- Definition: malignant tumor that develops from mesothelial cells
- Etiology
- Secondary to asbestos exposure
- Alcohol, smoking, and diet do not increase the incidence of mesothelioma.
- Clinical findings
- Dyspnea and nonpleuritic chest pain (most common)
- Fever, sweats, weight loss, fatigue
- Features of pleural effusion: dull percussion; absent or reduced breath sounds on affected side
- Diagnosis
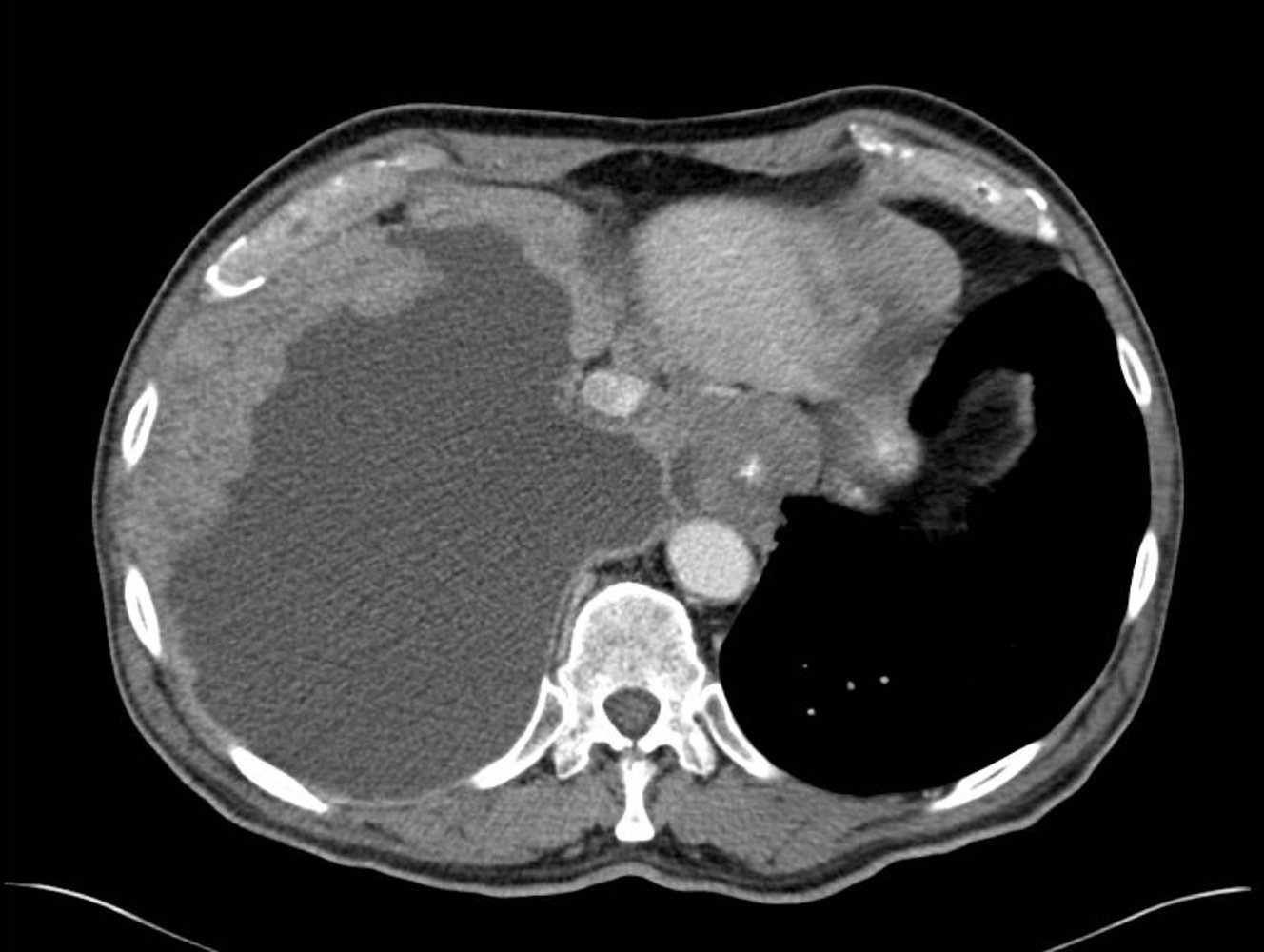
- Pleurocentesis : bloody (exudative) pleural effusion
- Imaging (chest x-ray and CT)
- Multiple nodular pleural lesions (pleural thickening)
- Laparoscopy, thoracoscopy, and pleuroscopy with stained biopsy: reveal mesothelioma cells and psammoma bodies
- It is important to differentiate mesothelioma from adenocarcinoma.
- Immunohistochemistry: Mesothelioma often stains positive for mesothelin, serum mesothelin-related protein (SMRP), calretinin, cytokeratin 5/6 (negative in most adenocarcinomas), and vimentin.
- Electron microscopy shows tumor cells with long and slender microvilli (in contrast to the short and stubby microvilli found in adenocarcinomas), tonofilaments, and desmosomes.
