- Definition: an infectious disease caused by Tropheryma whipplei, an intracellular gram-positive bacteria
Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Somehow related to autoimmune process
Clinical features
Mnemonic
PAS the foamy Whipped cream in a CAN.
- A multisystemic disease, often with a long prodromal phase.
- Classic Tetrad (CAN):
- Cardiac: Endocarditis (often culture-negative), pericarditis, heart failure.
- Arthralgias: Migratory, non-deforming polyarthralgias are often the earliest symptom, preceding GI symptoms by years.
- Neurologic: Dementia, memory loss, confusion, and pathognomonic oculomasticatory myorhythmia (pendular eye movements with concurrent jaw contractions).
- GI Manifestations:
- Malabsorption leading to steatorrhea (foul-smelling, fatty stools), chronic diarrhea, and abdominal pain.
- Significant weight loss is a hallmark feature.
- Other common findings:
- Generalized lymphadenopathy.
- Fever.
- Hyperpigmentation of the skin, especially in sun-exposed areas.
Diagnostics
- Small intestine biopsies: detection of PAS-positive foamy macrophages in the lamina propria
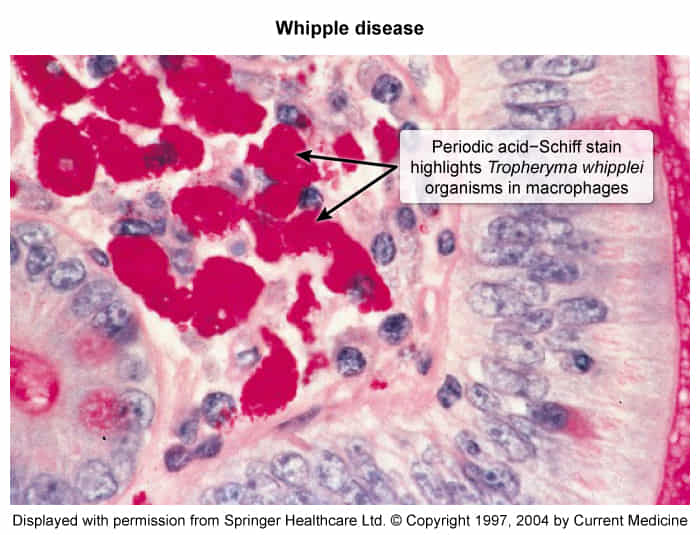
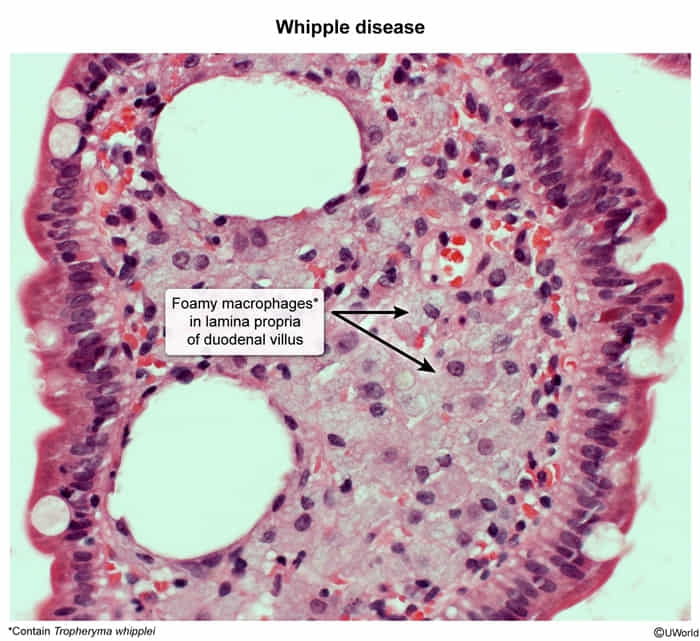
- The purple highlights whipplei organisms in macrophages
- Imaging may show enlarged mesenteric nodes.
Tip
AAT deficiency also has PAS-positive
Treatment
- IV ceftriaxone for 2 weeks
- Maintenance treatment with oral trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for 1 year