Diffuse proliferative glomerulonephritis
Epidemiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Can also be nephritic with nephrotic-range proteinuria (nephritic-nephrotic syndrome)
- Can lead to immune complex RPGN
Diagnostics
- ↓ Serum C3 complement levels
- ANA, anti-dsDNA antibodies
- LM
- Thickening of glomerular capillaries (appear as wire loops)
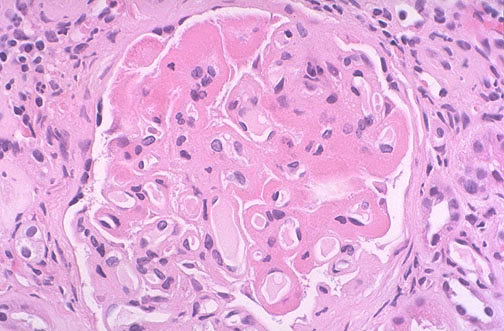
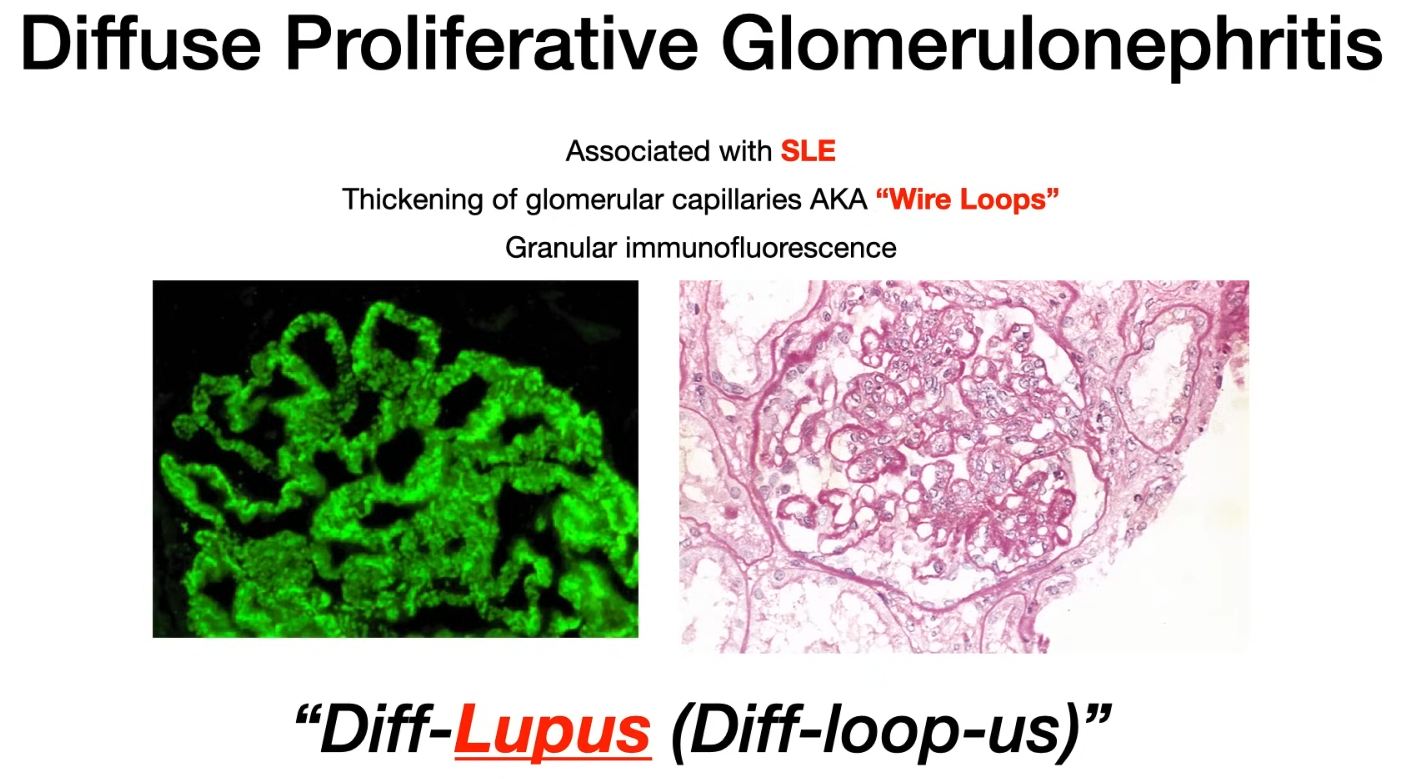
- Characterized by increased glomerular cellularity in more than half of the glomeruli
- EM
- An immunofluorescence pattern containing IgG, IgM, IgA and C3, C1q is highly characteristic of lupus nephritis and is referred to as a full-house (三带一对, ie, a poker hand with three of a kind 3 immunoglobulin classes and two of a kind 2 complement components).

- The full-house pattern reflects the pathogenesis of lupus: loss of immune tolerance to self-antigens (eg, double-stranded DNA) leads to generation of polyclonal autoantibodies that form circulating immune complexes; these deposit in the glomeruli, where they cause local injury by activating the classical complement cascade.
Treatment


