| If you see… | Because of unable to… | Think Deficiency In… |
|---|---|---|
| Recurrent Neisseria | Complement cascade | Terminal Complement (C5-C9) |
| Catalase+ Organisms (Staph, Aspergillus, Nocardia) | Ingest or kill bacteria | Phagocyte (CGD) |
| Giardia + Sinopulmonary infxns | Opsonization and mucosal defense | B-Cell (IgA or CVID) |
| Pneumocystis (PCP), Candida, CMV | Kill intracellular pathogens and prevent fungal overgrowth | T-Cell |
| Umbilical cord won’t fall off + No pus | Phagocyte (LAD) | |
| Abscesses + Eczema + Retained primary teeth | Hyper-IgE (Job Syndrome) |
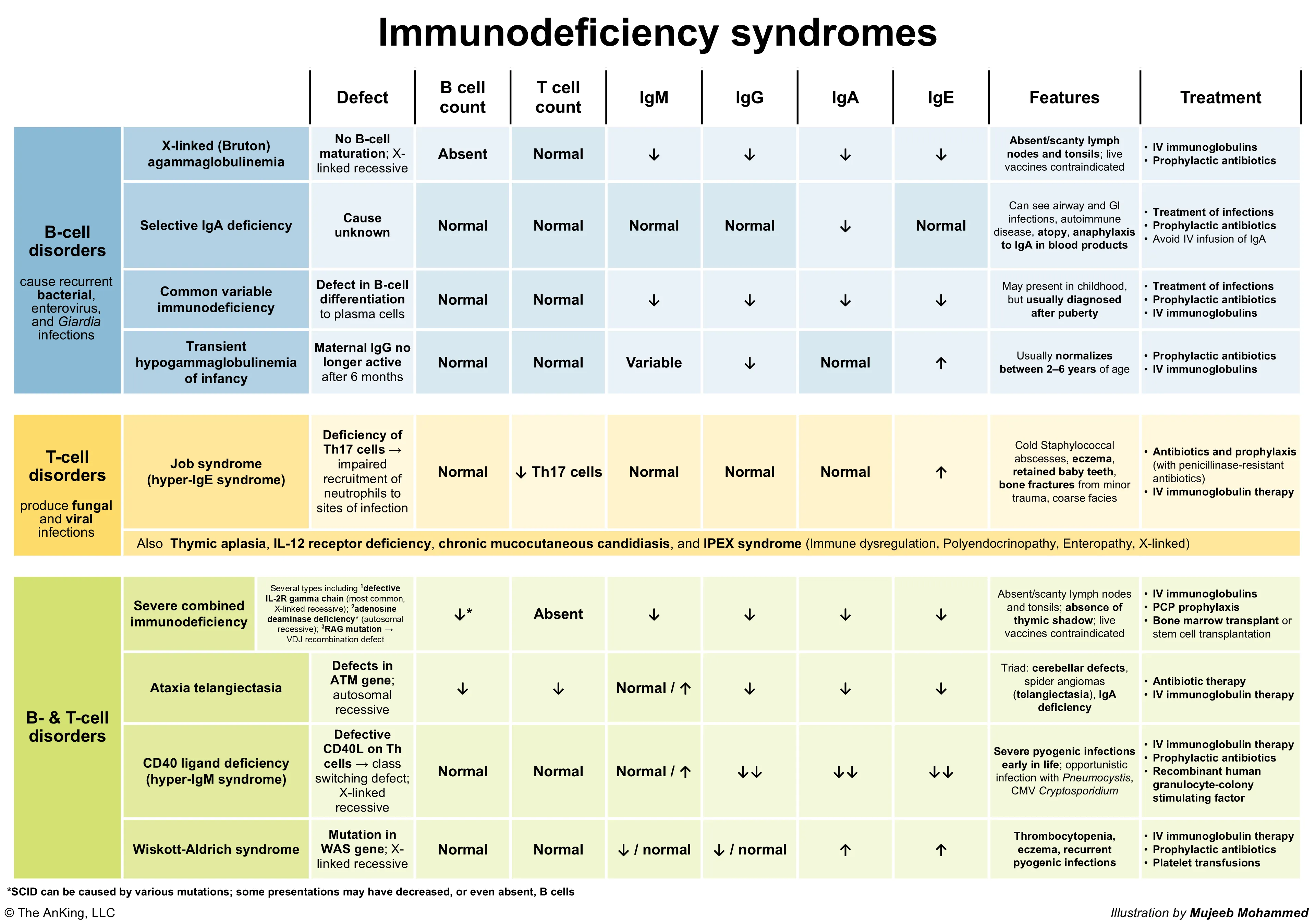
- B-cell immunodeficiencies (pyogenic and sinopulmonary infections, especially by encapsulated bacteria. See Asplenia)
- X-linked (Bruton) agammaglobulinemia
- Patho: Defect in BTK gene (tyrosine kinase) → Blocks B-cell maturation.
- T: Normal, B: ↓↓/Absent.
- Feature: Absent B cells/Igs, absent tonsils, bacterial infx after 6mo.
- Selective IgA deficiency
- Patho: Unknown defect impairing class switching to IgA.
- T: Normal, B: Normal # but no IgA secretion.
- Feature: Most common; IgA anaphylaxis risk.
- Common variable immunodeficiency
- Patho: Defect in B-cell differentiation into plasma cells (heterogeneous causes).
- T: Normal, B: Normal #, ↓plasma cells/Igs.
- Feature: Late onset, ↓IgG/A/M, lymphoma/autoimmune risk.
- X-linked (Bruton) agammaglobulinemia
- T-cell immunodeficiencies (more abnormalities)
- DiGeorge syndrome
- Patho: 22q11.2 deletion → Failure of 3rd/4th pharyngeal pouch development.
- T: ↓↓/Absent (thymic aplasia), B: Normal #.
- Feature: CATCH-22 (Thymic/Parathyroid aplasia).
- Autosomal dominant hyper-IgE syndrome (Job syndrome)
- Patho: AD STAT3 mutation → Impaired Th17 differentiation → Impaired neutrophil recruitment.
- T: ↓Th17, B: ↑↑IgE.
- Feature: FATED (Cold abscesses, retained teeth, eczema, ↑IgE).
- IL-12 receptor deficiency
- Patho: Defective IL-12 receptor → Reduced Th1 response, ↓IFN-γ production.
- T: ↓Th1 function, B: Normal.
- Feature: Disseminated mycobacteria/fungi.
- Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
- Patho: T-cell dysfunction specifically against Candida antigens (various genetic causes, e.g., AIRE).
- T: Anti-Candida defect, B: Normal.
- Feature: Persistent Candida (skin/mucosa only).
- IPEX syndrome
- Patho: FOXP3 mutation (X-linked) → Defective regulatory T cells (Tregs).
- T: ↓Tregs, B: Normal #.
- Feature: Severe Autoimmunity (Enteropathy, Endocrinopathy).
- DiGeorge syndrome
- Combined immunodeficiencies
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Patho: Various defects (e.g., IL-2R gamma chain [X-linked], ADA deficiency [AR]) → Failure of T-cell +/- B/NK cell development.
- T: ↓↓/Absent, B: ↓↓/Non-functional.
- Feature: Severe infections early, absent thymus shadow, live vaccine contraindicated.
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)
- Patho: WAS gene mutation (X-linked) → Defective WASp protein impairs actin cytoskeleton in hematopoietic cells.
- T: ↓Progressive, B: ↓IgM, ↑IgA/E.
- Feature: WATER (Thrombocytopenia with small platelets, Eczema, Infections).
- Hyper-IgM syndrome
- Patho: Most commonly CD40L defect (T-cell, X-linked) → Failure of T-cell help for B-cell class switching.
- T: No CD40L function, B: No class switch.
- Feature: ↑IgM, ↓Others; Pneumocystis risk.
- Ataxia telangiectasia
- Patho: ATM gene mutation (AR) → Defective DNA double-strand break repair.
- T: ↓, B: ↓ (esp. IgA).
- Feature: Triad (Ataxia, Telangiectasias, Infections); ↑AFP, radiation sensitivity.
- Severe combined immunodeficiency
- Neutrophil and phagocyte disorders
- Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)
- Patho: Defect in NADPH oxidase (e.g., CYBB gene) → Impaired generation of reactive oxygen species → Defective killing of catalase-positive organisms.
- Cells: Phagocytes ingest but can’t kill certain pathogens.
- Feature: Recurrent infections (catalase+ bacteria/fungi like S. aureus, Aspergillus), granulomas. DHR test for diagnosis.
- Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD-1)
- Patho: Defect in β2 integrin (CD18) (ITGB2 gene) → Impaired leukocyte adhesion and migration.
- Cells: ↑↑Neutrophils in blood (leukocytosis) as they can’t exit vessels.
- Feature: Recurrent bacterial/fungal infections without pus, delayed umbilical cord separation, impaired wound healing.
- Chédiak-Higashi syndrome
- Patho: LYST gene mutation → Defective lysosomal trafficking → Impaired phagosome-lysosome fusion; abnormal giant granules.
- Cells: Neutropenia, defective degranulation/chemotaxis, giant granules in leukocytes.
- Feature: Recurrent pyogenic infections, partial albinism, neuropathy, bleeding tendency, risk of lymphoproliferative phase.
- Myeloperoxidase deficiency
- Patho: MPO gene defect → Deficient myeloperoxidase → Reduced hypochlorous acid production.
- Cells: Impaired killing of Candida and some bacteria by neutrophils.
- Feature: Mostly asymptomatic; increased risk of Candida infections (especially disseminated in diabetics).
- Chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)
- Complement deficiencies
Common Pathogens and Mechanisms
| Immunodeficiency Type | Common Pathogens | Common Infection Sites | Underlying Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| B-cell Deficiencies | - Encapsulated bacteria (S. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, M. catarrhalis) - Giardia lamblia - Nonenveloped viruses (enterovirus, rotavirus) | - Sinuses - Ears - Lungs - Bloodstream - GI tract | Decreased or absent antibody production impairs opsonization and neutralization of pathogens, especially encapsulated bacteria that require antibody-mediated clearance |
| T-cell Deficiencies | - Viruses (CMV, EBV, VZV, HSV) - Fungi (Candida, P. jirovecii) - Mycobacteria - Intracellular parasites | - Skin/mucous membranes - Lungs - CNS - Systemic dissemination | Impaired cell-mediated immunity against intracellular pathogens, defective cytokine production, and decreased killing of infected cells |
| Combined Immunodeficiencies | - Broad spectrum of pathogens - Bacteria, viruses, fungi, protozoa - Opportunistic infections - Live vaccine strains | - Multiple organ systems - Lungs - GI tract - Skin - Systemic infections | Profound defects in both cellular and humoral immunity, affecting both adaptive and innate immune functions |
| Neutrophil/Phagocyte Disorders | - Catalase-positive bacteria (S. aureus, Burkholderia, Serratia, Nocardia) - Fungi (Aspergillus, Candida) - Gram-negative bacteria | - Skin/soft tissue abscesses - Lungs - Liver abscesses - Lymph nodes - GI tract | Defective phagocyte recruitment, ingestion, or killing of pathogens; impaired respiratory burst (in CGD); defective chemotaxis |
| Complement Deficiencies | - Encapsulated bacteria - Neisseria species (meningitidis, gonorrhoeae) - S. pneumoniae - H. influenzae | - Meninges - Bloodstream - Respiratory tract - Urogenital tract | Impaired opsonization and bacterial killing (like B cell deficiency) |
Clinical Pearls:
- Recurrent sinopulmonary infections with encapsulated bacteria suggest antibody deficiency
- Mucocutaneous candidiasis points toward T-cell dysfunction
- Severe, life-threatening infections beginning in early infancy suggest SCID
- Deep-seated abscesses with catalase-positive organisms suggest chronic granulomatous disease
- Recurrent Neisserial infections are hallmarks of terminal complement deficiencies