Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
- Unknown etiology; likely immune-mediated vasculitis triggered by infection
- Medium-vessel vasculitis affecting coronary arteries primarily
- Risk of coronary artery aneurysms (CAA) if untreated
Clinical features
- Fever ≥ 5 days; Usually > 39°C
Info
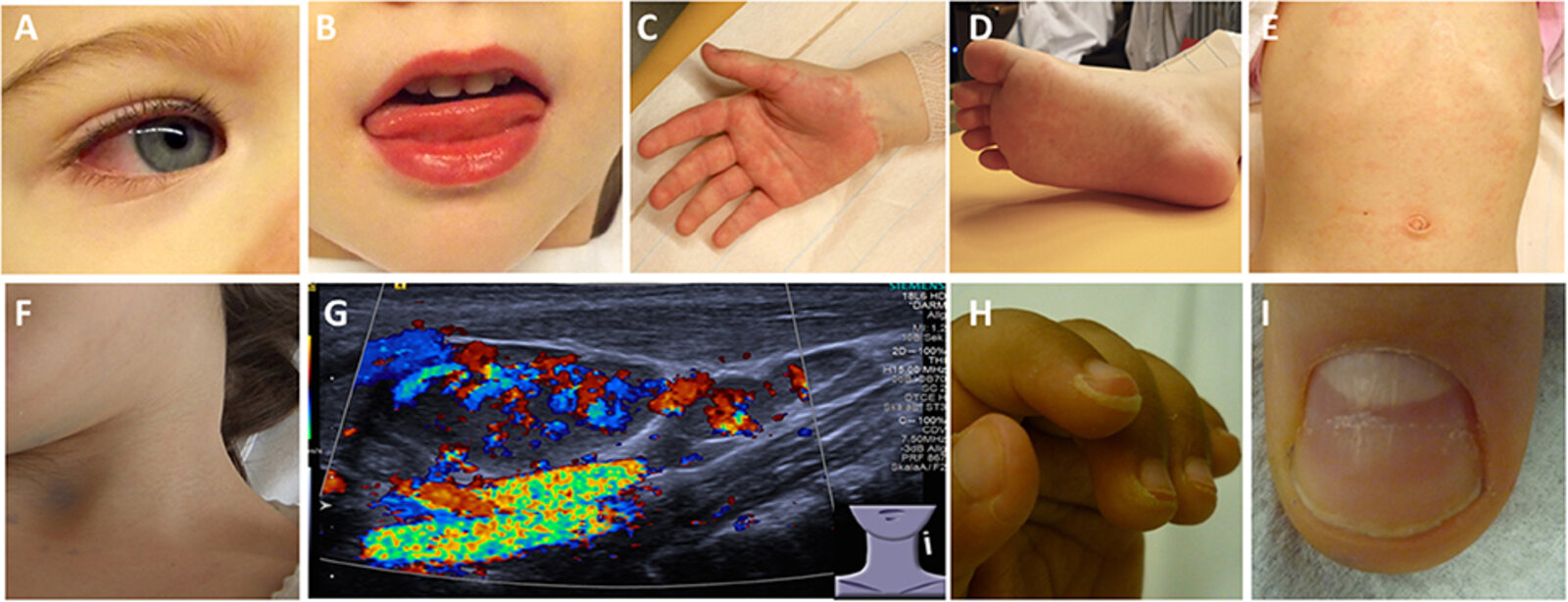
(A) Bilateral, nonpurulent conjunctivitis (B) Stomatitis with bright red lips (C) Erythema and edema of the hands (D) Erythema and edema of the feet (E) Truncal rash (F) Cervical lymphadenopathy (G) Ultrasound of an enlarged cervical lymph node: increased perfusion (H) Desquamation of fingertips (I) Deep grooves in the nail (Beau lines)
Tip
Always consider Kawasaki disease in small children with a rash and high fever unresponsive to antibiotics.
Diagnostics
Treatment
- High-dose IVIG (2 g/kg single infusion) + High-dose aspirin (80-100 mg/kg/day)
- Must be given within 10 days of fever onset to reduce CAA risk
- After fever resolves: Switch to low-dose aspirin (3-5 mg/kg/day) for antiplatelet effect; continue 6-8 weeks if no CAA, indefinitely if CAA present
- Refractory cases: Consider corticosteroids or infliximab
Complications
- Coronary artery aneurysm
- The risk of developing coronary artery aneurysm in untreated patients is 15–25%
- Rupture or thrombosis of the aneurysm can be lethal.
- Myocardial infarction
- Myocarditis
- Ventricular dysfunction