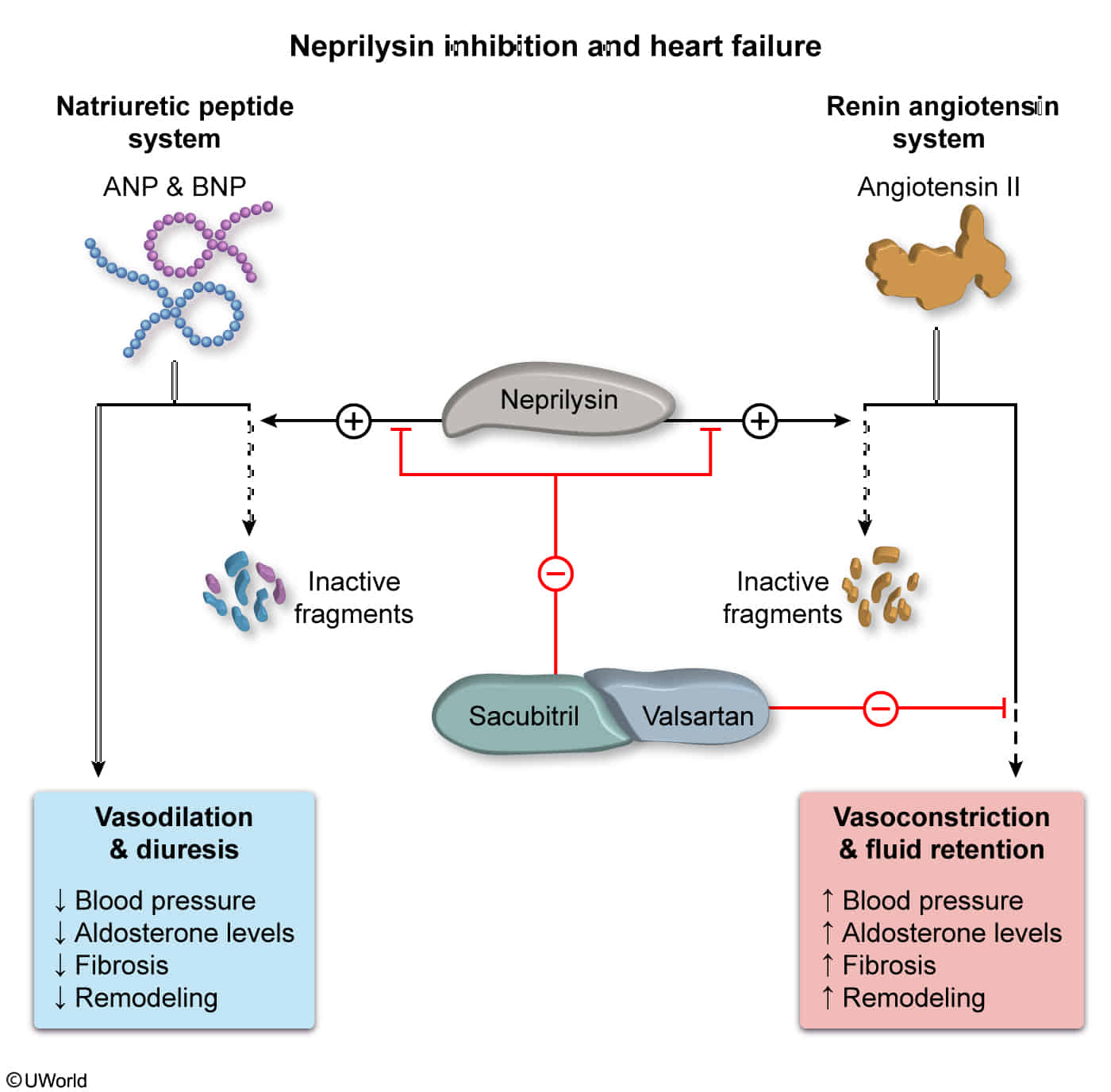
| Angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitor (e.g., sacubitril-valsartan) OR ACE inhibitor (e.g., lisinopril) OR Angiotensin II receptor blocker (e.g., losartan) |
Yes |
| Beta blocker (e.g., metoprolol, carvedilol) |
Yes |
| Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (e.g., spironolactone, eplerenone) |
Yes |
| Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (e.g., dapagliflozin, empagliflozin) |
Yes |
| Diuretic (e.g., furosemide, metolazone) |
No, only improves symptoms & reduces hospitalization. |
| Digoxin |
No, only reduces hospitalization. |

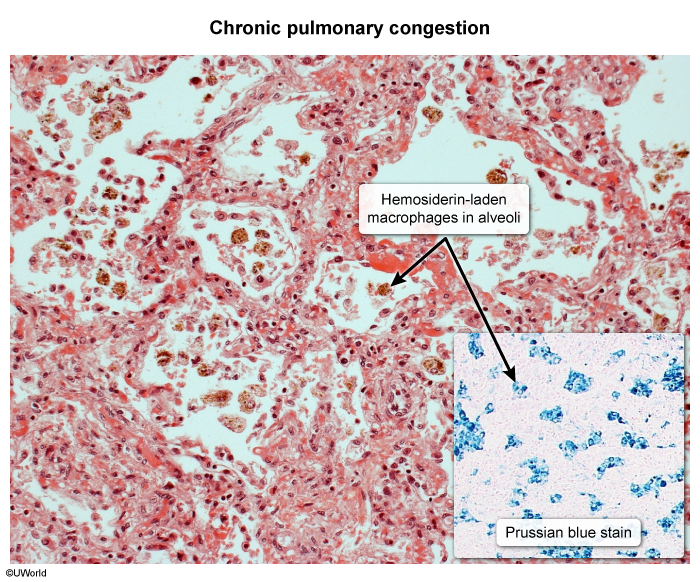 Pulmonary venous congestion may result in intra-alveolar bleeding. Macrophages that subsequently phagocytose the erythrocytes are called “heart failure cells.�?/span> These cells may also be detected in the sputum of patients with pulmonary infarction, vasculitis, or aspiration of blood.
Pulmonary venous congestion may result in intra-alveolar bleeding. Macrophages that subsequently phagocytose the erythrocytes are called “heart failure cells.�?/span> These cells may also be detected in the sputum of patients with pulmonary infarction, vasculitis, or aspiration of blood.