- Primary Function: Main parasympathetic (“rest and digest”) innervation to thorax and abdomen up to the splenic flexure.
- Key Anatomy:
- Exits skull via jugular foramen.
- Brainstem Nuclei:
- Nucleus Ambiguus: Motor to larynx/pharynx (swallowing, phonation).
- Dorsal Motor Nucleus: Parasympathetics to heart, lungs, GI.
- Nucleus Solitarius: Visceral sensory (taste, baroreceptors).
- Major Branches & Clinical Correlates:
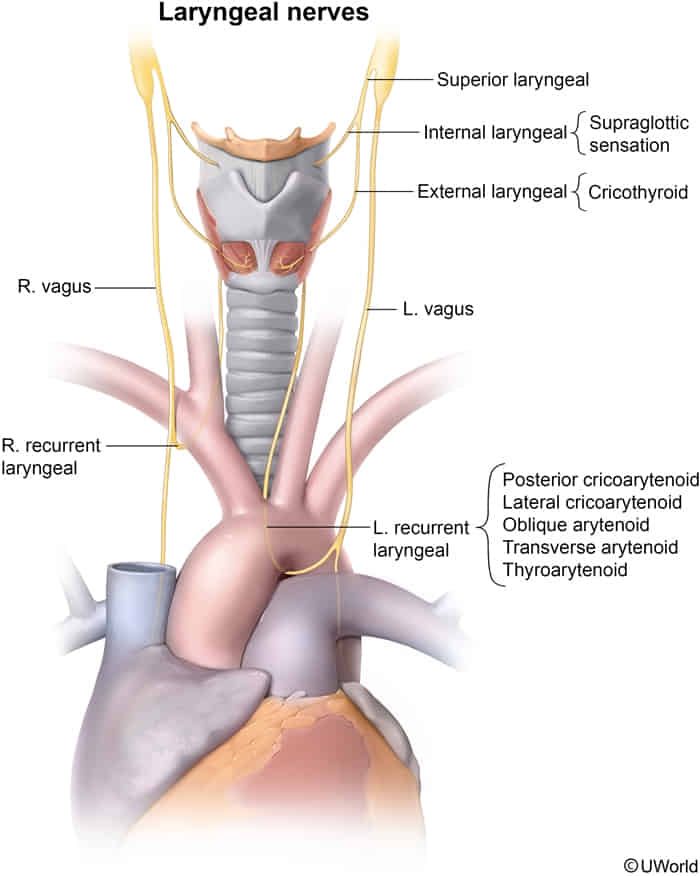
- Superior Laryngeal Nerve (SLN)
- External branch innervates Cricothyroid muscle (tensors vocal cords) → Damage causes monotone voice/loss of high pitch. (出门在外要低调)
- Internal Branch: Sensory innervation to mucosa above the vocal cords (afferent limb of cough reflex). (喝水往里咽)
- Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve (RLN)
- Innervates all intrinsic laryngeal muscles except Cricothyroid.
- Sensory: Mucosa below the vocal cords.
- Right RLN: Loops under Right Subclavian artery.
- Left RLN: Loops under Aortic Arch (lateral to Ligamentum Arteriosum).
- Clinical: Compression by Pancoast tumor, aortic aneurysm, or LA dilation (Ortner syndrome) → Hoarseness.
- Vagal Trunk Lesion (e.g., at jugular foramen):
- Hoarseness (laryngeal muscle paralysis).
- Dysphagia (pharyngeal muscle paralysis).
- Uvula deviates AWAY from the side of the lesion.
- Reflexes:
- Gag Reflex: Afferent = CN IX, Efferent = CN X.
- Baroreceptor Reflex: Aortic arch afferent and all parasympathetic efferent signals are carried by CN X.
