Fever Patterns
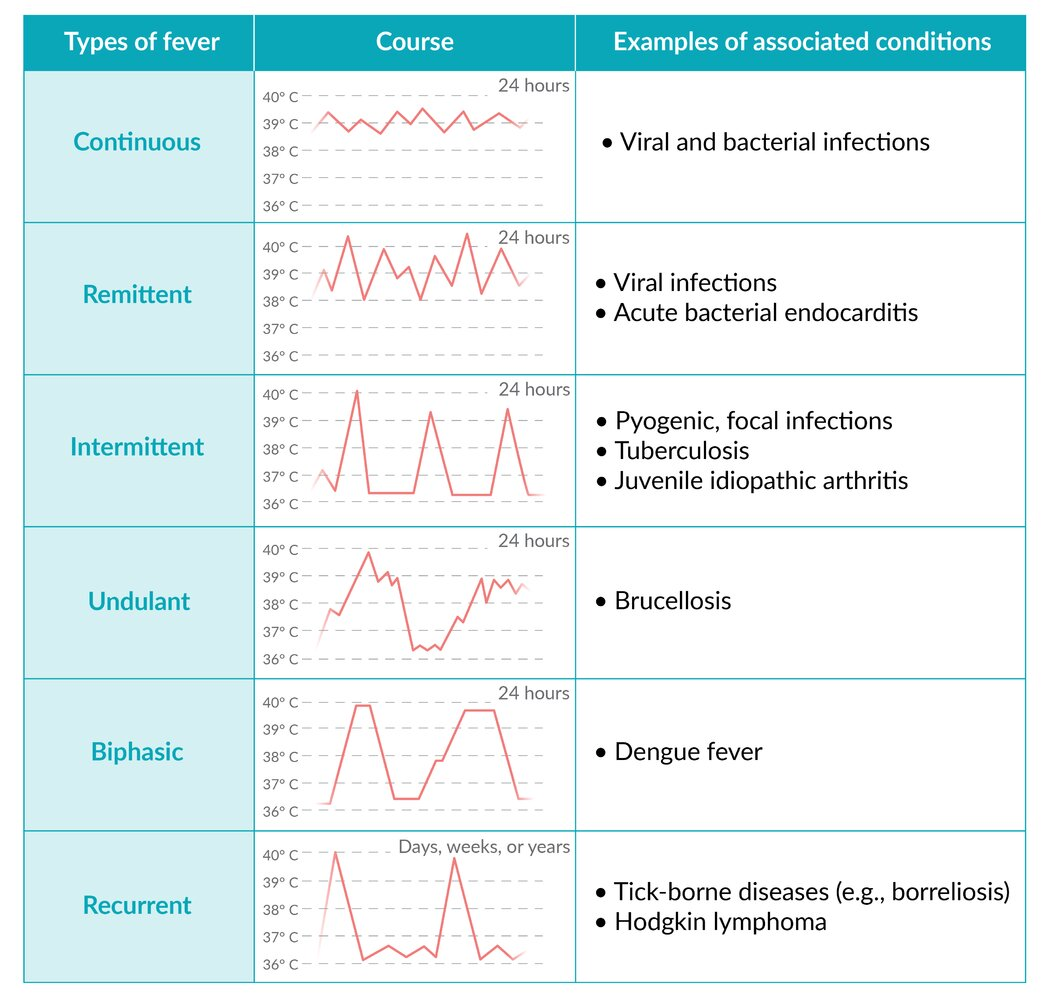
- Continuous: Temp stays elevated with minimal fluctuation.
- DDx: Typhoid fever, lobar pneumonia, brucellosis.
- Intermittent: Temp spikes then returns to normal daily.
- DDx: Malaria, pyogenic abscess, sepsis, TB.
- Relapsing: Febrile episodes separated by afebrile days.
- DDx: Borrelia spp. (relapsing fever), rat-bite fever.
- Pel-Ebstein: Cyclical fever (1-2 weeks on, 1-2 weeks off).
- Classic Association: Hodgkin lymphoma.
Mnemonic
1、稽留热(continuous):稽大爷上班
稽大爷(大叶性肺炎)上(伤寒)班(斑疹伤寒)。
2、弛张热:张飞拜师结盟
张飞拜(败血症)师(风湿热)结(重症肺结核)盟(化脓性炎症)。
3、间歇热:急于歇息
急(疟疾)于(肾盂肾炎)歇(间歇热)息。
4、回归热(Relapsing):回家挥霍
回(回归热)家挥霍(霍奇金病)。 5、波状热(Undulant):布鲁氏病
Key Fever Associations
- Fever + Relative Bradycardia (Faget Sign): Pulse is inappropriately slow for temp.
- DDx: Typhoid fever, Legionella, Yellow fever, brucellosis.
- Fever + Rash on Palms/Soles:
- DDx: Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF), secondary syphilis, meningococcemia, Coxsackie A (Hand-Foot-Mouth).
- Fever + Eschar: Dark, crusted ulcer at bite site.
- DDx: Scrub typhus (Orientia), Rickettsialpox, anthrax.
- Fever + Biphasic (“Saddleback”) Pattern: Fever, remission, then second fever.
- DDx: Dengue fever, leptospirosis.
Fever of Unknown Origin (FUO)
- Definition: Temp >38.3°C for ≥3 weeks with no Dx after 1 week of inpatient workup.
- Common Causes (atypical presentation of common disease):
- Infection: Occult abscess (e.g., abdominal), TB (esp. extrapulmonary), endocarditis.
- Neoplasm: Lymphoma, leukemia, renal cell carcinoma.
- Autoimmune: Still’s disease, Giant Cell Arteritis (elderly), SLE.