Left part is for HIV, right part is for other virus.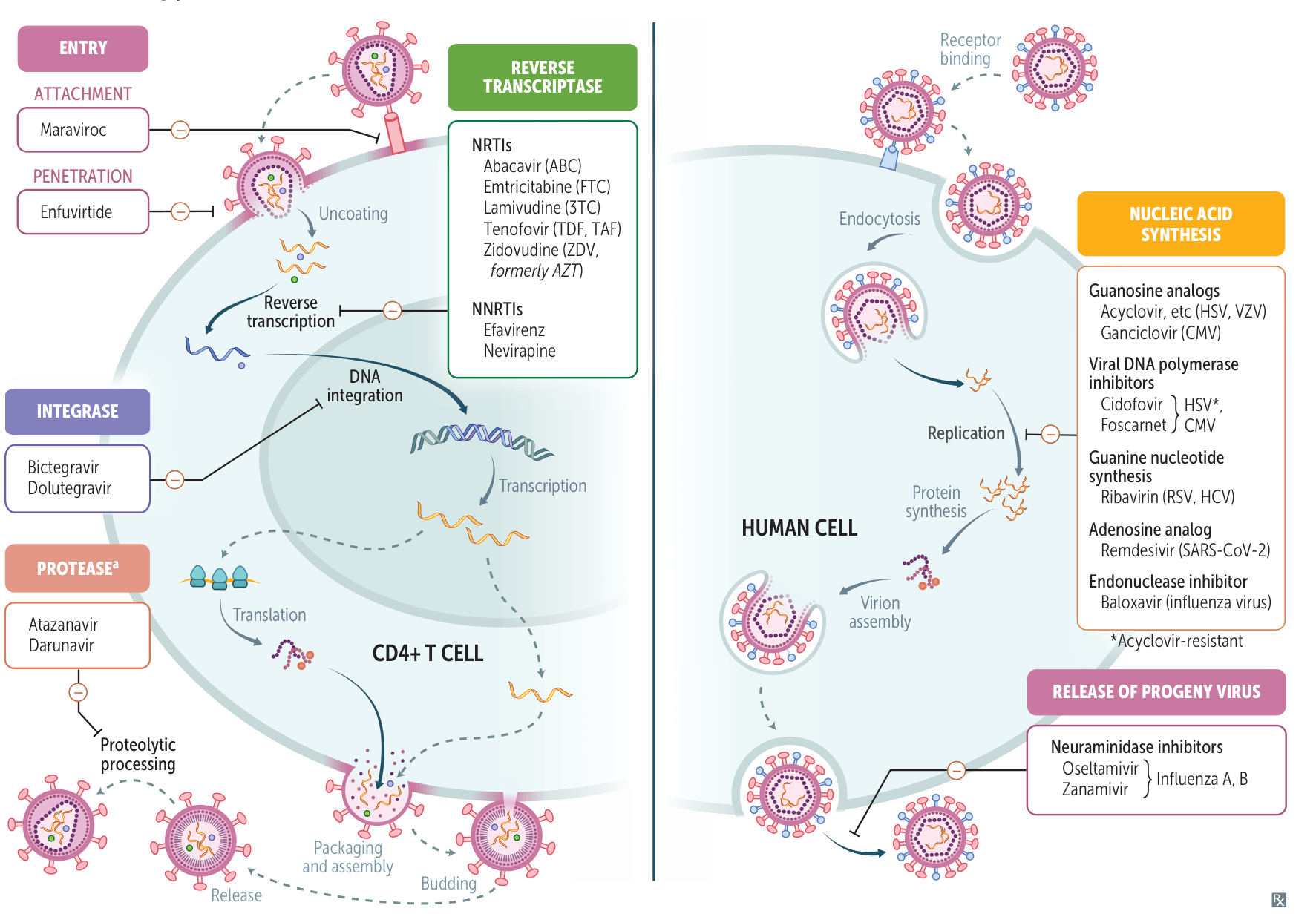
| Class | Example(s) | Mechanism of action |
|---|---|---|
| NRTI | Tenofovir, emtricitabine, lamivudine, abacavir, zidovudine | Inhibits HIV DNA synthesis from RNA template by terminating DNA chain elongation NRTI: Competitive nucleoside/nucleotide RT inhibitor |
| NNRTI (-vir-) | Efavirenz, nevirapine | NNRTI: Allosteric RT inhibitor |
| PI (-navir) | Atazanavir, darunavir, indinavir, ritonavir | Inhibits HIV polyprotein cleavage |
| Integrase inhibitor (-gravir) | Dolutegravir, raltegravir | Inhibits HIV DNA integration into host genome |
| Fusion inhibitor | Enfuvirtide | Inhibits HIV fusion with target cell membrane by binding to HIV gp41 |
| CCR5 antagonist | Maraviroc | Inhibits HIV entry by blocking the HIV gp120 allosteric interaction with CCR5 (tropism testing required) |
Nucleoside/Nucleotide Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NRTIs)
- Medications in class
- Abacavir (ABC)
- Didanosine (ddI)
- Emtricitabine (FTC)
- Lamivudine (3TC)
- Stavudine (d4T)
- Tenofovir (nucleotide analog, also called nucleotide reverse-transcriptase inhibitor; NtRTI)
- Tenofovir disoproxil (TDF)
- Tenofovir alafenamide (TAF)
- Zidovudine (ZDV, formerly AZT)
- Mechanism of action
- Competitive inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase.They are nucleoside/tide analogs that lack a 3’-OH group, causing chain termination upon incorporation into viral DNA.
- Require intracellular phosphorylation to become active.
- thus, NRTI efficacy is reliant on kinase availability and activity, which varies depending on cell functionality and activation state.
- Adverse effects
- Abacavir hypersensitivity reaction
- Potentially life-threatening systemic reaction consisting of fever, rash, constitutional symptoms, vomiting, diarrhea, and, occasionally, respiratory distress
- Avoid abacavir in HLA-B*5701-positive patients.
- Pancreatitis: didanosine, stavudine
- HIV-associated lipodystrophy (Cushing syndrome-like appearance): abnormal distribution of fat
- Can caused by NRTI or PI
- Loss of subcutaneous fatty tissue (lipoatrophy) in the face, extremities, and buttocks
- Probable accumulation of fat in liver, muscles, abdomen, breasts, neck (double chin), and upper back (enlarged dorsocervical fat pad)
- Metabolic changes: impaired glucose tolerance, hyperlipoproteinemia (elevated triglycerides, elevated total cholesterol, lowered HDL)
- Abacavir hypersensitivity reaction
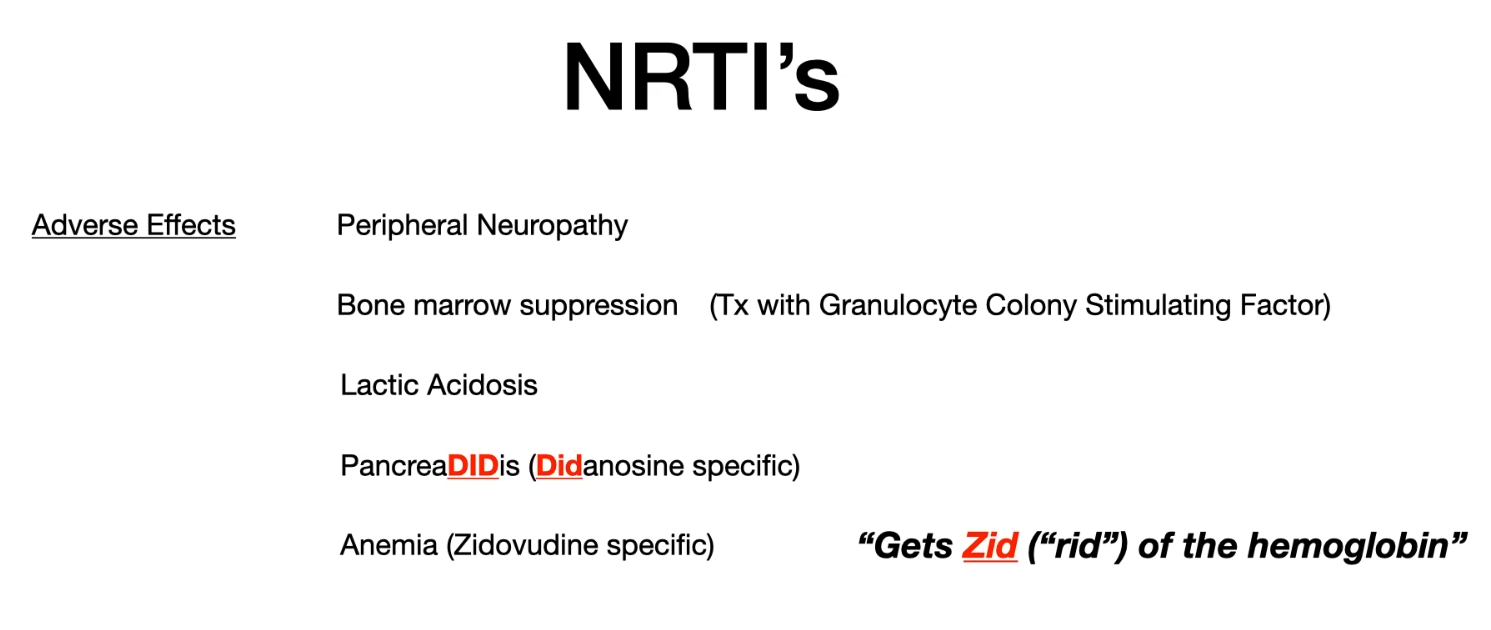
Mnemonic
Zidovudine → get rid of hemoglobin → anemia
Non-Nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors (NNRTIs)
- Mechanism of action
- Allosteric (non-competitive) inhibitors of HIV reverse transcriptase. Bind to a different site than NRTIs.
- NNRTIs do not require intracellular phosphorylation for activation because they are direct inhibitors.

 (The dog is trying to poop in the den)
(The dog is trying to poop in the den)
Protease inhibitors
- All protease inhibitors end in “-navir”.
- Mechanism of action: inhibition of viral HIV-1 protease (encoded by pol gene) → inability to cleave viral polyproteins into functional units → generation of impaired viral proteins → production of immature (noninfectious) virions
- Adverse Effects (Class-wide)
- Metabolic complications:
- Hyperglycemia: Due to insulin resistance. t
- Dyslipidemia: ↑ triglycerides and LDL cholesterol.
- Lipodystrophy: Redistribution of body fat (e.g., central obesity, buffalo hump, facial wasting).
- Gastrointestinal intolerance: Nausea, diarrhea (most common).
- Hepatotoxicity.
- Metabolic complications:




Mnemonic
Navir (never) tease a protease.
Integrase inhibitors


Mnemonic
Integrase → -tegravir
Fusion inhibitors
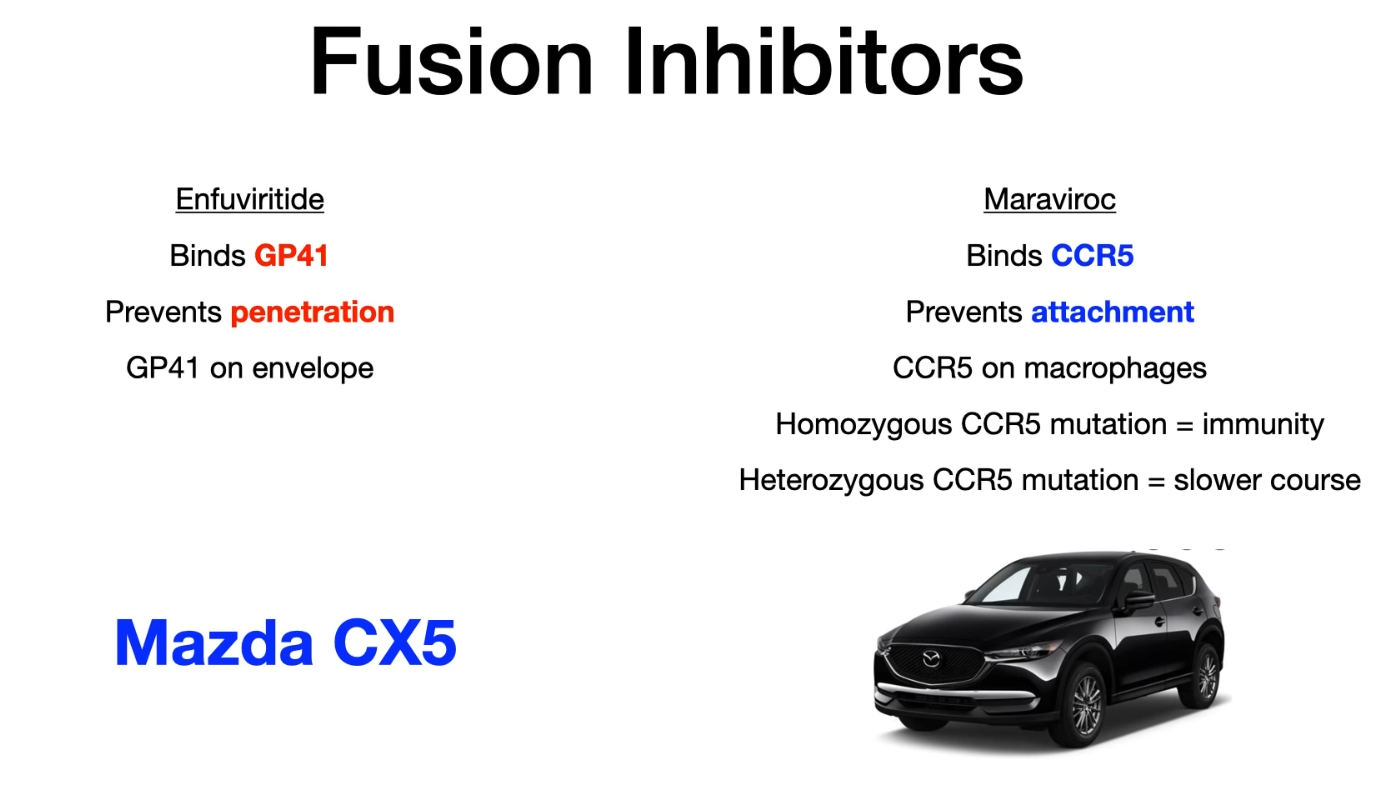
Mnemonic
- Enfuvirtide inhibits fusion.
- Mazda → Maraviroc
ART regimens
- 2 NRTIs PLUS 1 NNRTI
- 2 NRTIs PLUS 1 PI (boosted)
- 2 NRTIs PLUS 1 INI