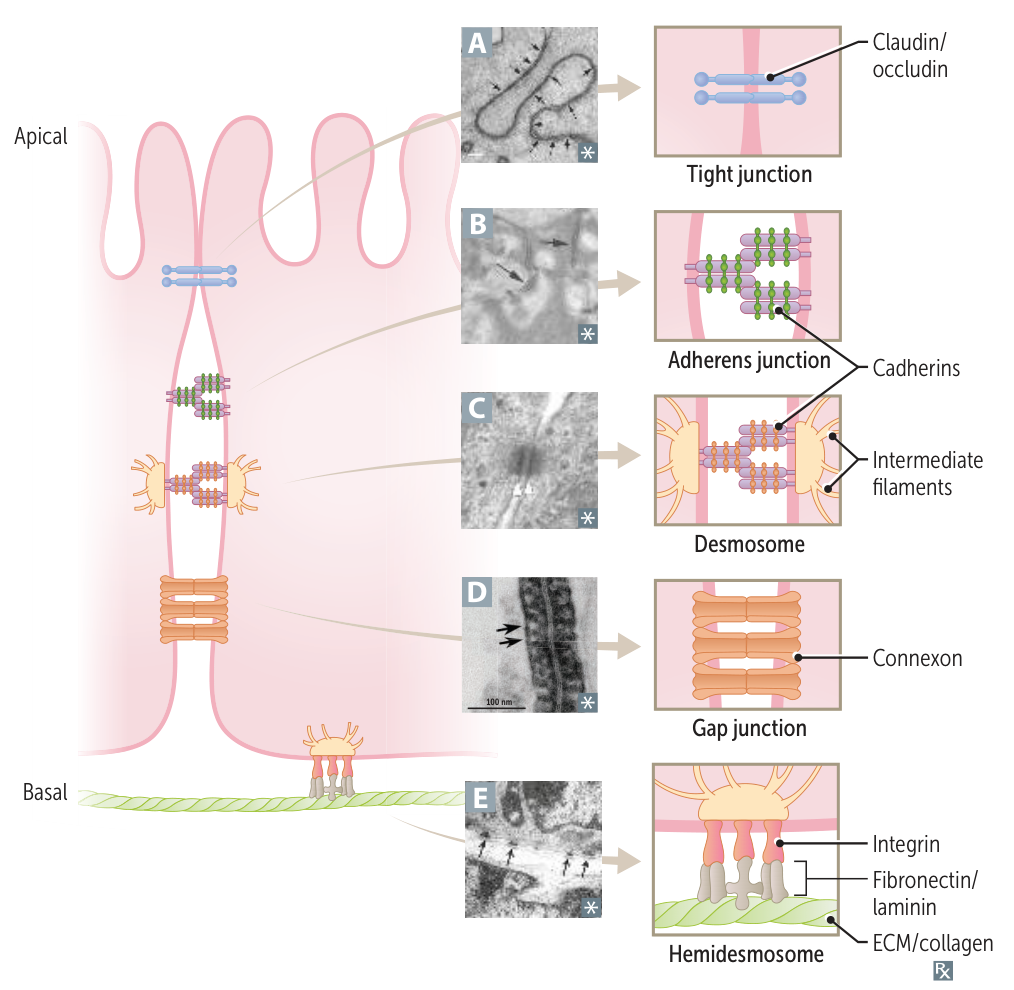
- Tight Junctions (Zonula Occludens)
- Function: Prevents paracellular movement of solutes; maintains cellular polarity by separating apical from basolateral membrane spaces.
- Components: Claudins, Occludins.
- Location: Most apical junction.
- Clinical Association:
- Compromised in certain bacterial infections (e.g., C. perfringens enterotoxin affects claudins).
- Blood-Brain Barrier integrity relies heavily on these.
- Adherens Junctions (Zonula Adherens)
- Function: Forms a “belt” connecting actin cytoskeletons of adjacent cells.
- Components: E-cadherins (Ca2+-dependent adhesion proteins) connect to actin filaments via catenins.
- Clinical Association:
- Loss of E-cadherin promotes metastasis (allows tumor cells to detach and invade).
- Desmosomes (Macula Adherens)
- Function: Structural support via “spot welds”; anchors intermediate filaments (cytokeratin) of adjacent cells.
- Components: Desmoglein, Desmocollin (members of the cadherin family).
- Clinical Association:
- Pemphigus Vulgaris: Autoantibodies (IgG) against Desmoglein (desmosomes).
- Results in acantholysis (separation of keratinocytes).
- Flaccid bullae, (+) Nikolsky sign, oral mucosa involvement.
- Immunofluorescence: Net-like pattern around epidermal cells (“chicken wire”).
- Gap Junctions
- Function: Channel proteins that permit electrical and chemical communication between cells.
- Components: Connexons (composed of 6 connexin subunits).
- Clinical Association:
- Critical in cardiac muscle (intercalated discs) for synchronized contraction.
- Upregulated in myometrium before delivery (labor) to coordinate contractions.
- Hemidesmosome
- Function: Anchors the intermediate filaments of a basal epithelial cell to the underlying basement membrane. Connects Keratin in Basal cells to the Basement membrane.
- Location: Basal surface of keratinocytes in the epidermis.
- Key Proteins: Integrins.
- Clinical Correlation: Autoantibodies against hemidesmosomal proteins (e.g., BP180, BP230) cause Bullous pemphigoid, leading to subepidermal blistering.
