- Anatomy & Embryology
- Sits in the sella turcica.
- Anterior Pituitary (Adenohypophysis): Derived from Rathke’s pouch (oral ectoderm). Receives blood from the hypothalamo-hypophyseal portal system.
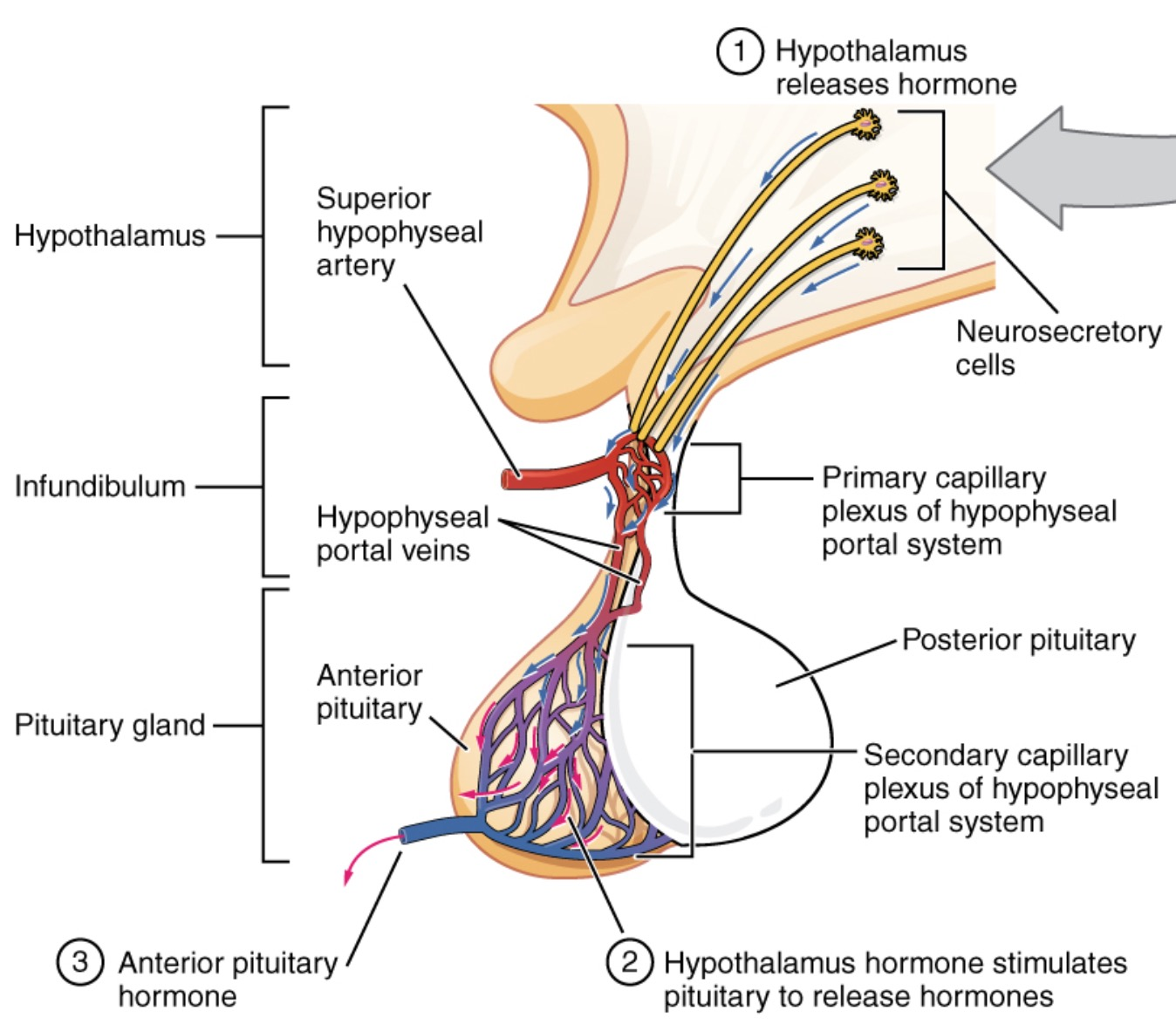
- Posterior Pituitary (Neurohypophysis): Derived from neuroectoderm. Contains axon terminals from the hypothalamus.
- Hormones (Anterior)
- Mnemonic: FLAT PiG (FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, GH).
- Basophils (B-FLAT): FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH.
- Acidophils (GPA): GH, Prolactin.
- Prolactin: Stimulates milk production. Its secretion is tonically inhibited by dopamine.
- GH (Growth Hormone): Mediates growth via IGF-1.
- ACTH: Derived from POMC (which also produces MSH, hence hyperpigmentation in high ACTH states).
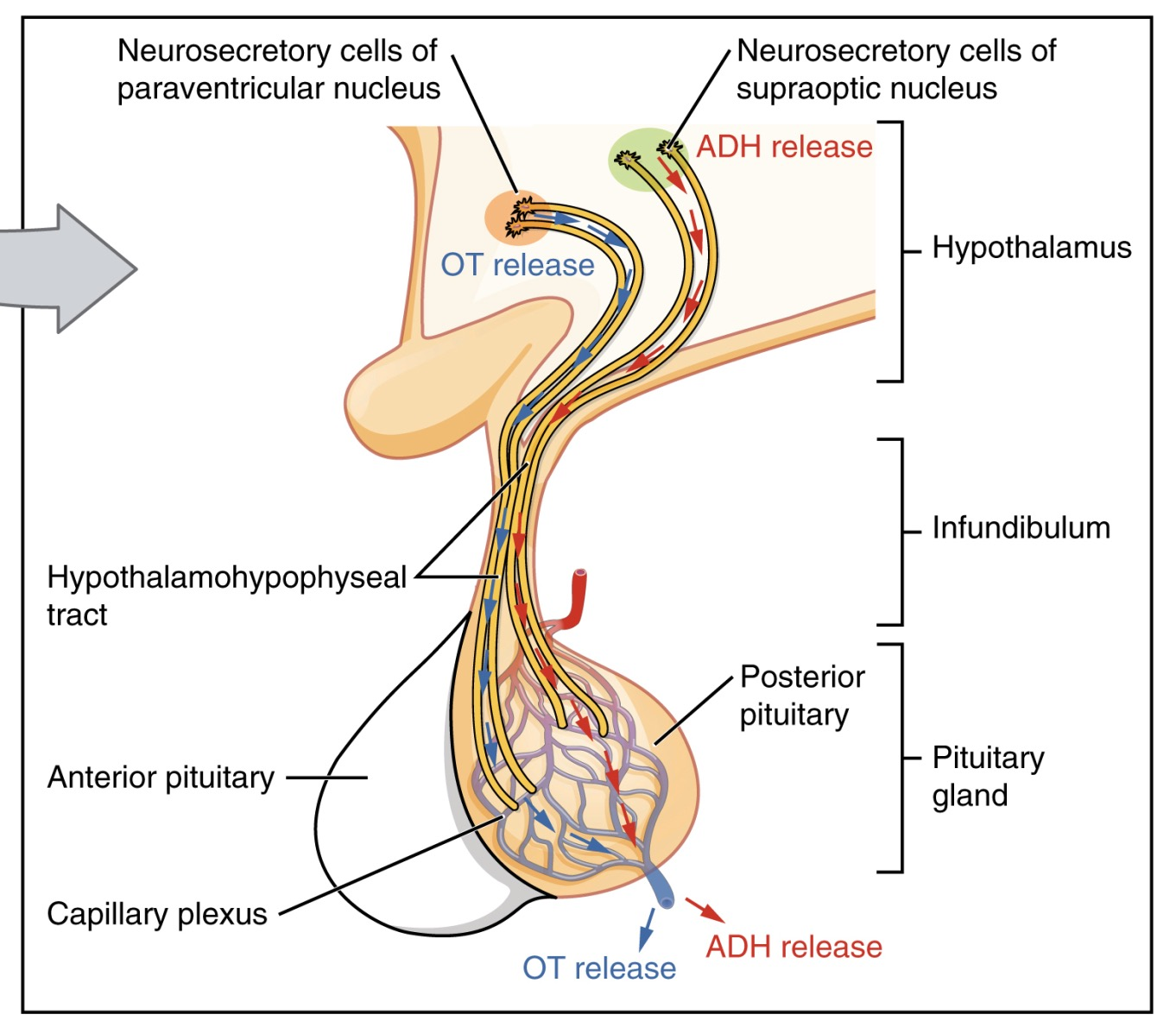
- Hormones (Posterior)
- Stores and releases hormones synthesized in the hypothalamus.
- ADH (Vasopressin): Synthesized in the supraoptic nuclei. Manages water balance by acting on renal collecting ducts.
- Oxytocin: Synthesized in the paraventricular nuclei. Responsible for uterine contractions and milk letdown.
Mnemonic
Posterior = “Piss and Pregnancy”
- High-Yield Pathology
- Pituitary Adenoma: The most common cause of pituitary hormone excess.
- Prolactinoma: The most frequent type. It causes galactorrhea, amenorrhea, and decreased libido. Treatment involves dopamine agonists like cabergoline.
- Somatotroph (GH) Adenoma: Leads to Acromegaly in adults (coarse facial features, large hands) or Gigantism in children.
- Mass Effect: Large adenomas can compress the optic chiasm, causing bitemporal hemianopsia (loss of peripheral vision).
- Hypopituitarism:
- Sheehan Syndrome: Postpartum pituitary necrosis due to severe hemorrhage and hypotension during childbirth.
- Pituitary Apoplexy: Sudden hemorrhage into a pituitary adenoma, presenting as a severe headache and visual defects.
- Posterior Lobe Disorders:
- Diabetes Insipidus (DI): Due to a deficiency of ADH. Characterized by intense thirst and polyuria with dilute urine.
- SIADH (Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH): Caused by excessive ADH secretion, leading to water retention and hyponatremia.
- Pituitary Adenoma: The most common cause of pituitary hormone excess.