Epidemiology
Etiology
- Benign growth hormone-secreting pituitary adenoma (> 95% of cases)
Pathophysiology
Question
- IGF-1 is produced primarily by the liver in response to Growth Hormone (GH) stimulation and mediates most of GH’s anabolic and growth-promoting effects. t
- Insulin-like growth factor is just a growth hormone, except
- It binds to insulin receptor, but not metabolizing glucose, thus contributing to glucose intolerance?
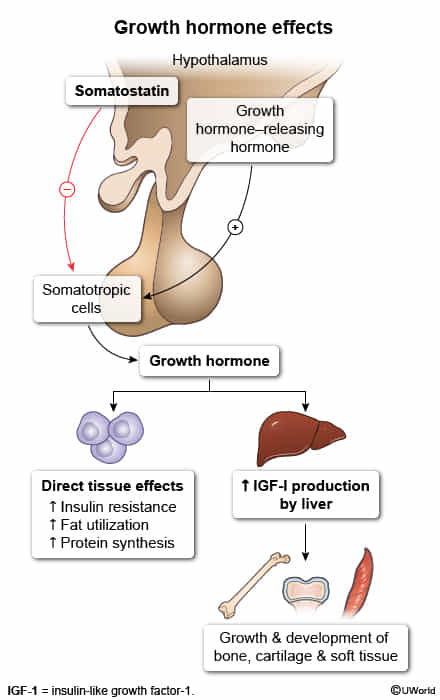
- Physiology of GH and IGF-1
- GH secretion induced by stress, sport, and hypoglycemia; inhibited especially by hyperglycemia or food intake
- Hypothalamus secretes GHRH → ↑ secretion of GH → GH induces IGF-1 synthesis → ↑ serum IGF-1 via liver synthesis which leads to the following effects:
- Binding to IGF-1 and insulin receptors → stimulation of cell growth and proliferation, inhibiting programmed cell death
- Proliferative effects especially on bone, cartilage, skeletal muscle, skin, soft tissue, and organs
- Impaired glucose tolerance caused by binding to insulin receptors
- ↑ Secretion of somatostatin from the hypothalamus → ↓ serum GH and IGF-1 (negative feedback)
- Binding to IGF-1 and insulin receptors → stimulation of cell growth and proliferation, inhibiting programmed cell death
- Core Pathophysiology: A GH-secreting pituitary adenoma leads to ↑ Growth Hormone (GH), which stimulates the liver to produce excess IGF-1. This occurs after epiphyseal plate fusion.
- Key Systemic Effects (Mediated by IGF-1):
- Skeletal: Overgrowth of acral areas (hands, feet), prominent jaw (prognathism), and frontal bossing.
- Metabolic: GH antagonizes insulin → insulin resistance, leading to hyperglycemia and secondary diabetes. t
- Cardiovascular: Cardiomyopathy and hypertension (HTN) are the leading causes of death.
- Soft Tissue: Macroglossia (→ obstructive sleep apnea), carpal tunnel syndrome, and arthralgias.
- Mass Effect of Adenoma:
- Compression of the optic chiasm causes bitemporal hemianopsia.
- Headaches and hypopituitarism are also common.
Clinical features
- General Appearance:
- Coarse facial features, frontal bossing.
- Macrognathia (protruding jaw), malocclusion.
- Macroglossia (enlarged tongue) → can cause obstructive sleep apnea.
- Large hands and feet (pt reports ↑ ring or shoe size).
- Skin & Soft Tissue:
- Hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
- Thick, oily skin; skin tags.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome (due to soft tissue overgrowth).
- Musculoskeletal:
- Arthralgias and arthritis.
- Proximal muscle weakness.
- Cardiovascular (Most common cause of death):
- Concentric hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
- Hypertension, heart failure.
- Metabolic:
- Insulin resistance → glucose intolerance or overt Diabetes Mellitus (GH is a counter-regulatory hormone).
- Local Tumor Effects:
- Headaches.
- Bitemporal hemianopsia (compression of the optic chiasm).
Tip
Consider acromegaly in patients who report having had to increase hat, shoe, glove, and ring sizes in the past!
Diagnostics
Treatment
- Surgery
- Transsphenoidal adenomectomy (preferred method)
- Medication
- Somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide, lanreotide)
- Dopamine agonists (e.g., cabergoline): reduce tumor size and GH secretion
- GH receptor antagonists (e.g., pegvisomant)