Definitions
- Cryoglobulins: a group of immunoglobulins (IgM, IgG, IgA) that precipitate in vitro at cold (< 37°C).
- Cryoglobulinemia: a condition characterized by elevated serum cryoglobulin concentration
- Cryoglobulinemic vasculitis: a vasculitis caused by the deposition of temperature-dependent IgG and IgM immunoglobulins/immune complexes (i.e., cryoglobulins), with subsequent inflammation of surrounding tissue
Etiology
Strongly associated with Hepatitis C virus (HCV) (most common). t Other causes: B-cell lymphoproliferative disorders (esp. Type I), other autoimmune diseases (e.g., SLE, RA), other infections.
Clinical features
- Meltzer’s Triad: Palpable purpura (lower extremities), arthralgias, weakness/myalgias.
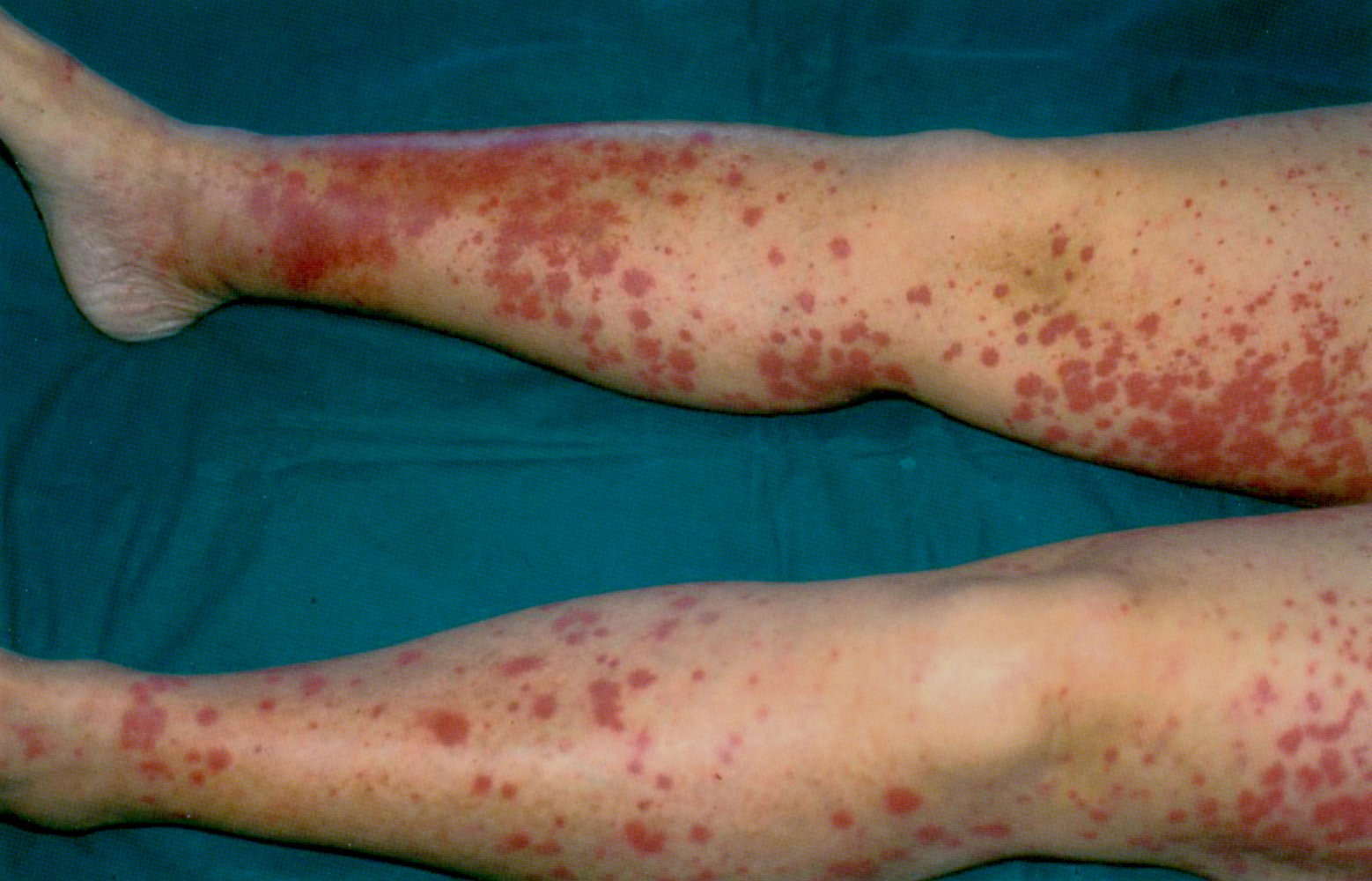
- Peripheral neuropathy (sensory > motor), renal involvement (glomerulonephritis, often MPGN), Raynaud phenomenon.
- Fatigue, fever, hepatosplenomegaly.
Diagnostics
- Serology
- Cryoglobulinemia (type II and/or III; rarely type I)
- Rheumatoid factor: elevated in almost 100% of cases
- ↓ C4 (90% of cases)
- Hepatitis C diagnostics
- Urinalysis: microhematuria, proteinuria, erythrocyte casts