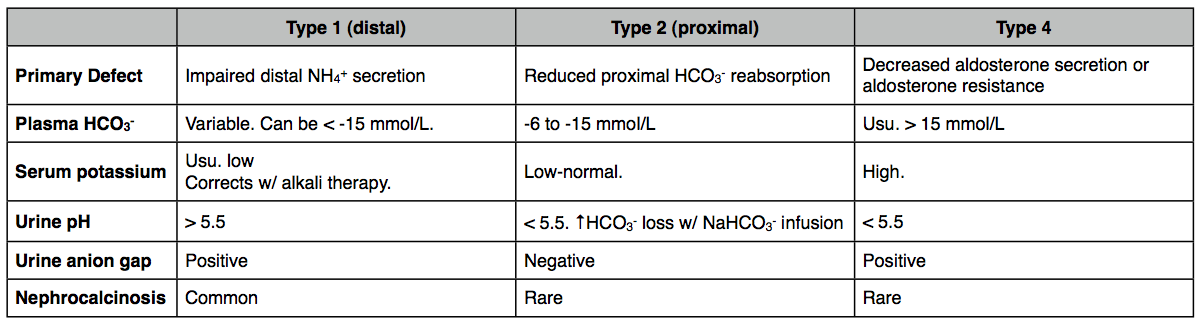
Proximal renal tubular acidosis (type 2)
Etiology
- Drugs: acetazolamide
Pathophysiology
- Isolated proximal RTA: The proximal convoluted tubule cells are unable to reabsorb HCO3-.
- Fanconi syndrome: Impaired reabsorption of HCO3- and other compounds (e.g., potassium, glucose, phosphate, and amino acid reabsorption) in the PCT
Clinical features
- Vitamin D-resistant hypophosphatemic rickets/osteomalacia (caused by phosphaturia and hypophosphatemia; individuals with Fanconi syndrome typically have more severe symptoms)
- Short stature
- Polyuria → polydipsia, dehydration
Tip
Excessive tubular glucose impairs renal concentrating ability by acting as an osmotic diuretic, contributing to development of polyuria (eg, more wet diapers) and episodes of hypovolemia . However, plasma glucose is tightly regulated by mechanisms (eg, insulin, glucagon) independent of renal reabsorption. Therefore, serum glucose remains normal.
Diagnostics
- Fanconi syndrome
- Aminoaciduria
- Glucosuria despite normal or low serum glucose
- Phosphaturia
Differential diagnosis