- Severe mucocutaneous reactions characterized by necrosis and detachment of the epidermis.
- Distinguished by Body Surface Area (BSA) involvement:
- SJS: <10% BSA
- SJS/TEN Overlap: 10–30% BSA
- TEN: >30% BSA
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Adverse Drug Reaction (most common cause):
- Allopurinol
- Antiepileptics (Lamotrigine, Carbamazepine, Phenytoin, Phenobarbital)
- Antibiotics (Sulfonamides, Penicillins)
- NSAIDs (Piroxicam)
- Infections: Mycoplasma pneumoniae (common in children), CMV, HSV.
- Idiopathic (~25-50% of cases).
Pathophysiology
- Type IV Hypersensitivity reaction (T-cell mediated).
- Cytotoxic T-cells and NK cells release granulysin/perforin/granzyme B → massive keratinocyte apoptosis.
- Separation of epidermis from dermis at the dermo-epidermal junction.
Clinical features
- Prodrome: Fever, influenza-like Sx (1–3 days prior to skin eruption).
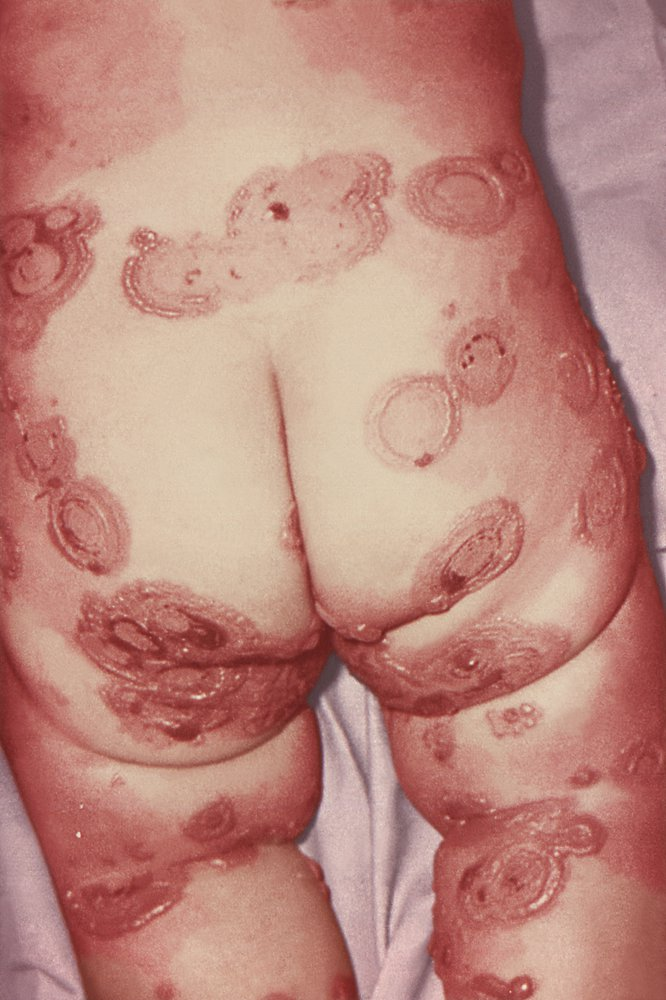
- Skin:
- Macules with purpuric centers (targetoid lesions) → coalesce to form bullae/sheets of skin sloughing.
- (+) Nikolsky sign: Slight rubbing of the skin results in exfoliation of the outermost layer.
- Skin is exquisitely tender.
- Mucosal: Involvement of 2+ mucous membranes (eyes, mouth, genitals) is characteristic (90%+ of cases).
Tip
The involvement of mucous membranes differentiates SJS from staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS) in which mucous membranes are spared!
Diagnostics
- Clinical Dx predominantly.
- Skin Biopsy:
- Full-thickness epidermal necrosis.
- Subepidermal bullae.
- Minimal inflammatory infiltrate in the dermis (distinguishes from Erythema Multiforme).
- Differential Diagnosis
- Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS):
- Exotoxin-mediated cleavage of desmoglein-1.
- Superficial splitting (granular layer).
- Usually young children; mucosa spared.
- Erythema Multiforme (EM):
- <10% BSA; classic target lesions.
- Often assoc. with HSV.
- Drug Reaction with Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DRESS):
- Eosinophilia, systemic organ involvement (liver, kidney), morbilliform rash.
- Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS):