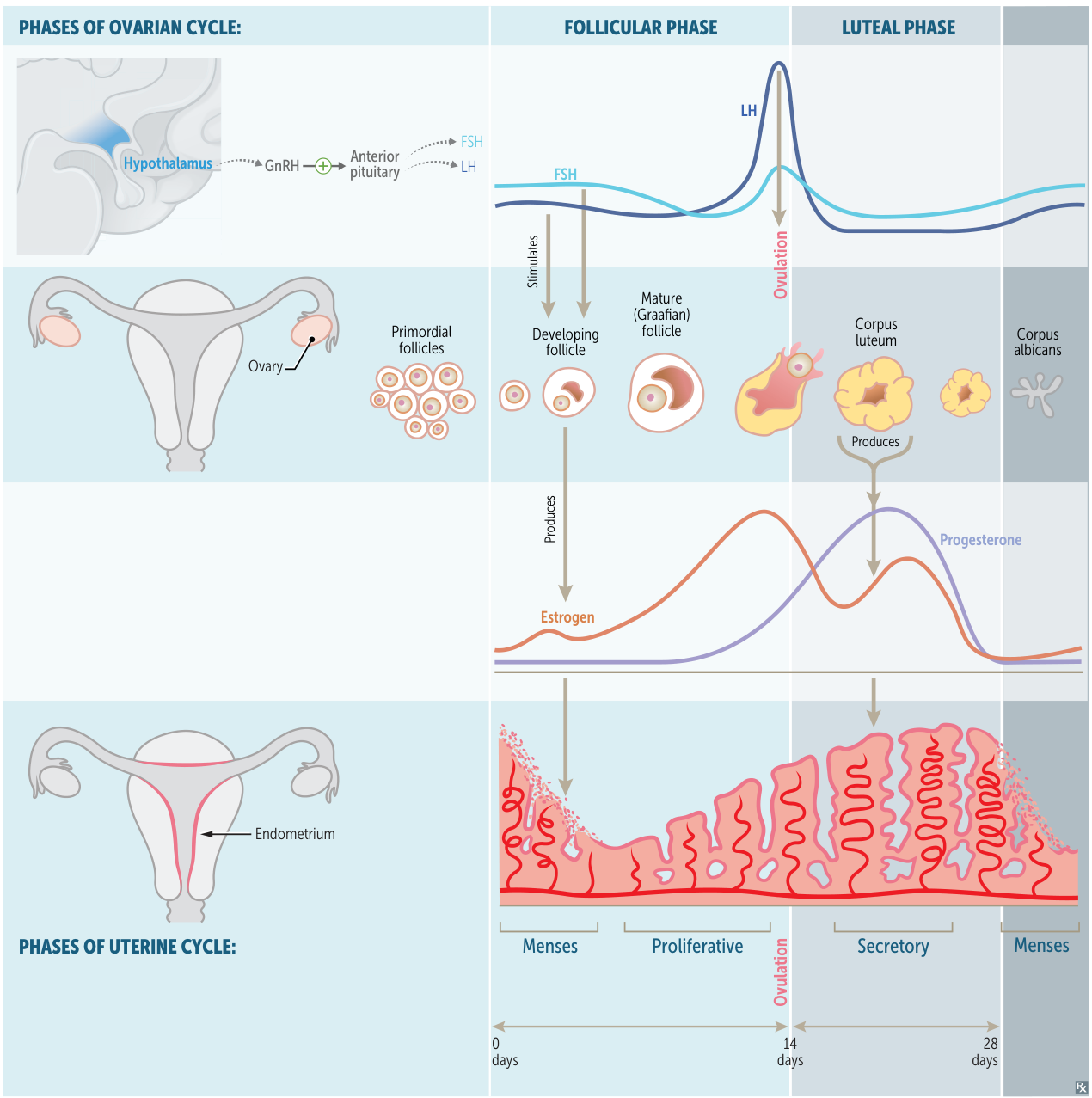
Ovarian Cycle Phases
-
Follicular Phase (Days 1-14, variable length):
- Hormones: Begins with a rise in FSH, which stimulates a group of follicles to grow.
- Follicular Development: Developing follicles secrete estrogen. One follicle becomes dominant while others undergo atresia.
- Key Event: Rising estrogen levels initially have a negative feedback effect, but then switch to positive feedback, leading to the LH surge.
-
Ovulation (Mid-cycle, ~Day 14):
- Hormones: The LH surge is the primary trigger. A smaller FSH surge also occurs.
- Key Event: The dominant follicle ruptures and releases a secondary oocyte.
-
Luteal Phase (Days 14-28, constant 14-day length):
- Hormones: The remnant of the follicle becomes the corpus luteum, which secretes high levels of progesterone and some estrogen. Progesterone is the dominant hormone of this phase.
- Key Event:
- No Fertilization: If fertilization doesn’t occur, the corpus luteum degenerates into the corpus albicans. The subsequent sharp drop in progesterone and estrogen leads to menstruation.
- Fertilization: If fertilization occurs, the implanted blastocyst secretes hCG, which “rescues” the corpus luteum, maintaining progesterone production until the placenta takes over.
Uterine (Endometrial) Cycle Phases
-
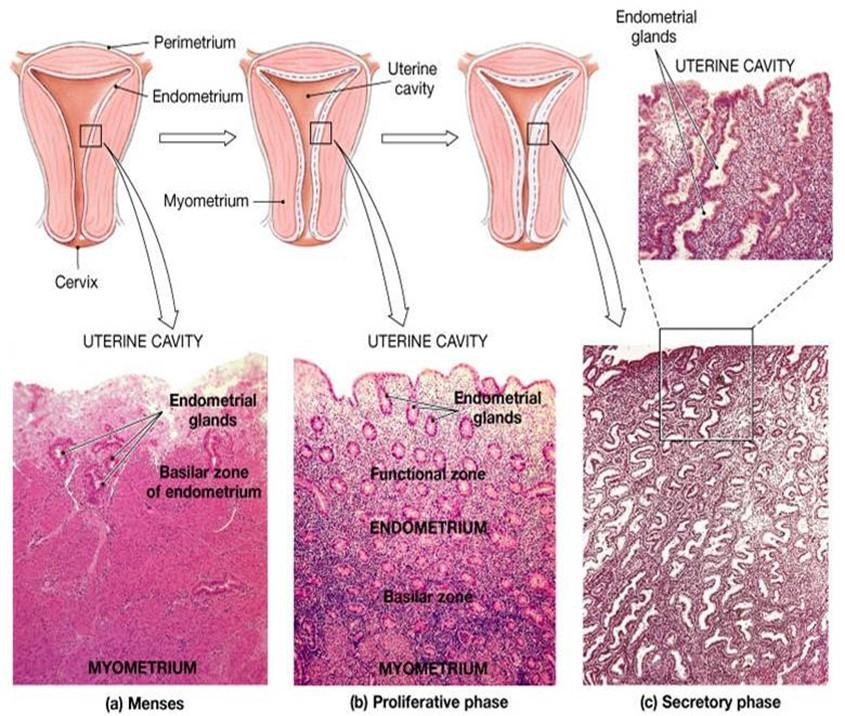
Menstrual Phase (Days 1-5):
- Corresponds to the early follicular phase.
- Cause: Progesterone and estrogen withdrawal causes spiral artery constriction, leading to shedding of the stratum functionalis (functional layer). The deeper stratum basalis remains to regenerate the endometrium.
-
Proliferative Phase (Days 5-14):
- Corresponds to the mid-to-late follicular phase.
- Hormonal Driver: Rising estrogen levels stimulate the regrowth and proliferation of the stratum functionalis.
-
Secretory Phase (Days 14-28):
- Corresponds to the luteal phase.
- Hormonal Driver: High progesterone levels from the corpus luteum cause the endometrium to become highly vascularized and glandular, secreting glycogen-rich mucus (“uterine milk”) in preparation for implantation.
| Feature | Menstrual Phase | Proliferative Phase | Secretory Phase |
|---|---|---|---|
| Days | ~1-5 | ~6-14 | ~15-28 |
| Key Hormone | ↓ Progesterone | Estrogen | Progesterone |
| Endometrium | Shedding of stratum functionalis | Growth / Proliferation | Secretion / ↑ Vascularity |
| Cervical Mucus | Scant | Thin, watery, fertile | Thick, viscous plug |
| Ovarian Phase | Early Follicular | Late Follicular | Luteal |
| Feature | Estrogen (“Growth”) | Progesterone (“Maintenance”) |
|---|---|---|
| Endometrium | Proliferative | Secretory |
| Myometrium | ↑ Contractility | ↓ Contractility (Uterine Quiescence) |
| Cervical Mucus | Thin, watery (Pro-sperm) | Thick, scant (Anti-sperm) |
| Breasts | Ductal development | Lobular-alveolar development |
| CNS Feedback | Negative → Positive (LH Surge) | Negative only |
| Systemic Effect | ↑ Bone Density, ↑ HDL | ↑ Body Temperature |
Abnormalities of the menstrual cycle
Anovulatory cycle
- Pathophysiology
- Unopposed Estrogen stimulation of endometrium.
- Failure of ovulation → No Corpus Luteum → No Progesterone.
- Endometrium becomes unstable → Estrogen Breakthrough Bleeding.
- Etiology
- Clinical Features
- Menometrorrhagia: Irregular, frequent, often heavy bleeding.
- Painless: Lack of prostaglandins (no ovulation).
- Absence of premenstrual symptoms (molimina).
- Diagnostics
- First step: β-hCG (rule out pregnancy).
- Endometrial Biopsy: Rule out cancer if:
- Age >45.
- Age <45 with risk factors (Obesity, chronic anovulation/PCOS).
- Treatment
- Bleeding Control: COCPs (1st line), Cyclic Progestins, LNG-IUD.
- Fertility: Letrozole (PCOS), Clomiphene.
- Acute Hemorrhage: High-dose IV Estrogen or Progestins.
- Key Complication
- Endometrial Hyperplasia/Carcinoma (due to chronic unopposed estrogen).