Epidemiology
Etiology
- Abnormal accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leading to ventricular enlargement and ↑ intracranial pressure (ICP).
- Non-communicating (Obstructive)
- Caused by a structural blockage of CSF flow within the ventricular system.
- Leads to enlargement of ventricles proximal to the obstruction.
- Common causes:
- Aqueductal stenosis (most common cause in newborns)
- Tumors (e.g., colloid cyst of the 3rd ventricle, posterior fossa tumor)
- Arnold-Chiari malformation
- Dandy-Walker malformation: congenital malformation caused by failure of the fourth ventricle to close, which leads to persistence of Blake’s pouch (cyst in the 4th ventricle) and cerebellar vermis hypoplasia
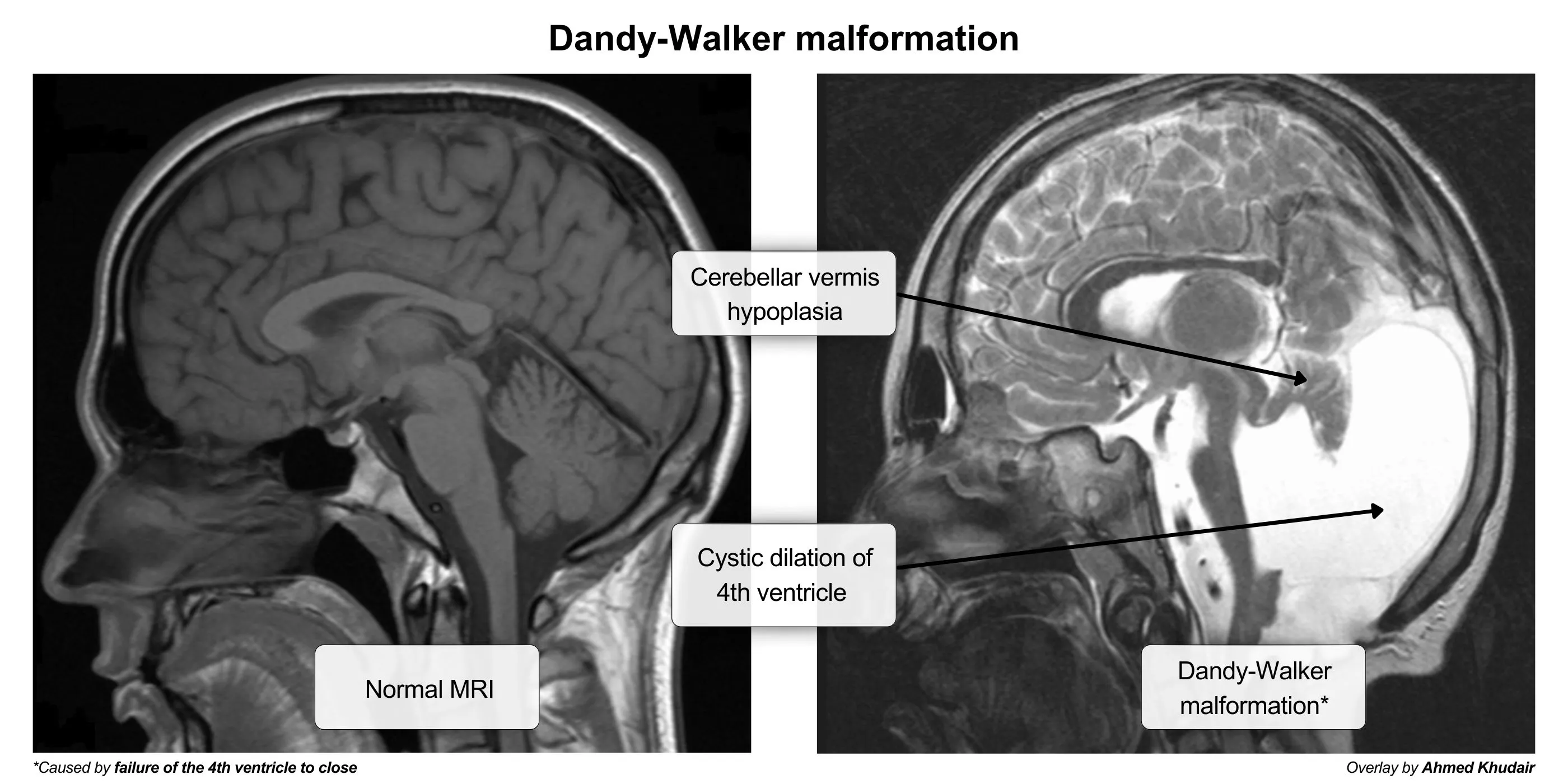
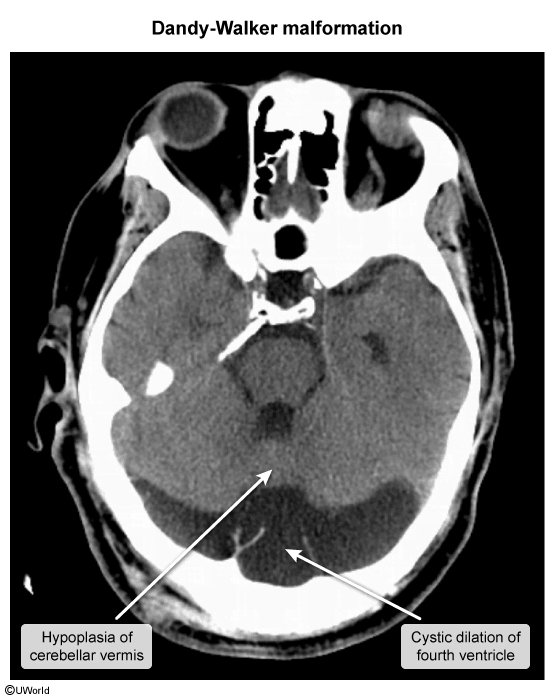
- Causes a variety of neurologic abnormalities (e.g., ataxic gait) and noncommunicating hydrocephalus
- Associated with a variety of extracranial abnormalities (e.g., craniofacial abnormalities, cardiac defects, spina bifida)
- Communicating
- Caused by ↓ CSF absorption by arachnoid granulations.
- All ventricles are symmetrically enlarged.
- Common causes:
- Post-meningitis scarring
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (blood clogs granulations)
- Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)
- Chronic form of communicating hydrocephalus in the elderly.
- CSF pressure is episodically elevated but often normal on lumbar puncture.
- Pathophysiology: Impaired absorption at arachnoid granulations leads to ventricular expansion that stretches the corona radiata fibers.
Chiari malformation vs Dandy-Walker malformation
Feature Chiari Malformation Dandy-Walker Malformation Pathophysiology Cerebellum herniates through foramen magnum due to small posterior fossa. Agenesis of cerebellar vermis allows 4th ventricle to enlarge into a cyst. Posterior Fossa Small / Normal Enlarged Key Abnormality Tonsillar (Type I) or vermis + tonsillar (Type II) herniation. Absent cerebellar vermis. Hydrocephalus Common, due to CSF outflow obstruction. Very common, due to cystic 4th ventricle. Key Associations - Type I: Syringomyelia.
- Type II: Myelomeningocele.Hydrocephalus, Spina Bifida, Agenesis of corpus callosum. Typical Presentation - Type I: Adult w/ headaches.
- Type II: Infant w/ brainstem dysfunction.Infant w/ macrocephaly. Chiari畸形:过度拥挤的房间
请把后颅窝想象成一个小卧室,把小脑和脑干想象成里面的家具。
- 问题所在: 在Chiari畸形中,这个房间建得太小了,无法容纳所有它需要放置的家具。
- 后果: 为了把所有东西都塞进去,一部分家具(小脑扁桃体)被挤了出来,并从唯一的开口——门道(枕骨大孔)——伸了出去。
- 结果: 这些堵在门口的家具阻碍了交通(脑脊液流动),导致房间内压力积聚(脑积水),并影响到走廊的墙壁(脊髓空洞症)。
核心:Chiari是一个_拥挤_问题。
Dandy-Walker畸形:缺失的帐篷支柱
请把后颅窝想象成一个大帐篷,把小脑蚓部想象成它主要的中央支撑柱。
- 问题所在: 在Dandy-Walker畸形中,这根中央帐篷支柱缺失了(蚓部发育不全)。
- 后果: 没有了支柱的支撑,帐篷的顶部(第四脑室)无法正常成型。它会塌陷并被“雨水”(脑脊液)充满,形成一个巨大的、充满液体的囊肿。
- 结果: 这个不断膨胀的水囊肿将帐篷壁向外推(后颅窝扩大),并堵住了拉链出口(脑脊液流出道),将所有的水都困在里面,导致整个帐篷都肿胀起来(脑积水)。
核心:Dandy-Walker是一个_结构缺陷_问题。
Link to original
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>