-2 & FBPase-2 → control amount of F-2,6-BP → direction towards gluconeogenesis or glycosis.
Mnemonic
FaBian the Peasant (FBP) has to work hard when starving. Prince FrederricK (PFK) works only when fed.
Enzymes Increased in Fed State (High Insulin:Glucagon Ratio)
The fed state focuses on using and storing incoming fuel (anabolism). Insulin is the dominant hormone.
- Glycolysis & Glucose Uptake (Energy Production & Storage Precursors):
- Glucokinase (Liver) / Hexokinase (Most Tissues): Traps glucose in the cell by phosphorylating it to glucose-6-phosphate. Glucokinase in the liver is induced by insulin. t
- Phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1): The rate-limiting enzyme of glycolysis. Activated by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (F-2,6-BP).
- Phosphofructokinase-2 (PFK-2): Activated by insulin. PFK-2 produces F-2,6-BP, which strongly activates PFK-1, pushing glycolysis forward.
- Pyruvate Kinase: Catalyzes the final, irreversible step of glycolysis.
- Glycogen Synthesis (Glucose Storage):
- Glycogen Synthase: The rate-limiting enzyme for glycogenesis. Activated by insulin-mediated dephosphorylation.
- Fatty Acid & Triglyceride Synthesis (Fat Storage):
- Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase (ACC): The rate-limiting enzyme for fatty acid synthesis. Activated by insulin and citrate.
- Fatty Acid Synthase: Synthesizes fatty acids from acetyl-CoA and malonyl-CoA.
- Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL): Found on endothelial cells; breaks down triglycerides from chylomicrons and VLDL for uptake into adipose tissue and muscle. Activated by insulin.
Enzymes Increased in Fasting State (Low Insulin:Glucagon Ratio)
The fasting state focuses on mobilizing stored fuel to maintain blood glucose for the brain and RBCs (catabolism). Glucagon and epinephrine are the dominant hormones.
-
Glycogenolysis (Glucose Release from Storage):
- Glycogen Phosphorylase: The rate-limiting enzyme of glycogenolysis. Activated by glucagon and epinephrine via a cAMP-mediated cascade.
-
Gluconeogenesis (New Glucose Synthesis):
- Pyruvate Carboxylase: Converts pyruvate to oxaloacetate. Activated by acetyl-CoA.
- Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase (PEPCK): Converts oxaloacetate to PEP. Upregulated by glucagon and cortisol. t
- Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase: Bypasses PFK-1 in glycolysis. Inhibited by F-2,6-BP.
- Glucose-6-phosphatase: Found only in the liver; dephosphorylates G6P to release free glucose into the blood. t
-
Lipolysis & Fatty Acid Oxidation (Fat Breakdown for Energy):
- Hormone-Sensitive Lipase (HSL): Breaks down stored triglycerides in adipocytes into free fatty acids and glycerol. Activated by glucagon and epinephrine; inhibited by insulin.
- Carnitine Palmitoyltransferase I (CPT-I): Rate-limiting enzyme for β-oxidation; transports fatty acids into the mitochondria.
-
Ketogenesis (Alternate Fuel Production):
- HMG-CoA Synthase: Rate-limiting enzyme for ketone body synthesis in the liver mitochondria.
- HMG-CoA Lyase: Produces acetoacetate from HMG-CoA.