Epidemiology
- Most common viable autosomal chromosome aberration (∼ 1:700 live births) and most common genetic cause of cognitive impairment
- The risk of a Down syndrome pregnancy increases with maternal age.
- Incidence at 20 years: ∼ 1:2000
- Incidence at 45 years: ∼ 1:30
Etiology
Full trisomy 21 (∼ 95% of cases)
- Definition: three complete copies of chromosome 21 are present in all cells, with a total of 47 chromosomes
- Pathogenesis: meiotic nondisjunction
- Karyotype: ♀: 47,XX,+21 or ♂: 47,XY,+21
Translocation trisomy 21 (3–4% of cases)
- Definition: three copies of chromosome 21 are present, one of which is attached to another chromosome, usually chromosome 14 (less likely attached to chromosomes 13, 15, or 22)
- Pathogenesis and karyotype
- Balanced Robertsonian translocation: translocation of the long arm of chromosome 21 to the long arm of chromosome 14. Not symptomatic, but can affect future generations
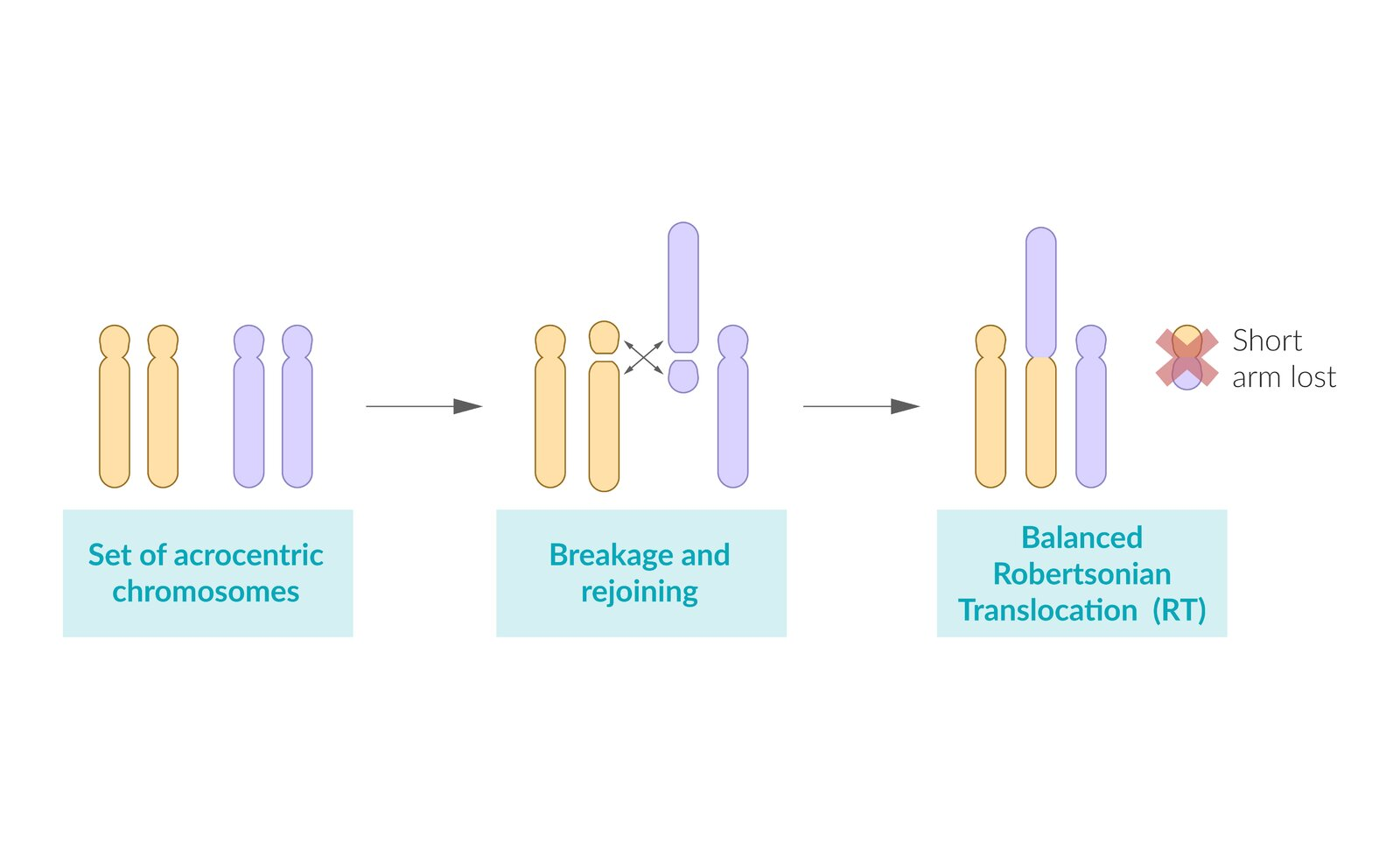
- Unbalanced Robertsonian translocation: clinical features of trisomy 21 caused by inheritance of a translocation chromosome and a normal chromosome
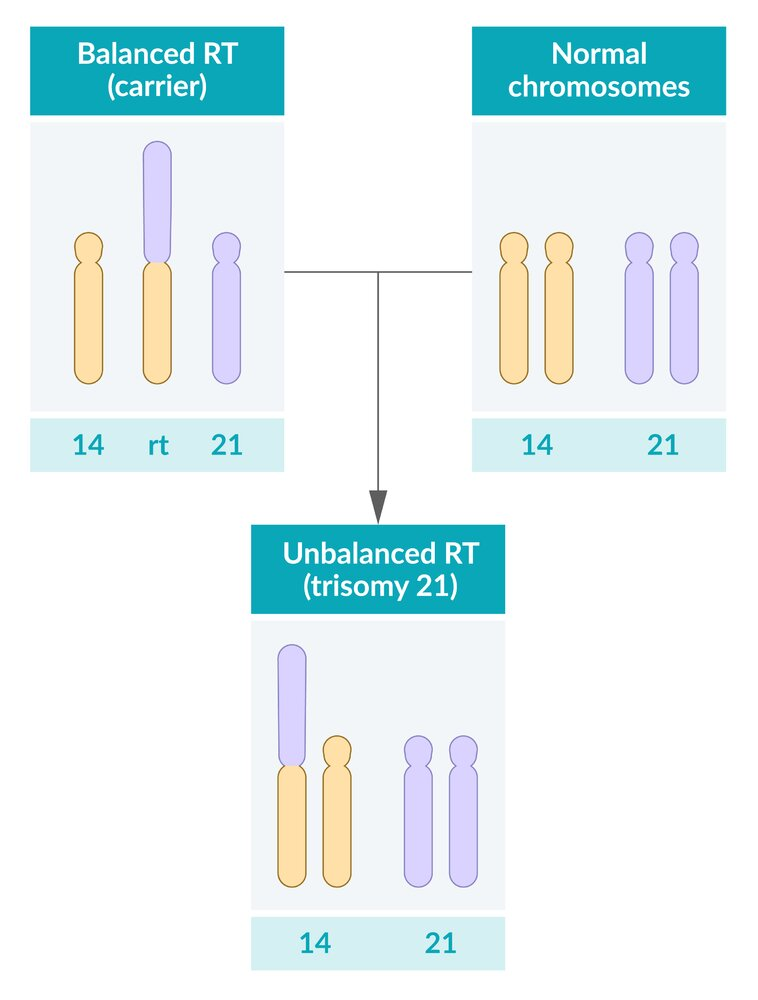
- Balanced Robertsonian translocation: translocation of the long arm of chromosome 21 to the long arm of chromosome 14. Not symptomatic, but can affect future generations
Mosaic trisomy 21 (1–2% of cases)
- Definition: two cell lines are present, the trisomy 21 cell line and the normal cell line
- Phenotypic expression varies according to the ratio of healthy to trisomic cells.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
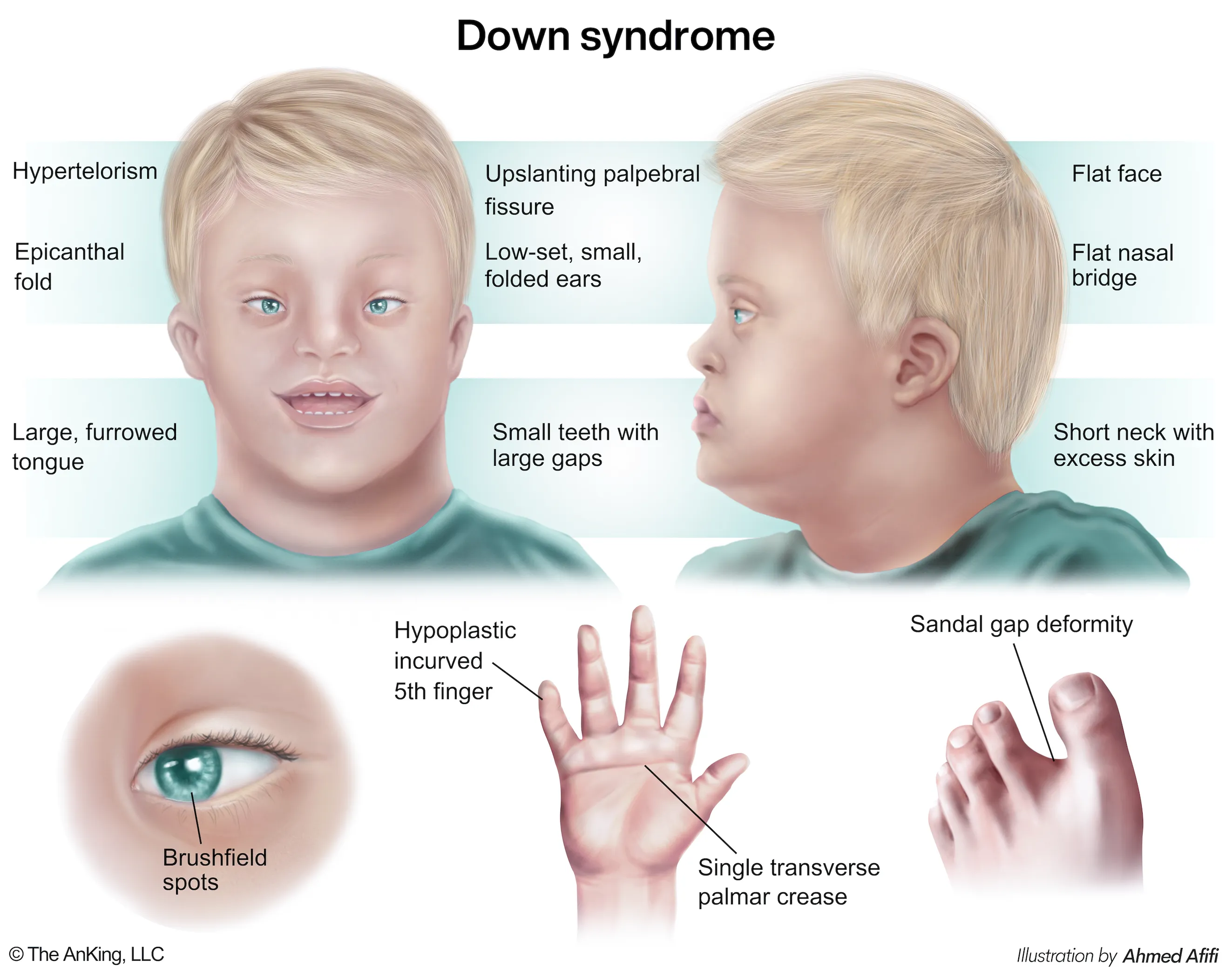
Facial and cranial features (craniofacial dysmorphia)
- Flattened facial profile and nasal bridge, upward-slanting palpebral fissures, prominent epicanthal folds, and a small head (brachycephaly). A protruding tongue and small, rounded ears are also common.


- Eyes: Brushfield spots (small white or grayish spots on the periphery of the iris).
Extremities, soft tissue, and skeletal features
- Extremities
- Transverse palmar crease: single crease that runs across the palm, along the metacarpophalangeal joints perpendicular to the fingers
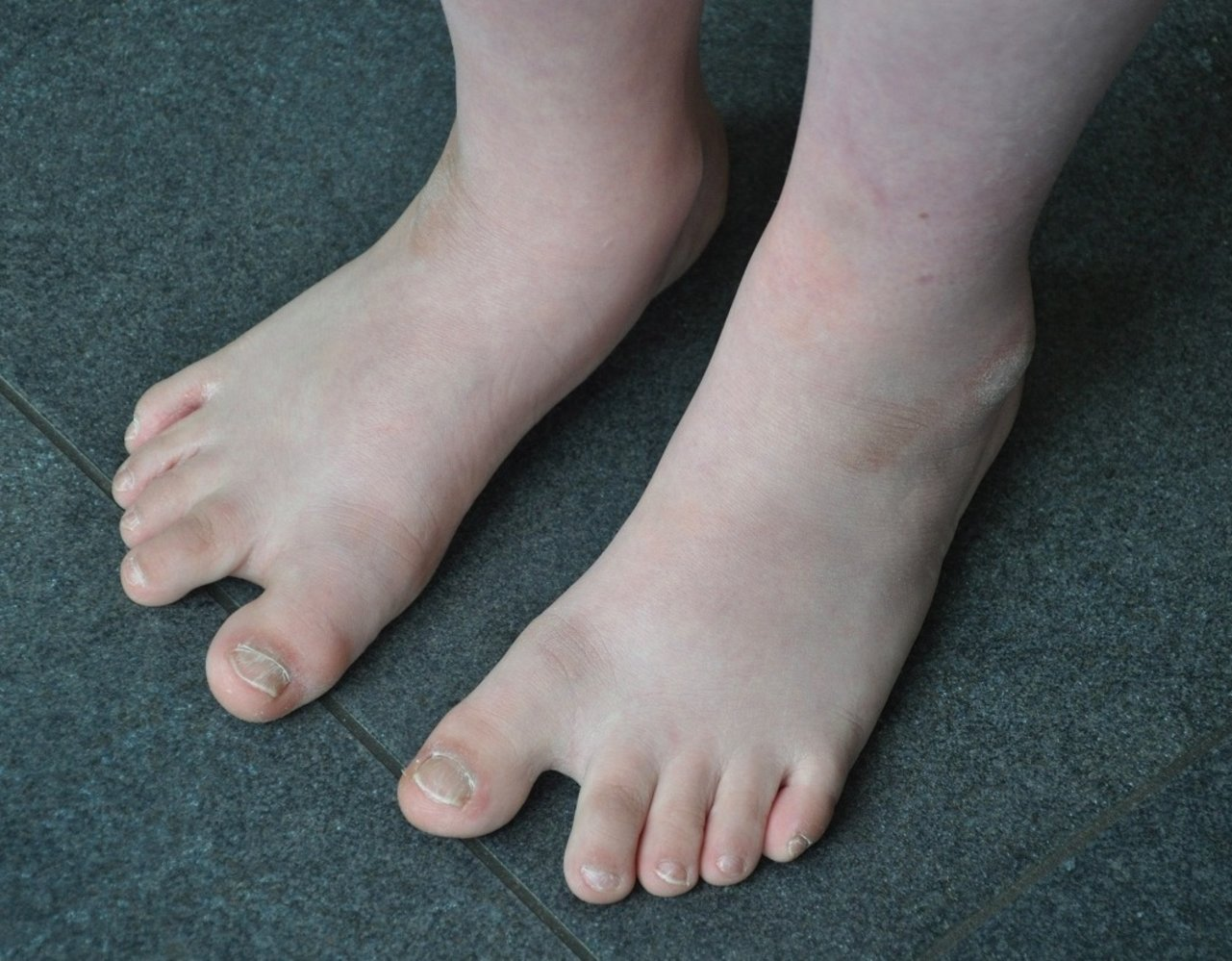
- Sandal gap: a medial displacement of the first toe leading to a large space between the first and second toes
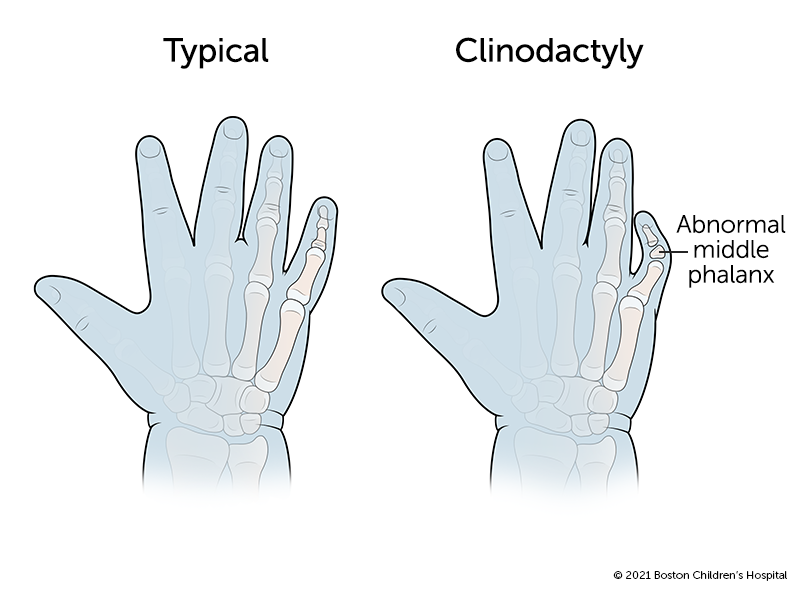
- Clinodactyly: abnormal curvature of a finger (typically refers to inward curvature of the 5th finger)
- Skeletal features
- Atlantoaxial instability
- Short stature
Organ malformations and associated conditions
- Heart: congenital heart defects in ∼ 50% of cases
- Atrioventricular septal defect (endocardial cushion defect) is the most common heart defect in individuals with Down syndrome.
- Ventricular septal defect
- Atrial septal defects
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Duodenal atresia/stenosis
- Hirschsprung disease
- Early-onset Alzheimer disease (The amyloid precursor protein, which generates amyloid beta, is located on chromosome 21.)
Diagnostics
Treatment
Prenatal testing
Screening Tests (Assess Risk)
- cffDNA (NIPT): Best screening test (>99% detection rate). Analyzes fetal DNA in maternal blood from 10 wks.
- 1st Trimester Combined Screen (10-14 wks):
- ↑ Nuchal Translucency (US)
- ↑ β-hCG
- ↓ PAPP-A
- 2nd Trimester Quad Screen (15-22 wks):
- ↓ AFP
- ↑ β-hCG
- ↓ uE3
- ↑ Inhibin A
- US “Soft Markers”: Thickened nuchal fold, absent nasal bone, echogenic intracardiac focus.
Diagnostic Tests (Confirm Dx)
They are offered to women with high-risk screening results or those who desire definitive information
- Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS):
- When: Early (10-13 wks).
- How: Biopsy of placental tissue.
- Risk: Higher risk of miscarriage.
- Amniocentesis:
- When: Later (15-20 wks).
- How: Aspirates amniotic fluid.
- Risk: Lower risk of miscarriage; can also check AFP for neural tube defects.