A genetic syndrome caused by a G-protein activating mutation and subsequent continuous stimulation of endocrine functions
Epidemiology
Etiology
- Somatic mosaicism (post-zygotic mutation; germline is lethal).
- Activating GNAS mutation constitutive Gs-protein activation cAMP.
- Result: Overproduction of hormones and abnormal bone growth.
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
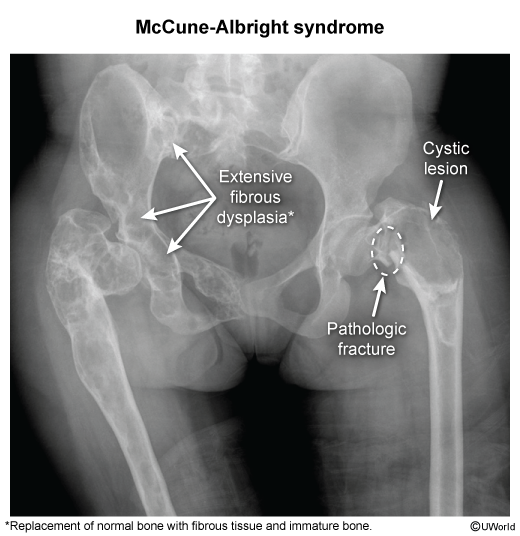
- Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia: Bone replaced by fibrous tissue. “Ground-glass” opacity on X-ray. Shepherd’s crook deformity (femur).
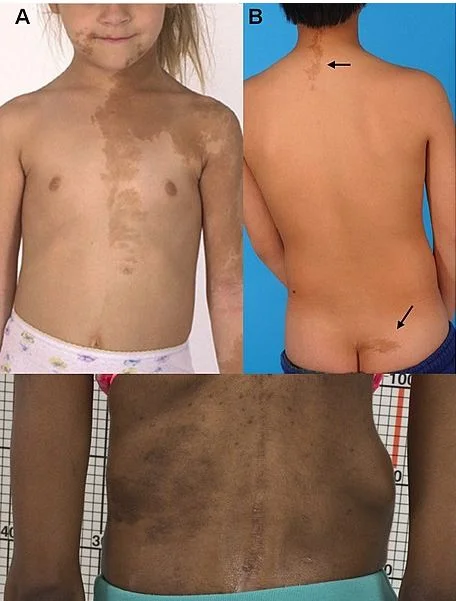
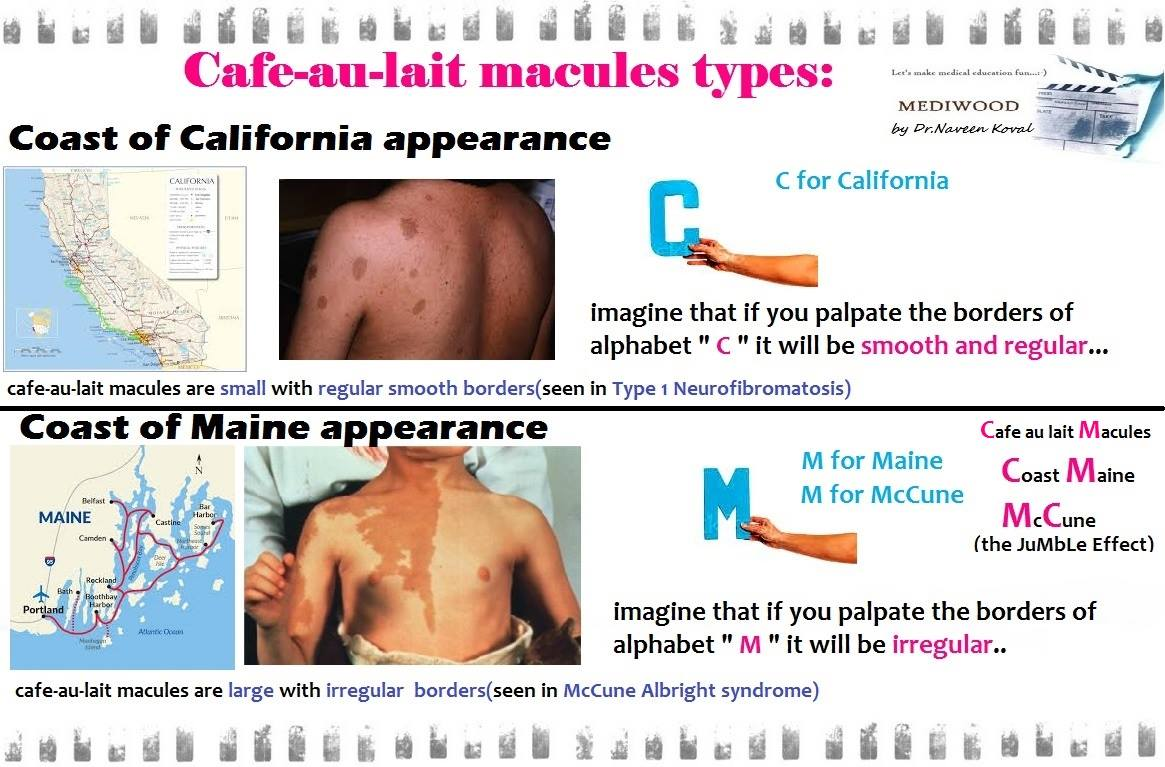
- Café-au-lait spots: Unilateral, large. “Coast of Maine” (jagged/irregular borders).
- Endocrinopathy: Precocious puberty (peripheral) is most common. Also Hyperthyroidism, Acromegaly, Cushing’s.