Epidemiology
Etiology
- Dapsone
- Local/topical anesthetics (eg, benzocaine, teething medications)
- Nitrates/nitrites (eg, drinking ground water)
Pathophysiology
- Methemoglobin is created when reduced ferrous iron (Fe2+) bound to oxyhemoglobin is oxidized to ferric iron (Fe3+).
- Ferric iron in methemoglobin cannot bind oxygen→ ↓ total blood oxygen content and ↓ blood oxygen saturation → tissue hypoxia
Tip
The ferric iron in methemoglobin has a high affinity for cyanide, thus, amyl nitrite-induced methemoglobin is used as a competitive inhibitor in the treatment of cyanide poisoning.
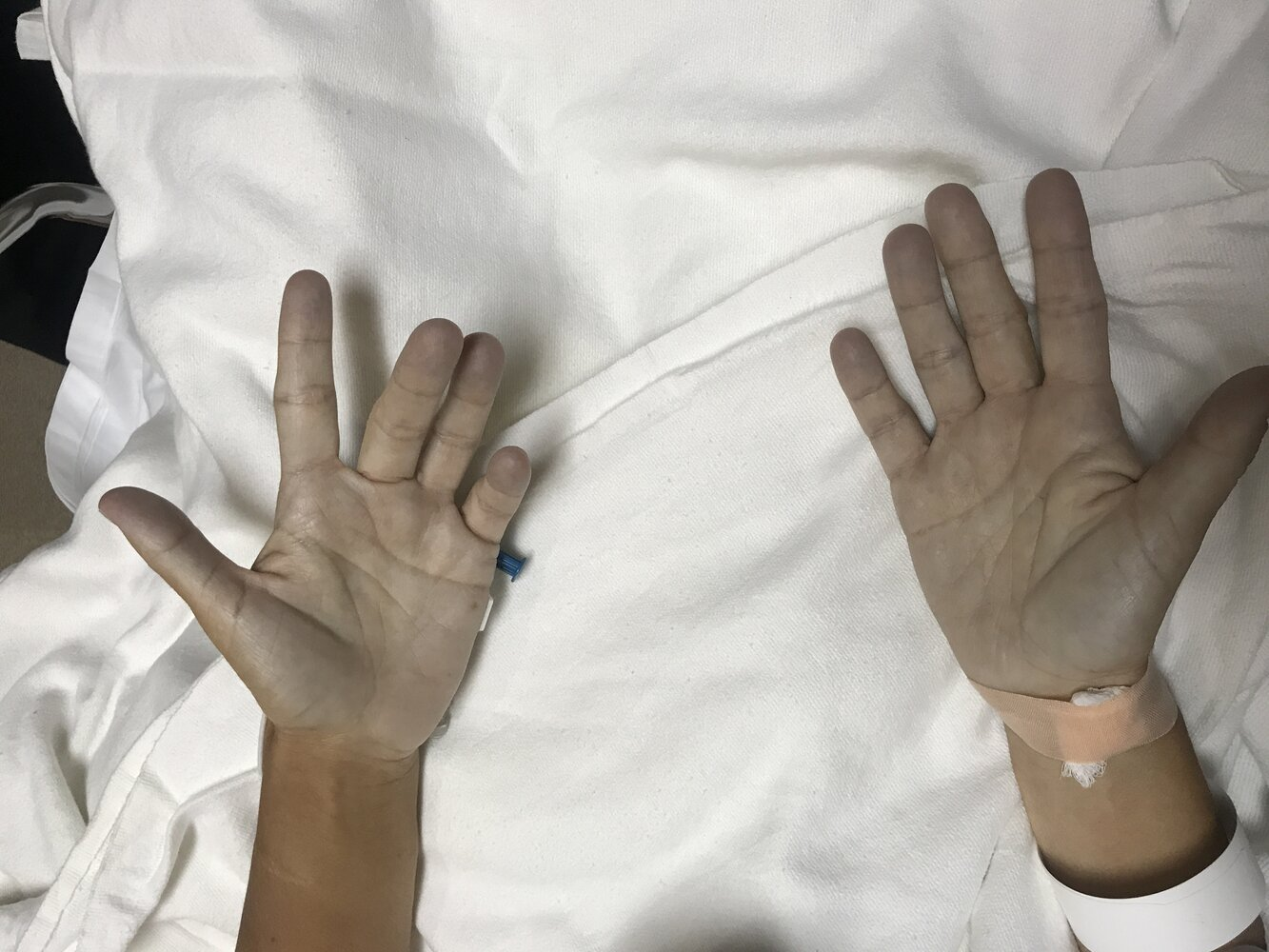
Clinical features
- Cyanosis (brownish-blue or gray skin and membranes) t
Diagnostics
- Due to the wavelength of light absorbed by Fe3+ heme, pulse oximetry converges on 85% as the proportion of methemoglobin increases, regardless of the true oxygen saturation status.
- Bedside testing: Blood appears dark brown (“chocolate-colored”) and does not turn red with exposure to oxygen.
Cyanide poisoning vs CO poisoning
Feature Carbon Monoxide (CO) Methemoglobinemia Cyanide (CN) Mechanism Binds Hb (200x affinity); Left Shift Fe³⁺ (ferric) state; Left Shift Inhibits Complex IV (ETC); Normal Curve Causes Car exhaust, gas heaters, house fires Nitrites, Benzocaine, Dapsone, Sulfonamides Burning rubber/plastic, Nitroprusside Key Sign ”Cherry Red” skin ”Chocolate Brown” blood, Cyanosis ”Bitter Almond” breath Pulse Ox Falsely Normal ~85% (Fixed) Normal PaO₂ Normal Normal Normal Treatment 100% O2, Hyperbaric O2 Methylene Blue (Vit C if G6PD def.) Hydroxocobalamin, Nitrites, Thiosulfate Link to original
Feature Carbon Monoxide (CO) Poisoning Cyanide (CN) Poisoning Methemoglobinemia (MetHb) Mechanism Binds Hemoglobin (forms COHb) → ↓ O2 carrying & delivery. Inhibits Cytochrome C Oxidase (Complex IV) → blocks ATP prod. Iron in heme oxidized (Fe2+ → Fe3+) → cannot bind O2. Source Incomplete combustion (fires, car exhaust, faulty heaters). Fires (plastics, wool), industrial, nitroprusside. Oxidizing drugs (dapsone, nitrites, benzocaine), G6PD deficiency. Presentation Gradual onset: headache, dizziness, N/V. Cherry-red skin (late, unreliable). Normal SaO2 on pulse ox. Rapid onset: confusion, seizures, coma. Cherry-red skin. Almond breath (unreliable). Cyanosis (dusky/brown skin/blood) unresponsive to O2. Dyspnea. Dx ↑ COHb level (CO-oximetry). Pulse ox misleadingly normal. ↑ Lactate. Clinical suspicion + history. High venous O2. ↑ MetHb level (co-oximetry). “Saturation gap” (pulse ox ~85%). Chocolate-brown blood. Tx 100% O2. Hyperbaric O2 (HBO) if severe. Hydroxycobalamin or Nitrites + Sodium Thiosulfate. Methylene blue. O2. (Avoid MB in G6PD def.). CT/MRI Brain Bilateral globus pallidus lesions (hypodense CT, T2 hyper MRI). Less specific; diffuse edema or basal ganglia lesions possible. Non-specific hypoxic changes if severe. O2-Myoglobin Curve Shifts Left (impairs O2 release to muscle). No direct significant effect. No direct significant effect; O2-HGB curve shifts left for normal Hb. Buzzwords ”Faulty heater,” “car exhaust,” “globus pallidus lesions." "Almond breath,” “plastic fire,” “nitroprusside." "Dapsone,” “benzocaine,” “chocolate-brown blood,” “saturation gap.”
Treatment
- Methylene blue is the first-line treatment for acquired methemoglobinemia.
- Acts as a cofactor to reduce methemoglobin to hemoglobin
Tip
100% supplemental oxygen is not useful in methemoglobinemia, in contrast to monoxide poisoning and cyanide poisoning.