Definition: inherited genetic disorder characterized by the impaired metabolism of deoxyadenosine during DNA breakdown
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
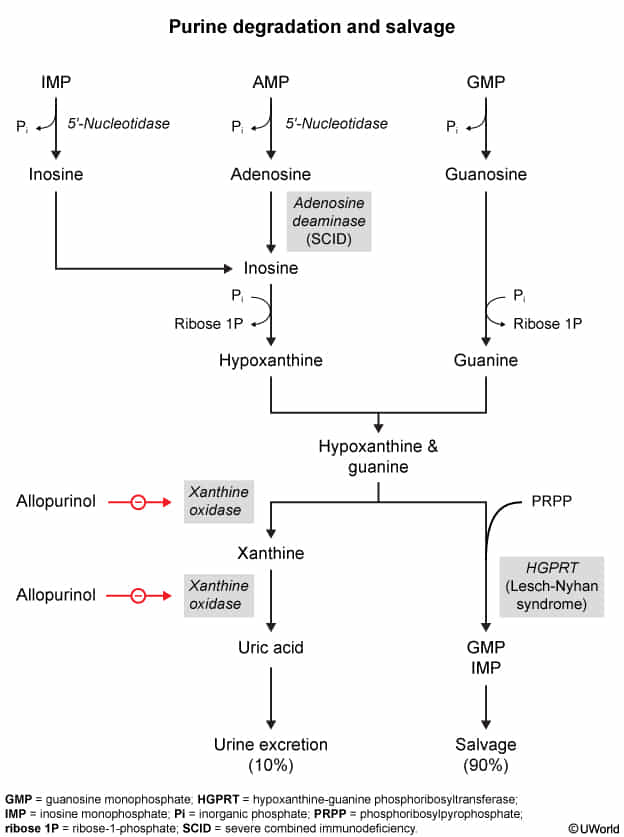
- Defect in Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) enzyme involved in the purine salvage pathway.
- Mechanism of Toxicity:
- ADA normally deaminates adenosine inosine.
- Deficiency leads to accumulation of adenosine and deoxyadenosine (dATP) within cells.
- ↑ dATP inhibits ribonucleotide reductase.
- Result: Impaired DNA synthesis toxicity and apoptosis of rapidly dividing cells, specifically lymphocytes.
- Leads to Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) (2nd most common cause after X-linked IL-2R -chain defect).
Clinical features
- Presents in infancy with Failure to Thrive (FTT).
- Chronic diarrhea and recurrent, severe infections.
- Susceptibility to all pathogen types due to lack of both humoral (B-cell) and cell-mediated (T-cell) immunity:
- Fungal: Oral thrush (Candida), Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia.
- Viral: CMV, VZV, HSV, RSV.
- Bacterial: Otitis media, pneumonia, sepsis.
- Protozoal: Cryptosporidium, Giardia.
Diagnostics
- CBC: Profound lymphopenia (↓ T cells and ↓ B cells).
- CXR: Absent thymic shadow (also seen in DiGeorge syndrome).
- Flow Cytometry: Absent/low CD3+ (T cells) and CD19+ (B cells).
- Newborn Screening: Detected via T-cell receptor excision circles (TRECs).